
32 Unique Facts About Ancient Greeks You Probably Never Knew
Facts About Ancient Greeks
Although countless studies have explored ancient greeks and their extraordinary world, many readers still search for deeper facts about ancient greeks that reveal who these people truly were. Because their legacy stretches across philosophy, politics, language, architecture, and mythology, curiosity about this civilization has only grown.
Moreover, modern greece today still echoes traditions shaped during ancient times, from the greek alphabet to cultural celebrations like name day. As a result, learning these facts about ancient greeks can feel like opening a window into the cradle of western civilization.
Consequently, this article was crafted to provide a warm, authoritative, and empathetic guide for anyone eager to uncover interesting facts rooted in the ancient greek civilization.
Additionally, it includes reliable historical context, a snippet-friendly facts section, a verified fact with its source, and insights into greek culture, greek language development, ancient greek mythology, the olympian gods, their political systems, and everyday life in classical greece.
Furthermore, these facts about ancient greeks help readers understand how their ideas shaped the modern world—from democracy and science to marathon events and modern-day olympics.
A Quick, Snippet-Ready Overview of Essential Facts About Ancient Greeks
- Ancient greeks lived across mainland greece, greek islands, and coastal regions of the mediterranean sea.
- The classical period shaped athenian democracy, western philosophy, and monumental architecture.
- Mount olympus was believed to be the home of the olympian gods.
- The first olympic games took place in 776 BCE in ancient olympia.
- Olive oil played a major role in trade, cooking, and religious rituals.
- The greek alphabet evolved from the phoenician alphabet and influenced many english words used today.
Verified Historical Fact:
The first olympic games were held in 776 BCE, according to historical analysis by the International Olympic Committee (Source: IOC Historical Archives).

Understanding the Foundation: Early Facts About Ancient Greeks
Although the history of ancient greece spans multiple eras, each period contributed unique developments. Consequently, understanding these phases helps readers see how different events shaped greek cities and greek people over time.
The Dark Ages (c. 1100–800 BCE)
Even though little writing survived from this era, archaeologists have uncovered evidence of small settlements that eventually grew into early greek city-states. Moreover, this period prepared the groundwork for the archaic period, where greek culture began taking recognizable shape.
The Archaic Period (c. 800–480 BCE)
During this era, the greek alphabet emerged, derived partly from the phoenician alphabet. Additionally, many english words can be traced back to this early linguistic system. Likewise, the first olympic games began during this time, marking a tradition that survives in modern-day olympics. As these facts about ancient greeks reveal, the archaic period ignited major cultural development.
Cultural Expansion in the Classical Period

Although earlier centuries laid important foundations, the classical period (c. 480–323 BCE) is often viewed as the height of ancient greek civilization. Consequently, many of the most important facts about ancient greeks emerge from this era, when philosophy, political systems, sculpture, architecture, and drama flourished.
Additionally, the city of athens rose as a cultural powerhouse, supported by the principles of direct democracy. Even though only certain groups—primarily ancient greek men—could participate, the early democratic structure influenced modern political thinking. Moreover, philosophers such as Socrates, Plato, and Aristotle laid the groundwork for western philosophy, shaping how people reason, question, and understand the world.
Athens and the Birthplace of Democracy
Although athenian democracy was limited in who could vote, it represented a groundbreaking idea in ancient history. Consequently, citizens gathered in assemblies to decide legal and political issues. Furthermore, these public forums helped spread values that later influenced other greek cities and eventually modern greece.
The Role of Greek Temples and Religion
Although religion differed across regions, belief in greek gods unified many communities. Consequently, mount olympus was revered as the dwelling place of the twelve primary olympian gods. Additionally, the goddess athena became a powerful symbol for the city of athens, and her sacred olive tree was said to bless the land with prosperity.
Moreover, ancient greek religion intertwined with daily life. Festivals, musical instruments, and athletic events honored gods such as god apollo and the god of wine, Dionysus. Even though modern-day practices have changed, many greek myths continue to influence literature and storytelling today.
