Interesting Facts About the Urinary System You Should Know
Facts About the Urinary System
The urinary system, also known as the renal system, plays a crucial role in maintaining the body’s internal balance. It is responsible for filtering waste products from the blood, regulating blood pressure, and ensuring that the right balance of water and electrolytes is maintained. Understanding the facts about the urinary system can help us appreciate its importance and identify potential health issues early. This article delves into various aspects of the urinary system, including its functions, common problems, and ways to maintain a healthy bladder.
Table Of Content
- The Components of the Urinary System
- Common Issues with the Urinary System
- Maintaining a Healthy Urinary System
- Surprising Facts About the Urinary System
- Treatment Options for Common Urinary System Issues
- About the Urinary System
- Facts About the Urinary System: Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- More Surprising Facts About the Urinary System
- Facts About the Urinary System
- About the Urinary System
The Components of the Urinary System
What Makes Up the Urinary System?
The urinary system consists of several key components that work together to remove waste and regulate the body’s fluids. These include:
- Kidneys: The primary organs of the urinary system, responsible for filtering blood and producing urine. These bean-shaped organs are located below the rib cage, on either side of the spine.
- Ureters: Thin tubes that transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder.
- Bladder: A hollow organ that stores urine until it is ready to be expelled from the body.
- Urethra: A small tube that carries urine from the bladder to the outside of the body.
The Role of the Kidneys
The kidneys are essential for filtering blood and removing waste products. They contain tiny filtering units called nephrons, which include a renal tubule and small blood capillaries. Each day, the kidneys filter around 150 quarts of blood to produce 1 to 2 quarts of urine, which contains waste substances and extra water.
Common Issues with the Urinary System
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
Urinary tract infections are among the most common medical problems affecting the urinary system. They can occur in different parts of the urinary system, including the bladder, urethra, and kidneys. Symptoms of a UTI include a burning sensation during urination, frequent urges to urinate, and cloudy or strong-smelling urine.
Kidney Stones
Kidney stones are hard deposits of minerals and salts that form inside the kidneys. They can cause severe pain, blood in the urine, and difficulty passing urine. In some cases, kidney stones can lead to more serious problems, such as infections or kidney damage.
Overactive Bladder
An overactive bladder is a condition characterized by a sudden and urgent need to urinate, often leading to frequent urination. This condition can be disruptive to daily life and may require treatment options such as medication or physical therapy.
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
Chronic kidney disease is a long-term condition where the kidneys gradually lose their ability to function properly. It can lead to kidney failure, requiring dialysis or a kidney transplant. Symptoms of CKD include fatigue, high blood pressure, and fluid retention.
Maintaining a Healthy Urinary System

Tips for Bladder Health
Maintaining a healthy bladder is crucial for overall urinary system health. Here are some tips:
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water helps flush out waste products and keeps the urinary system functioning properly.
- Practice Good Hygiene: Clean the genital area regularly to prevent infections.
- Avoid Irritants: Limit intake of caffeine, alcohol, and spicy foods, which can irritate the bladder.
- Pelvic Floor Exercises: Strengthening the pelvic floor muscles can help prevent urinary incontinence and other bladder problems.
Diet and Lifestyle
A healthy lifestyle and diet can significantly impact the health of your urinary system. Eating fiber-rich foods, avoiding smoking, and maintaining a healthy weight are all important steps to support your renal system.
In the next section, we will explore more interesting facts about the urinary system, delve deeper into its functions, and discuss common urinary symptoms and their possible causes. Stay tuned for more insights!
Surprising Facts About the Urinary System
How the Urinary System Works
Understanding how the urinary system works can reveal surprising facts about its efficiency and complexity. The process of urine formation involves several steps:
- Filtration: Blood enters the kidneys through the renal arteries. In the kidneys, blood is filtered through the nephrons, removing waste products and extra water.
- Reabsorption: Essential substances like glucose, certain salts, and water are reabsorbed back into the bloodstream from the renal tubules.
- Secretion: Additional waste substances are secreted into the renal tubules from the blood.
- Excretion: The final product, urine, is collected in the renal pelvis and transported to the bladder via the ureters.
The amount of urine produced varies based on factors like hydration levels, diet, and overall health. On average, an adult produces about 6 to 8 cups of urine each day.
