73 Amazing Facts About Computers That Will Fascinate You
Facts About Computers
Indeed, the world of computers has come a long way, evolving from massive machines that occupied an entire room to sleek personal computers and mobile phones used today. Moreover, facts about computers reveal not just their history but also their impact on society, culture, and technology.
Since early computers were built with vacuum tubes and required square feet of space, they have transformed into modern computers capable of terabytes of memory and lightning-fast performance.
Furthermore, computers are not just machines; they are part of human life, influencing how people work, communicate, and even think.
For instance, comparisons between the human brain and digital computers are often made, with fascinating facts showing that computers can process billions of instructions per second, though they still lack the creativity of the mind.
Therefore, exploring facts about computers provides an engaging way to understand their development, significance, and future potential.
The Origins of Computers
The First Mechanical Computer
Interestingly, the first mechanical computer was designed by Charles Babbage, often called the “Father of Computers.” His analytical engine laid the foundation for what would eventually become modern computers.
In fact, Ada Lovelace, known as the first computer programmer, created the first algorithm intended for this machine. As a result, she is remembered as a pioneer in computer science.
The First Electronic Computer ENIAC
Additionally, the Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer (ENIAC) is often cited as the first electronic computer.
Built in the United States during World War II, it required an entire room to operate and used thousands of vacuum tubes.
Surprisingly, the ENIAC covered about 1,800 square feet of space, showing just how massive early computers were compared to desktop computers today.
Fascinating Inventions Related to Computers
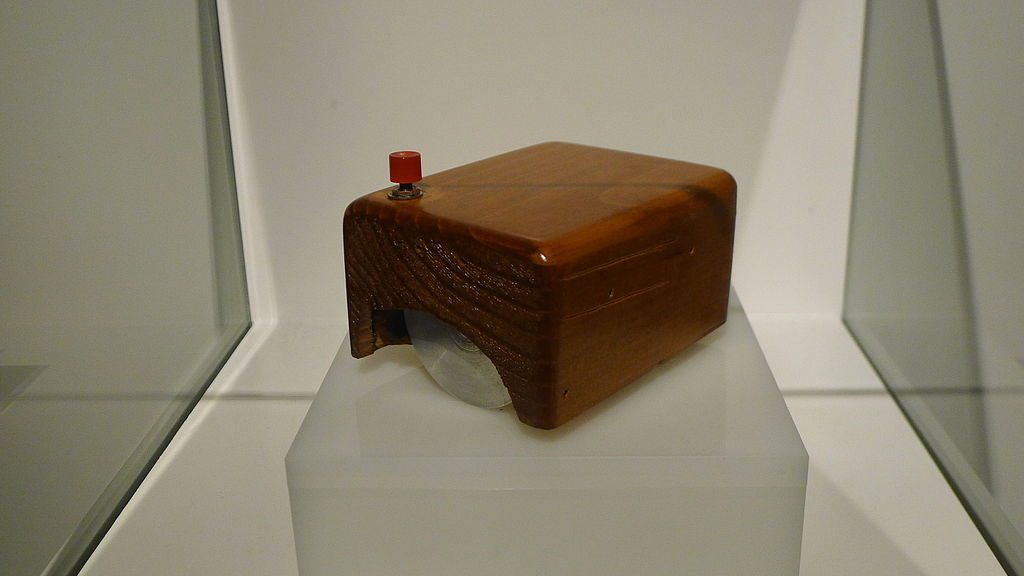