Art, Athletics, and Architecture
Although artistic styles evolved over time, the classical period produced architectural masterpieces still visited today. Consequently, structures like the Parthenon stand as reminders of the creativity and precision of ancient architects. Additionally, several greek temples are now recognized as UNESCO World Heritage Sites.
Likewise, athletic competitions reflected a deep appreciation for physical strength and discipline. Even though many events differ from their modern equivalent, ancient olympic games included contests like the running event, long jump, and other forms of competition. Moreover, the torch relay and ceremonial traditions seen in modern-day olympics were inspired by ancient practices.
The Hellenistic Period and Its Influence
Although the classical period ended with the death of alexander, the hellenistic period (323–31 BCE) spread greek culture across regions stretching into north africa and parts of the persian empire. Consequently, greek cities evolved into multicultural hubs where ideas blended and new innovations emerged.
Additionally, greek language became widespread, influencing trade, education, and diplomacy. Even though many empires rose and fell afterward, hellenistic culture continued shaping ancient rome and later civilizations, reinforcing more facts about ancient greeks that demonstrate their global impact.
Moreover, artifacts from this period show how greek people adapted to different environments while preserving their traditions. Likewise, the blend of artistic styles produced sculptures and mosaics still admired in museums around the world.
Daily Life and Social Customs in Ancient Greek Civilization

Although ancient greek civilization varied across regions, several customs remained common among greek people. Consequently, exploring these daily traditions reveals meaningful facts about ancient greeks that help readers understand how ordinary life unfolded across greek city-states.
Homes, Meals, and Clothing
Although social classes differed, most ancient greek men and women wore simple garments. Consequently, the long tunic or long t-shirt style clothing became widely seen across ancient athens and other greek cities. Additionally, high heels appeared in certain theatrical performances, though they were not everyday footwear.
Moreover, meals often included olives, grains, cheeses, and fish from the mediterranean sea. Olive oil was used in cooking, ceremonies, and skincare, emphasizing the importance of the olive tree in greek culture. Likewise, pottery found in archaeological digs shows scenes of family life, marketplace interactions, and communal gatherings.
Education and Learning
Although education depended on social status, many ancient greek boys received training in literacy, music, and physical exercise. Consequently, the greek alphabet played a major role in early schooling. Additionally, the use of vowel sounds helped shape the rhythm and structure of the greek language, which later influenced many english words.
Even though girls received different forms of instruction focused on household responsibilities, examples from sparta and other regions show variations in educational expectations. Moreover, teachers often taught students to memorize greek myths, providing common cultural references for festivals and storytelling.
Festivals, Beliefs, and Community Life
Although each city-state honored specific gods, many festivals celebrated major olympian deities. Consequently, events honoring god apollo, goddess athena, and Dionysus were marked with music, wine, dancing, and theatrical performances. Additionally, name day traditions survived into modern greece today, reflecting continuity with ancient customs.
Moreover, the evil eye symbol, known across the country of greece, represented protection from harmful energy. Likewise, myths such as the greek myth of hercules communicated lessons about perseverance, strength, and humility—stories still shared in classrooms worldwide.
Sports, Competitions, and the Ancient Olympic Games

Although the modern equivalent of the Olympics is global and technologically complex, many traditions trace back to ancient olympic games. Consequently, exploring the athletic world provides essential facts about ancient greeks that highlight their dedication to physical excellence.
Origins and Structure of Ancient Olympics
Although competitions changed over centuries, the first place winners were awarded crowns made from olive tree branches. Additionally, athletes competed barefoot, wearing minimal clothing that allowed free movement.
Moreover, events such as the running event, long jump, wrestling, and chariot races delighted spectators from different greek cities. Likewise, the marathon event—though modernized today—was inspired by the legendary run of Pheidippides following the greco-persian wars.
Religious and Cultural Significance
Although many see athletics as entertainment, ancient olympics were deeply religious. Consequently, rituals were dedicated to Zeus, and the high priestess of the temple of apollo often played ceremonial roles. Additionally, offerings, sacrifices, and hymns honored gods and reinforced community unity.