The Importance of Regular Urination
Regular urination is essential for maintaining bladder health and preventing infections. Holding urine for prolonged periods can lead to bladder infections or other urinary problems. It is recommended to empty the bladder every three to four hours during the day.
The Unique Structure of the Female Urethra
The female urethra is much shorter than the male urethra, measuring about 1.5 inches in length. This anatomical difference is one reason why women are more prone to urinary tract infections compared to men. Bacteria have a shorter distance to travel to reach the bladder, increasing the risk of infection.
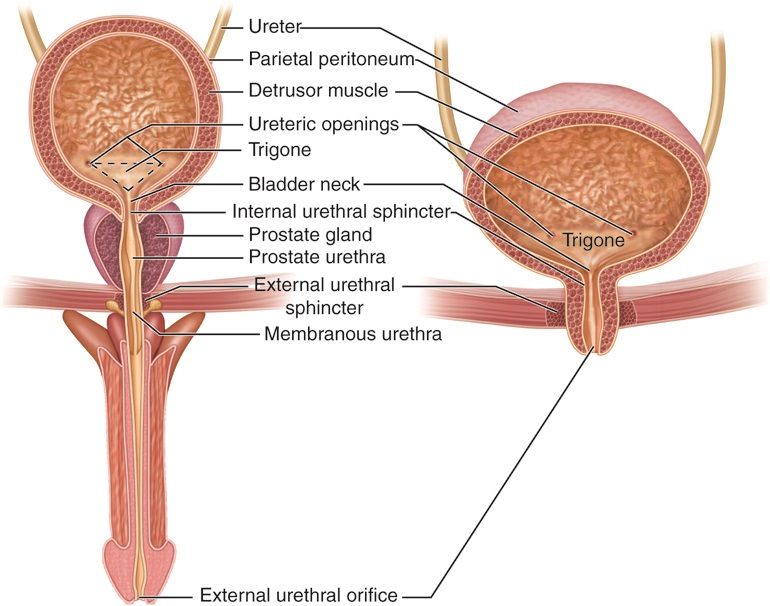
The Role of the Bladder
The bladder is a hollow organ located in the lower belly, protected by the pelvic bones. It can expand and contract to store and release urine. The average bladder can hold about 1.5 to 2 cups of urine comfortably. When the bladder reaches its capacity, stretch receptors signal the brain, creating the urge to urinate.
Interesting Fact: Red Blood Cell Production
The kidneys play a crucial role in red blood cell production by releasing a hormone called erythropoietin. This hormone stimulates the bone marrow to produce red blood cells, which are essential for carrying oxygen throughout the body. According to the National Kidney Foundation, this function highlights the kidneys’ importance beyond just waste removal.
Frequent Urination and Its Causes
Frequent urination can be a symptom of various underlying conditions. Some possible causes include:
- Diabetes: High blood sugar levels can lead to increased urine production.
- Urinary Tract Infections: Infections can irritate the bladder, causing frequent urges to urinate.
- Overactive Bladder: This condition involves sudden, uncontrollable urges to urinate.
- Prostate Issues: An enlarged prostate can press against the urethra, causing frequent urination in men.
- Pregnancy: The growing uterus can put pressure on the bladder, leading to more frequent trips to the bathroom.
Urinary Incontinence
Urinary incontinence, or the loss of bladder control, is a common issue, especially among older adults. It can range from occasional leaks when coughing or sneezing to a sudden and urgent need to urinate that is difficult to control. There are several types of urinary incontinence:
- Stress Incontinence: Caused by pressure on the bladder from physical activities such as coughing or lifting.
- Urge Incontinence: A sudden, intense urge to urinate followed by involuntary leakage.
- Overflow Incontinence: When the bladder doesn’t empty completely, leading to dribbling.
- Functional Incontinence: Due to physical or mental impairments that prevent reaching the bathroom in time.
Preventing Kidney Stones
Kidney stones can be extremely painful and are often caused by a buildup of certain minerals in the urine. To prevent kidney stones, it is important to stay hydrated, limit salt intake, and consume a balanced diet rich in calcium and low in oxalates (found in foods like spinach and beets).
In the next section, we will discuss treatment options for common urinary system issues, answer frequently asked questions, and provide more insights into maintaining a healthy urinary system. Stay tuned for more essential information!