The First Computer Mouse
Equally important in the history of computing is the invention of the first computer mouse. Invented by Douglas Engelbart, also known as Doug Engelbart, in the 1960s, the device was originally made of wood.
Consequently, this small input device revolutionized how people interact with operating systems and computer programs.
The First Computer Bug
Curiously, the term “computer bug” originated when a real bug was found inside a computer, causing a malfunction.
Therefore, computer scientists began referring to glitches as “bugs.” Even today, software developers still use this term when describing errors in software development.
Interesting Facts About Computers
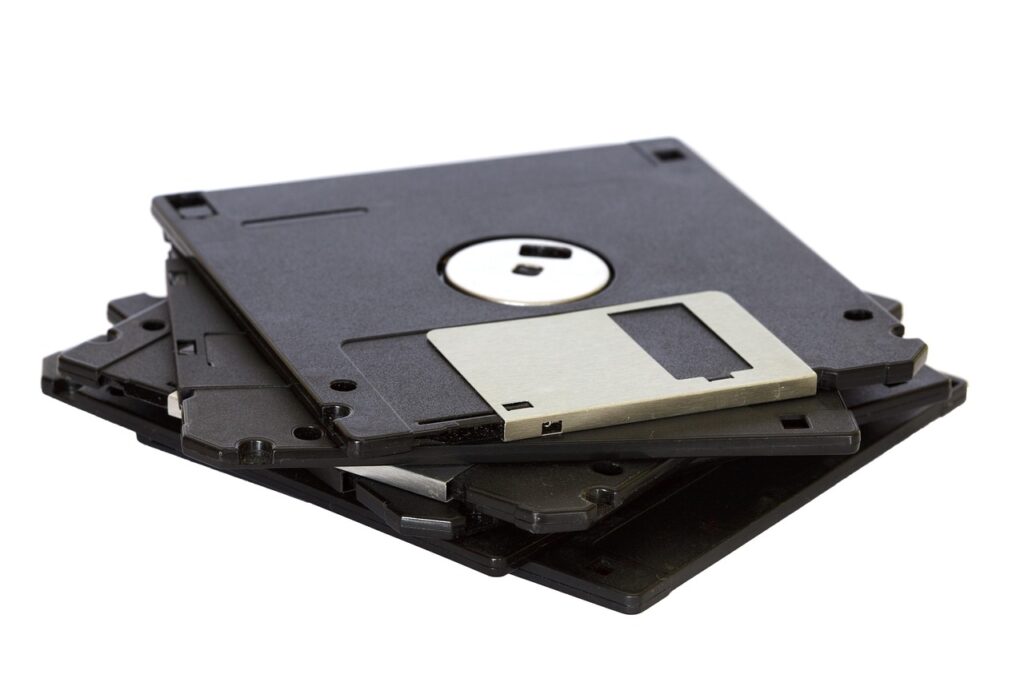

From Floppy Disks to Hard Disk Drives
- Originally, floppy disks stored just a few MB of data, but now hard disk drives and solid-state drives can store terabytes of memory.
- In fact, the first gigabyte hard drive, created by IBM, weighed over 500 pounds.
The Role of Programming Languages
Since computer programs need instructions, programming languages were developed. Moreover, the evolution of these languages enabled software developers to create operating systems, video games, and advanced software development tools.
Surprising Trivia
- The QWERTY keyboard, which is still used by most computer users today, was actually designed to prevent typewriters from jamming.
- The first computer game, developed in the 1950s, was a simple tennis-like simulation.
- Amazingly, the Fugaku supercomputer in Japan is one of the fastest in the world, performing quadrillions of calculations per second.
Evolution of Modern Computers
The Rise of Personal Computers
Gradually, computers shifted from massive machines filling entire rooms to personal computers that could sit on a desk. In the late 1970s and early 1980s, Apple Inc, co-founded by Steve Jobs and Steve Wozniak, released the Apple II, one of the first widely successful personal computers.
Additionally, IBM introduced the IBM PC in 1981, which helped standardize desktop computers across the world. As a result, millions of computer users began adopting these systems for business, education, and entertainment.
Operating Systems and Software Development
Eventually, operating systems became the backbone of modern computers, managing input devices, computer programs, and memory.
Consequently, software development expanded rapidly, introducing tools for data science, video games, and even quantum computing research.
Interestingly, early operating systems were text-based, but later ones introduced graphical user interfaces, making them far more user-friendly.
Data Storage and Accessibility
Over time, data storage has dramatically improved. Originally, computer programs and files were stored on floppy disks with limited capacity.
Later, hard disk drives became standard, and eventually, storage evolved into digital formats with terabytes of memory.
Moreover, cloud storage and search engines have changed how information is accessed and shared globally, allowing computer users to collaborate in real time.
Surprising and Fun Facts About Computers