Moreover, the torch relay seen in today’s games was inspired by ancient purification rituals. Likewise, athletic success symbolized harmony between the human body and divine favor, further proving how central sports were to ancient greek religion and society.
Political Structures That Shaped Classical Antiquity
Although political systems varied among greek city-states, several shared principles influenced later civilizations. Consequently, many facts about ancient greeks emphasize their impact on governance, law, and social order. Additionally, the development of political frameworks became essential to the identity of ancient greek civilization.
The Evolution of Greek City-States
Although most people associate ancient greece with athens, numerous greek cities flourished across mainland greece and the greek islands. Consequently, each city-state—known as a polis—created its own laws, customs, and cultural identity.
Additionally, city-states often competed for power, shaping alliances and rivalries that influenced historical events such as the second peloponnesian wars. Moreover, these conflicts demonstrated the strategic strength and resourcefulness of greek people defending their territory.
Direct Democracy in Athens
Although limited to free male citizens, direct democracy became a defining feature of the city of athens. Consequently, citizens participated in assemblies where they voted on laws, military decisions, and civic issues.
Additionally, public speaking became an essential skill, shaping how leaders communicated with communities. Moreover, this form of democracy inspired future governments, making it one of the most influential facts about ancient greeks relevant to modern political thought.
Interactions With Empires and Neighbors
Although greece remained independent for centuries, conflicts with the persian empire tested the strength of city-states. Consequently, battles during the greco-persian wars became defining moments in ancient history.
Additionally, military victories demonstrated how unity could overcome larger forces. Even though the persian army outnumbered greek forces in several battles, strategy and terrain gave greeks the advantage. Moreover, stories from this era highlight courage, sacrifice, and resilience—values admired by readers even today.
Language, Literature, and Communication

Although the greek language evolved over centuries, its influence remains difficult to overstate. Consequently, many facts about ancient greeks revolve around communication, writing, and storytelling traditions that shaped western literature.
The Greek Alphabet and Its Impact
Although adapted from the phoenician alphabet, the greek alphabet introduced written vowel sounds, which helped improve clarity and pronunciation. Consequently, readers gained the ability to understand texts with greater accuracy.
Additionally, many english words trace their roots to greek word origins, particularly in science, medicine, and philosophy. Moreover, linguistic historians believe the adoption of vowels expanded literary expression during the archaic and classical periods.
Myths, Legends, and Oral Traditions
Although writing became increasingly common, oral storytelling remained central to ancient greek mythology. Consequently, myths about heroes, monsters, and olympian gods shaped moral lessons and cultural identity.
Additionally, stories such as the greek myth of hercules emphasized bravery, persistence, and ethical dilemmas faced in ancient times. Moreover, mythological narratives helped unify communities across different regions, reinforcing shared values and customs.
If you have some free time, it might be helpful to check out this article The Exciting Allure of Aphrodite: Goddess of Love and Beauty. It covers some relevant points.
Influence on Later Civilizations
Although ancient rome conquered greece, roman culture absorbed greek beliefs, art, and intellectual traditions. Consequently, the roman empire helped spread greek literature across europe. Additionally, these preserved works later fueled the Renaissance and continue to influence modern education.
Moreover, the enduring power of greek storytelling remains one of the most compelling facts about ancient greeks examined by scholars today.
Geography, Environment, and Lifestyle Influences
Although ancient greeks lived across diverse landscapes, their environment strongly influenced how communities developed. Consequently, many facts about ancient greeks are tied directly to geography, climate, and natural resources. Additionally, archaeological findings confirm how the mediterranean sea shaped food, trade, exploration, and settlement patterns.
Mountains, Coastlines, and Agricultural Life
Although rugged mountains covered much of mainland greece, fertile valleys and coastal plains supported agriculture. Consequently, olives, grapes, and grains became staple crops. Additionally, the olive tree held symbolic and economic significance, appearing in myths about goddess athena and serving as a major source of olive oil.
Moreover, coastal access allowed trade networks to flourish. Even though travel across mountainous terrain proved challenging, the sea enabled interaction with egypt, north africa, and regions of the persian empire. Likewise, maritime exchange helped spread greek culture, beliefs, and artistic techniques.