Treatment Options for Common Urinary System Issues

Managing Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
Urinary tract infections are typically treated with antibiotics prescribed by a healthcare provider. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to prevent the infection from spreading to the kidneys. Drinking plenty of water and cranberry juice can also help flush out bacteria from the urinary tract. Preventive measures include proper hygiene practices, urinating after sexual intercourse, and avoiding irritants like douches and harsh soaps in the genital area.
Dealing with Kidney Stones
Treatment for kidney stones depends on their size and composition. Small stones often pass on their own with increased fluid intake. Pain relievers and medications that relax the ureter walls can help ease the passage. For larger stones, medical procedures like extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL) or ureteroscopy may be necessary. In severe cases, surgery might be required. Preventive measures include drinking plenty of fluids, reducing sodium and animal protein intake, and maintaining a diet that balances calcium and oxalates.
Addressing Overactive Bladder
An overactive bladder can significantly impact quality of life. Treatment options include:
- Behavioral Techniques: Bladder training, timed voiding, and pelvic floor exercises can help control symptoms.
- Medications: Anticholinergic drugs can reduce bladder spasms.
- Botox Injections: These can relax the bladder muscles and reduce urgency.
- Nerve Stimulation: Techniques like sacral nerve stimulation can help regulate bladder function.
About the Urinary System
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Management
Managing chronic kidney disease involves controlling underlying conditions like diabetes and high blood pressure. Lifestyle changes, such as adopting a kidney-friendly diet low in sodium and protein, are crucial. Regular monitoring through blood tests and urine samples can help track kidney function. In advanced stages, treatments may include dialysis or kidney transplants.
Bladder Infections
Bladder infections, a type of UTI, are treated similarly to other urinary tract infections with antibiotics. Ensuring complete emptying of the bladder during urination and maintaining proper hydration can help prevent bladder infections. For recurrent infections, a healthcare provider may suggest long-term, low-dose antibiotics.
Coping with Urinary Incontinence
Treatment for urinary incontinence depends on its type and severity. Options include:
- Lifestyle Changes: Weight loss, fluid management, and dietary adjustments can help.
- Pelvic Floor Exercises: Strengthening the pelvic floor muscles through exercises like Kegels can improve control.
- Medications: Drugs can help manage symptoms of urge and stress incontinence.
- Medical Devices: Pessaries and urethral inserts can provide support for those with stress incontinence.
- Surgery: Procedures like sling surgery can provide long-term relief for severe cases.
Bladder Health and Lifestyle Tips
Maintaining bladder health involves several lifestyle habits:
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water to flush out waste products and reduce the risk of kidney stones and UTIs.
- Diet: A balanced diet rich in fiber-rich food supports overall bladder health.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity, including pelvic floor exercises, can strengthen the bladder muscles.
- Avoiding Irritants: Limit intake of caffeine, alcohol, and artificial sweeteners, which can irritate the bladder.
- Scheduled Bathroom Visits: Regular urination helps prevent bladder overdistension and infections.
Facts About the Urinary System: Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the symptoms of a urinary tract infection (UTI)?
Common symptoms of a UTI include a burning sensation during urination, frequent urination, cloudy or strong-smelling urine, and pelvic pain in women. If the infection reaches the kidneys, symptoms may include back pain, fever, and nausea.
How can I prevent kidney stones?
To prevent kidney stones, drink plenty of water, reduce salt and animal protein intake, and consume a balanced diet with adequate calcium. Avoid foods high in oxalates, such as spinach and beets, and consult a healthcare provider for personalized dietary recommendations.
What causes overactive bladder?
An overactive bladder can be caused by several factors, including nerve damage, bladder infections, and conditions like diabetes and multiple sclerosis. Sometimes, the cause is unknown. Treatment options include medications, behavioral techniques, and nerve stimulation.
How does the urinary system affect blood pressure?
The kidneys play a key role in regulating blood pressure by controlling the balance of fluids and salts in the body. When the kidneys are not functioning properly, it can lead to high blood pressure. Conversely, high blood pressure can damage the kidneys, creating a vicious cycle.
What are the treatment options for chronic kidney disease (CKD)?
Treatment for CKD focuses on managing underlying conditions, such as diabetes and hypertension, through lifestyle changes, medications, and regular monitoring. In advanced stages, dialysis or kidney transplants may be necessary to manage kidney failure.
In the next section, we will delve deeper into surprising facts about the urinary system, discuss common urinary symptoms and their possible causes, and provide more insights into maintaining a healthy lifestyle for optimal urinary health. Stay tuned for more essential information!