Cool Facts That Might Surprise You
- The first computer virus was created in 1986 and spread among IBM PCs.
- The world’s first computer game, “Spacewar!”, was created in the 1960s at MIT.
- The first webcam at Cambridge University was set up to monitor a coffee pot.
- Some early computers were the size of a refrigerator and required entire rooms to operate.
- The term “dirty dozen” was once used to describe early malicious software.
Security Concerns
Importantly, computer science has revealed that security remains a significant challenge. Since new computer viruses emerge regularly, strong passwords and cybersecurity practices have become crucial for protecting data.
Furthermore, studies have shown that most common passwords like “123456” and “password” remain widely used, despite being unsafe.
Computers Compared to the Human Brain
Interestingly, facts about computers often highlight comparisons to the human brain.
While computers can perform billions of calculations per second, they still lack the ability to feel emotions, use common sense, or display true creativity.
Additionally, artificial intelligence has been developed to mimic human reasoning, yet it remains limited compared to the complexity of the human mind.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence
Consequently, artificial intelligence has become a cornerstone of modern computer science, with applications ranging from search engines to video games.
Moreover, AI is expected to play a major role in future technologies, including quantum computing and advanced data science.
Historical Contributions
Pioneers in Computing
Without a doubt, figures such as Charles Babbage and Ada Lovelace shaped the foundation of computers.
As noted earlier, Ada Lovelace is regarded as the first programmer, while Babbage conceptualized the analytical engine.
Later, computer scientists like Alan Turing contributed theories on digital computers and artificial intelligence, paving the way for the computer revolution.
Innovators Who Changed the World
- Doug Engelbart (Douglas Engelbart) invented the first computer mouse.
- Steve Jobs and Steve Wozniak revolutionized personal computers with Apple Inc.
- IBM shaped the business computing industry with the IBM PC.
Security, Viruses, and Protection
The First Computer Virus
Historically, the first computer virus appeared in the 1980s, spreading quickly across IBM PCs. Known as the “Brain” virus, it was created in Pakistan and targeted floppy disks.
Consequently, it marked the beginning of a new era in cybersecurity. Moreover, new computer viruses and malicious software continue to emerge, causing threats to both personal computers and enterprise systems.
Malicious Software and New Viruses
Over time, malicious software has grown increasingly complex. In fact, the appearance of the so-called dirty dozen viruses in the 1990s shocked the world of computers.
Furthermore, today’s new viruses can spread globally within minutes, threatening digital infrastructure and financial systems.
Therefore, computer users must remain vigilant, updating their operating systems and using antivirus software.
Importance of Strong Passwords
Additionally, one of the most fascinating facts about computers is how often weak passwords compromise security.
For example, most common passwords such as “123456” and “qwerty” are still widely used. Consequently, experts recommend strong passwords, two-factor authentication, and constant updates to safeguard sensitive data.
Computers in Education and Research
The Role in Academic Progress
Undoubtedly, computers have reshaped education. Since early computers appeared in universities like Cambridge University, they have been used for research, teaching, and software development.
Moreover, students rely on search engines, online tools, and digital libraries to access information instantly.
Contributions to Science
Computers also enable groundbreaking discoveries in science and engineering.
For instance, the Fugaku supercomputer in Japan is capable of simulating complex physical models and partial differential equations, advancing research in climate studies, healthcare, and quantum computing.
Therefore, facts about computers show how vital they are in modern scientific progress.
The World of Computers Today

Integration Into Daily Life
Presently, computers are everywhere: in mobile phones, cars, household appliances, and even medical devices.
Furthermore, personal computers and desktop computers remain common tools for work and entertainment.
Interestingly, facts about computers reveal that their integration into daily life has made them nearly invisible, as people now take them for granted.
Domain Names and the Internet
Equally important to the digital revolution was the introduction of domain names. Since domain names make websites easier to access, they became a foundation for the internet’s usability.
As a result, billions of computer users can now browse, shop, and connect online seamlessly.
Snippet-Friendly Section: Quick Computer Facts
- The first modern computer was ENIAC, built in the United States.
- Ada Lovelace is recognized as the first computer programmer.
- Doug Engelbart invented the first computer mouse.
- The first webcam at Cambridge University was used to monitor coffee.
- The IBM PC popularized desktop computers worldwide.
- The first computer bug came from a real bug trapped in hardware.
- The Fugaku supercomputer is among the fastest in the world.
(Source: University of Pennsylvania – History of ENIAC)
Future of Computers
Quantum Computers
Undoubtedly, one of the most fascinating facts about computers is their potential future.
Quantum computers are being developed to perform calculations that would take digital computers centuries to complete.
Moreover, quantum computing could revolutionize medicine, finance, and artificial intelligence by solving problems that are currently impossible.
Artificial Intelligence and Beyond
Furthermore, artificial intelligence is already transforming industries, from healthcare to entertainment.
Since AI is powered by data science and advanced computer programs, it continues to grow smarter with time.
Consequently, many experts believe AI will redefine the world of computers, enabling machines to reason, learn, and adapt more like the human brain.
Computers and Society