Climate and Daily Rhythms
Although summers were warm and dry, winters brought cooler temperatures ideal for indoor activities. Consequently, seasonal changes shaped farming cycles, religious festivals, and travel plans. Additionally, historians note that the quietest time of the year often occurred during midsummer when labor paused due to intense heat.
Moreover, outdoor theaters, gymnasiums, and market squares reflected how the climate encouraged open-air lifestyles. Even though modern greece has evolved significantly, similar weather patterns continue to influence social life today.
Architecture, Art, and Monumental Creations
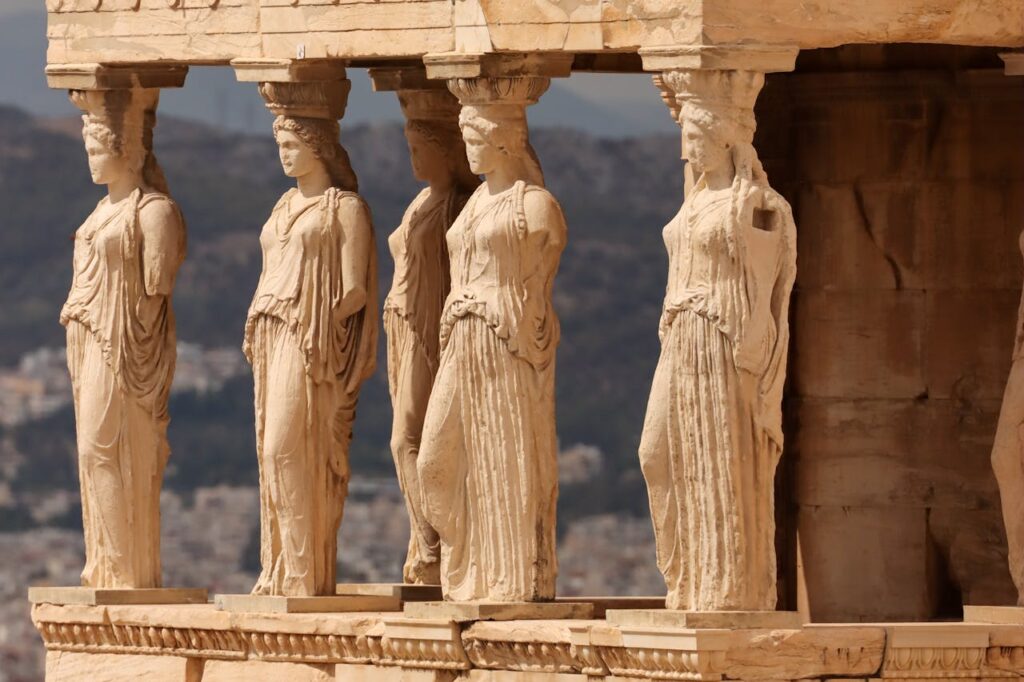

Although artistic expression varied across different time periods, many architectural structures remain admired today. Consequently, several facts about ancient greeks highlight the importance of temples, sculptures, and public buildings.
Greek Temples and Their Symbolism
Although temples honored specific gods, they also served as community landmarks. Consequently, structures dedicated to goddess athena, god apollo, and other olympian gods reflected both devotion and civic pride.
Additionally, greek temples were built using symmetrical designs, tall columns, and marble finishes. Moreover, many of these structures are now recognized as UNESCO World Heritage Sites, preserving the legacy of classical antiquity for visitors worldwide.
Sculpture and Pottery
Although sculptors experimented with realism and idealized forms, their work became renowned for precision and balance. Consequently, statues from the classical period influence modern art education.
Additionally, pottery designs revealed everyday scenes, myths, and athletic competitions. Moreover, these artifacts provide visual evidence supporting many facts about ancient greeks, helping historians recreate lost aspects of ancient life.
Technology, Innovation, and Surprising Inventions
Although many assume ancient technology was limited, numerous innovations originated in greek city-states. Consequently, exploring these inventions offers fascinating facts about ancient greeks that challenge common assumptions.