More Surprising Facts About the Urinary System
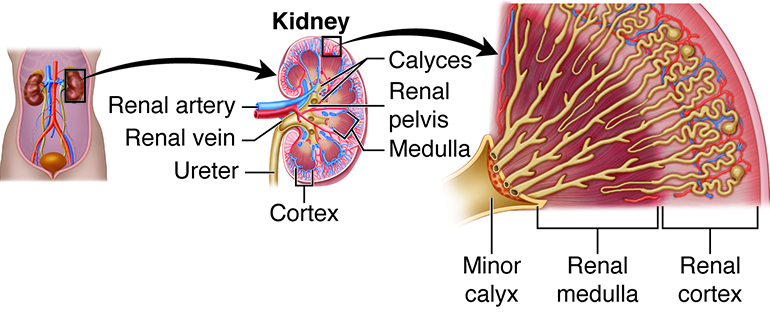
The Kidneys and Their Essential Role
One of the most surprising facts about the urinary system is the kidneys’ multifaceted role. These bean-shaped organs not only filter waste products but also regulate electrolyte balance, blood pressure, and red blood cell production. Each kidney contains about one million nephrons, the tiny filtering units responsible for removing waste substances and extra water from the blood. This complex filtration process results in the production of urine, which is then transported to the bladder.
The Bladder’s Adaptability
The bladder is a highly adaptable organ. It is lined with a special type of tissue called transitional epithelium, which allows it to stretch and accommodate varying amounts of urine. A healthy bladder can hold up to 16 ounces (about two cups) of urine for two to five hours. The bladder’s muscular walls contract to expel urine through the urethra, controlled by sphincter muscles.
The Female Urethra’s Unique Structure
The female urethra, which is much shorter than the male urethra, measures about 1.5 to 2 inches long. This anatomical difference makes women more susceptible to urinary tract infections (UTIs) because bacteria have a shorter distance to travel to reach the bladder. Proper hygiene and preventive measures are crucial for maintaining bladder health in women.
The Importance of Hydration
Staying well-hydrated is vital for urinary system health. Water helps dilute the urine, making it less likely for minerals and salts to form kidney stones. Adequate hydration also helps flush out bacteria from the urinary tract, reducing the risk of infections. It’s generally recommended to drink eight 8-ounce glasses of water daily, though individual needs can vary.
Facts About the Urinary System

About the Urinary System
Understanding Urinary Symptoms
Recognizing and understanding urinary symptoms can help identify potential health issues early. Some common symptoms include:
- Frequent Urination: This can be caused by various factors, including diabetes, UTIs, and overactive bladder.
- Painful Urination: Often a sign of a UTI or bladder infection.
- Blood in Urine: Known as hematuria, this can indicate kidney stones, infections, or more serious conditions like bladder cancer.
- Urinary Incontinence: The loss of bladder control, which can be due to weakened pelvic floor muscles, nerve damage, or other underlying conditions.
Addressing Bladder Cancer
Bladder cancer is a serious condition that affects the cells lining the bladder. Early symptoms include blood in the urine, frequent urination, and pelvic pain. Early detection and treatment are crucial for a better prognosis. Treatment options vary depending on the stage and may include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and immunotherapy. Regular check-ups and awareness of urinary symptoms can aid in early detection.
The Role of Health Professionals
Health professionals play a critical role in diagnosing and treating urinary system issues. Regular check-ups, including blood tests and urine samples, can help monitor kidney function and detect problems early. If you experience any persistent urinary symptoms, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider to determine the underlying cause and appropriate treatment.
Now you know more Facts About the Urinary System, next read Intriguing Facts About the Circulatory System
Facts About the Urinary System Conclusion
Understanding the facts about the urinary system highlights its vital role in maintaining overall health. From filtering waste products to regulating blood pressure and red blood cell production, the urinary system’s functions are intricate and essential. Awareness of common issues, such as urinary tract infections, kidney stones, and overactive bladder, can help in early detection and management. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, staying hydrated, and seeking regular medical care are crucial steps in supporting your urinary system.
In summary, the urinary system is a complex and crucial part of the human body. By learning about its components, functions, and common issues, we can take better care of our health and address any concerns promptly. Remember to stay hydrated, practice good hygiene, and consult health professionals regularly to keep your urinary system in optimal condition.