Impact on Daily Life
Clearly, facts about computers show that their influence extends beyond technology into culture, economics, and communication.
Since mobile phones, desktop computers, and tablets are used today by billions of people, society has become interconnected in ways that were unimaginable decades ago.
Additionally, computers have become essential for remote work, online education, and virtual collaboration.
The Long Way Computers Have Come
Indeed, computers have traveled a long way from the analytical engine of Charles Babbage to the compact mobile phones of today.
As fascinating facts reveal, computers that once required an entire room now fit into a pocket while carrying terabytes of memory.
Therefore, the journey of computers represents one of humanity’s greatest achievements.
Facts About Computers: Frequently Asked Questions
What was the world’s first computer?
The world’s first computer considered in modern terms was the Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer (ENIAC), built in the United States during World War II.
Who was the first computer programmer?
Ada Lovelace, who created the first algorithm for Charles Babbage’s analytical engine, is recognized as the first computer programmer.
What was the first computer mouse made of?
The first computer mouse, invented by Doug Engelbart, was made of wood.
What was the first-ever computer virus?
The first-ever computer virus, known as “Brain,” appeared in 1986 and spread via floppy disks.
How does a computer compare to the human brain?
While computers can perform billions of calculations per second, they lack the creativity, common sense, and emotions of the human brain.
What are some fun facts about computers?
Fun facts include that the first webcam at Cambridge University was used to monitor a coffee pot and that the first computer bug was caused by a real bug.
Facts About Computers Conclusion
In summary, facts about computers offer a journey through history, invention, and innovation. From Ada Lovelace’s first algorithm to quantum computing’s future, computers have changed the way people live, work, and connect.
Moreover, fascinating facts reveal that what began with vacuum tubes and square feet of space has evolved into devices that fit in the palm of a hand.
As computers continue to progress, their role in society will only grow stronger, making them one of the most powerful and transformative tools in human history.
Extra Insights and More Fascinating Facts About Computers

The Longest Word and Computer Storage
Interestingly, computers are often compared to language, and one surprising fact involves the longest word. In some programming experiments, extremely long words or variable names have been created to test the limits of systems.
However, computers process information not in letters but in binary code, the language of 0s and 1s.
Moreover, binary code remains the foundation of every operating system, hard disk drive, and software application in use today.
Additionally, memory and storage are closely tied to how data is represented. While early computers stored data using punch cards and analog methods, the introduction of the first hard drive by IBM revolutionized storage.
The hard disk drive could hold more data than floppy disks, enabling the growth of operating systems and programming languages that required more capacity.
Today, random access memory (RAM) and solid-state drives deliver speed and storage far beyond what early software developers could have imagined.
The Role of Operating Systems and Programming Languages
Furthermore, one of the most interesting things about computers is how an operating system bridges the gap between users and hardware.
Without operating systems, computer users would need to interact directly with binary code, which would be extremely complex.
Instead, software developers use programming languages to write instructions that operating systems translate into tasks the computer can perform.
As a result, modern computers support dozens of types of programming languages, each with unique strengths.
For example, some languages are designed for data science, while others are used for software development, artificial intelligence, or even video games.
Consequently, programming languages and operating systems together form the backbone of all types of computers in use today.
Types of Computers: From Analog to Digital
Historically, analog computers were used long before digital ones. These machines solved mathematical problems using continuously variable signals, often applied to engineering and scientific research.
However, digital computers replaced them because of their greater precision, flexibility, and compatibility with operating systems.
Today, types of computers range from desktop computers and mobile phones to supercomputers and quantum systems.
Interestingly, each type of computer has a specific purpose, but all rely on binary code, random access memory, and some form of data storage such as hard disk drives or cloud technology.
Economic and Global Influence of Computers
Computers are no longer just tools for calculation; they have become essential to managing the world’s currency.
Since most transactions no longer rely on physical money, computers handle digital transactions every second of the day.
Furthermore, banking systems, cryptocurrency platforms, and international markets depend on secure operating systems and software developers to ensure smooth functionality.
During the Soviet Union era, much effort was placed into developing computers to compete with the United States.
Although Soviet systems lagged behind in certain areas, their research contributed to early analog computers and later digital systems. Today, the legacy of that competition is seen in the global spread of computing technologies.

Human Connection to Computers
An interesting thing about the history of computers is the reference to the “first man” who interacted with them.
In truth, the first mouse invented by Douglas Engelbart became a symbol of how humans would connect more directly to technology.
Before that, input devices such as punch cards were impersonal and cumbersome. The first mouse represented not only a leap in usability but also a shift toward making computers a part of daily life.
Moreover, alphabetical order became a surprisingly useful tool in computing. From organizing file systems within operating systems to structuring domain names, alphabetical sorting simplified data management.
This small detail shows how even the most common-sense approaches became essential for computer usability.
Read this article when you have a moment. 32 Fascinating Facts About Radio Waves: The Invisible World
Computers in Use Today
Clearly, computers are deeply integrated into everyday activities. From the hard disk drive storing photos to the operating system running mobile phones, their use today is nearly universal.
Interestingly, one fact that often surprises people is just how much random access memory is required to run modern applications, compared to the minimal memory used in early analog systems.
Therefore, facts about computers reveal not only their technical growth but also their cultural impact.
The shift from physical money to digital transactions, from analog computers to quantum systems, and from binary code to user-friendly interfaces highlights how far the technology has come.