Early Tools and Devices
Although simple in design, several tools demonstrated remarkable engineering. Consequently, devices such as the early alarm clock—created using dripping water and mechanical triggers—showed impressive ingenuity. Additionally, scientific thinkers like Archimedes contributed principles that remain foundational in modern physics.
Moreover, musical instruments such as the lyre and aulos enriched festivals, educational rituals, and theatrical performances. Even though technology evolved slowly, the creativity displayed during ancient times continues to inspire modern researchers.
Athletic and Cultural Innovations
Although athletic contests existed elsewhere, ancient greek olympics formalized rules and introduced standardized events. Consequently, these innovations influenced the running event, long jump, and other competitions seen today.
Additionally, certain clothing styles such as the long tunic were adapted for movement and comfort during athletics. Moreover, the tradition of awarding first place victors with olive wreaths highlighted the symbolic importance of the olive tree in greek culture.
Trade, Economy, and Expansion of Influence
Although economies differed across regions, trade became central to prosperity in ancient greek civilization. Consequently, numerous facts about ancient greeks revolve around how markets, ports, and merchant networks shaped cultural and political development. Additionally, trade encouraged the movement of ideas, goods, and artistic styles between greek cities and distant lands.
Sea Trade Across the Mediterranean
Although land routes proved difficult due to mountainous terrain, the mediterranean sea allowed efficient travel. Consequently, greek ships carried pottery, olive oil, wine, and textiles to markets in egypt, north africa, and the persian empire.
Additionally, returning merchants brought back raw materials, luxury goods, and foreign customs that enriched greek culture. Moreover, maritime commerce encouraged technological improvements in shipbuilding, navigation, and port management.
Marketplaces and Local Commerce
Although long-distance trade was vital, local marketplaces—known as agoras—played a major role in daily life. Consequently, agoras became centers where people gathered to exchange goods, discuss politics, and share news.
Additionally, stalls offered produce, pottery, clothing, tools, and imported items. Moreover, agoras helped unify communities by providing shared spaces that blended economic, legal, and cultural interactions.
Major Conflicts That Shaped Greek History

Although ancient greece produced extraordinary achievements, its history also included wars that reshaped the region. Consequently, important facts about ancient greeks highlight how military challenges influenced alliances, strategies, and political transformations.
The Greco-Persian Wars
Although greek city-states often disagreed, threats from the persian empire forced them to unite. Consequently, key battles such as Marathon and Salamis showcased the strategic brilliance of greek commanders.
Additionally, victory over the persian army strengthened confidence in greek identity. Moreover, these triumphs inspired stories, festivals, and athletic traditions—such as the marathon event—that continue to be honored today.
The Peloponnesian Conflicts
Although unity once prevailed, tensions eventually grew between athens and sparta. Consequently, the second peloponnesian wars erupted, altering the balance of power across mainland greece.
Additionally, these conflicts weakened greek cities, leaving them vulnerable to outside influence. Moreover, historians cite these wars as significant facts about ancient greeks that explain the eventual rise of macedonian power.
Alexander the Great and the Hellenistic Expansion
Although macedonia had long been considered separate from southern greek cities, the rise of Alexander the Great changed the region’s course. Consequently, his campaigns spread greek culture far beyond its original borders.
Conquests and Cultural Spread
Although his empire expanded rapidly, greek language and customs spread even faster. Consequently, greek became the common tongue across newly conquered regions, and greek cities developed into multicultural centers.
Additionally, libraries, markets, and temples built in this era reflected mixed architectural styles. Moreover, the death of Alexander marked the beginning of political fragmentation but ensured the continuation of hellenistic influence.
Legacy of the Hellenistic Period
Although political unity faded, cultural unity remained strong. Consequently, art, science, mathematics, and philosophy expanded as scholars worked in centers like Alexandria.
Additionally, preserved writings from this era reveal deeper facts about ancient greeks, including advancements in astronomy, anatomy, and mechanics. Moreover, these developments shaped ancient rome and influenced the evolution of modern scientific thought.
Religion, Rituals, and the Sacred Landscape
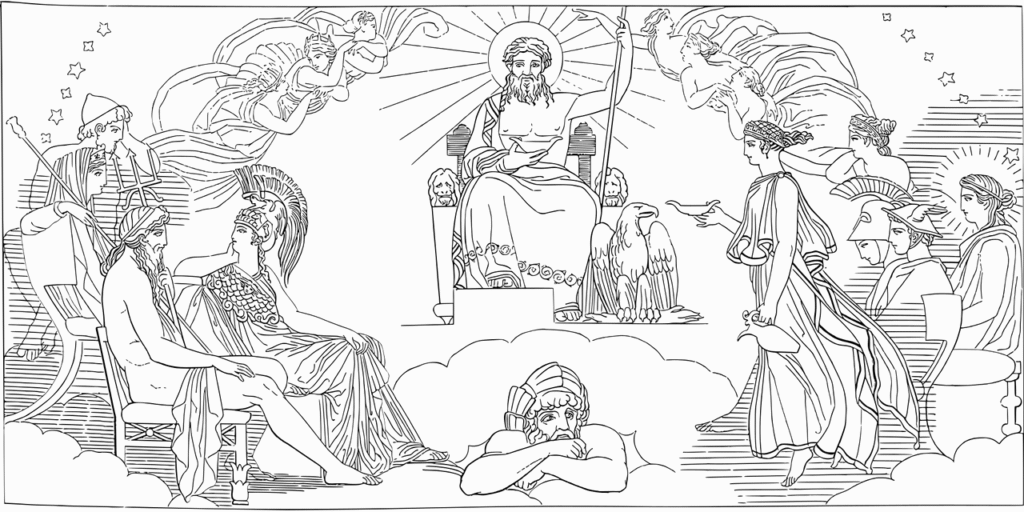

Although mythology often receives the most attention, the lived religious experience of ancient greeks reveals rich cultural meaning. Consequently, many facts about ancient greeks revolve around rituals, sacred spaces, and shared beliefs that shaped daily life. Additionally, evidence from temples, inscriptions, and festivals demonstrates how deeply religion influenced personal identity and community order.
Sacred Sites and Pilgrimage
Although temples honored specific gods, certain locations became renowned throughout classical greece. Consequently, the most famous oracle at Delphi drew visitors from across greek city-states seeking guidance from the high priestess of the temple of apollo.
Additionally, mount olympus remained central to belief as the legendary home of the olympian gods. Moreover, these sacred places were not just religious centers—they were social gathering points, political stages, and hubs of cultural expression.
Ritual Practices and Offerings
Although offerings varied, sacrifices of animals, wine, and olive oil were common. Consequently, rituals honored gods such as goddess athena, god apollo, and Dionysus, reinforcing trust in divine protection.
Additionally, hymns and prayers accompanied major ceremonies, many of which aligned with agricultural cycles or significant historical events. Moreover, these rituals reveal important facts about ancient greeks, showing how religion connected individuals to their community and environment.
Mythology and Its Enduring Impact
Although myths may seem like simple stories, they conveyed complex lessons about morality, bravery, and fate. Consequently, mythology remains one of the most accessible facts about ancient greeks for modern readers.
Heroes and Legends
Although heroes such as Hercules and Achilles stand out, lesser-known figures played equally important roles in ancient narratives. Consequently, their stories helped teach children about virtue and responsibility.
Additionally, the greek myth of hercules symbolized endurance and strength—values admired across ancient times. Moreover, these legends influenced artistic expression, theatrical performances, and ceremonial traditions.
Gods and Divine Roles
Although olympian gods were believed to control natural forces, they also symbolized human emotions. Consequently, myths offered explanations for storms, harvest cycles, illness, and unpredictable events.
Additionally, epics and hymns kept these stories alive, allowing them to spread across greek islands and mainland greece. Moreover, the survival of these myths in literature underscores how deeply they shaped ancient greek religion.

Enduring Influence on Modern Society
Although centuries have passed since the classical period, many modern customs trace back to ancient greek civilization. Consequently, numerous facts about ancient greeks explain why their legacy still shapes our world today.
Language and Vocabulary
Although languages evolve, countless english words have greek roots. Consequently, fields such as medicine, law, philosophy, and astronomy rely heavily on greek terminology.
Additionally, the greek alphabet influenced later writing systems, bridging ancient and modern communication. Moreover, even the latin word for greece reflects ancient cultural identities passed through history.
Sports, Arts, and Global Traditions
Although modern-day olympics have transformed dramatically, many traditions began in ancient olympics. Consequently, the torch relay, athletic ceremonies, and competitive spirit remain direct descendants of ancient events.
Additionally, artistic styles such as symmetry, geometric patterns, and naturalistic sculpture still inspire architects and designers. Moreover, these influences demonstrate that understanding facts about ancient greeks helps explain developments in global culture.
Fun Facts and Lesser-Known Insights
Although many historical records emphasize politics and warfare, daily curiosities also reveal enjoyable facts about ancient greeks. Consequently, exploring these details adds warmth and personality to the broader picture of ancient greek civilization.
Everyday Curiosities
Although it may surprise some readers, several inventions commonly used today can be traced to ancient greek ingenuity. Consequently, items such as the early alarm clock, early maps, and even theatrical stage techniques emerged during ancient times.
Additionally, ancient greek men often exercised in gymnasiums that served as both training areas and social spaces. Moreover, certain clothing styles—including long tunics worn during festivals—remained popular throughout different time periods.
Cultural Traditions That Continue Today
Although modern greece differs greatly from classical antiquity, traditions such as name day celebrations, the use of olive oil in cooking, and community festivals demonstrate cultural continuity. Consequently, these living customs form part of the most compelling facts about ancient greeks that still influence greece today.
Additionally, visitors to greek islands and national parks often encounter landscapes described in old myths and legends. Moreover, UNESCO World Heritage Sites across the country of greece preserve temples, theaters, and monuments that connect modern travelers with ancient history.

Facts About Ancient Greeks: Frequently Asked Questions
What were some important contributions made by ancient greeks?
Although ancient greeks lived thousands of years ago, they contributed democracy, philosophy, theater, the greek alphabet, and the ancient olympic games.
Why was mount olympus significant in ancient greek religion?
Although a real mountain, mount olympus was believed to be home to the olympian gods and symbolized divine authority.
Did ancient greeks create the modern-day olympics?
Although modern events differ, the foundation of today’s Olympics came from ancient olympics established in the 8th century BCE.
How did greek culture spread beyond mainland greece?
Although political control shifted, greek culture spread through trade, colonization, and the conquests of Alexander the Great.
What role did goddess athena play in ancient athens?
Although many gods were honored, goddess athena served as the protector of athens and symbolized wisdom, courage, and craftsmanship.
How has the greek alphabet influenced english words?
Although languages evolve, many english words derive from greek origins, especially in scientific and academic fields.
Facts About Ancient Greeks Conclusion

Although centuries have passed, the remarkable story of ancient greek civilization continues to captivate scholars, travelers, and curious readers. Consequently, learning facts about ancient greeks helps reveal how their ideas shaped democracy, language, mythology, architecture, and global culture.
Additionally, their influence continues to appear in modern-day olympics, academic traditions, artistic expression, and everyday vocabulary.
Moreover, exploring ancient greek history fosters a deeper appreciation for the resilience, creativity, and wisdom of greek people.
Even though the world has changed dramatically, their legacy remains alive through preserved temples, literary masterpieces, enduring myths, and cultural traditions woven into the fabric of modern societies.
Because these facts about ancient greeks highlight achievements spanning politics, art, science, and daily life, readers gain a fuller understanding of why greece is celebrated as the cradle of western civilization.
Ultimately, the story of ancient greeks serves not only as a record of the past but as an inspiration for the future—reminding us that knowledge, courage, and curiosity can shape the world for generations.
If it’s not too much trouble, I’d recommend reading this article Fascinating Facts About Hades: Greek God of the Underworld. It could add some valuable context to our discussion.



