
Interesting Facts About E.coli – The Best 15
Interesting Facts About E.coli: Unraveling the Mysteries of a Microbial World
Welcome to the fascinating world of E.coli! In this article, we will delve into the intriguing facts about E.coli that surround this enigmatic bacterium.
Escherichia coli, commonly known as E.coli, is a type of bacteria that is both awe-inspiring and potentially harmful.
While some strains of E.coli reside peacefully in the intestines of healthy humans and warm-blooded animals, others can lead to severe illness and even death.
Through this exploration, we aim to provide you with valuable insights into this diverse group of bacteria.
Including their impact on public health, symptoms of infection, and methods of prevention.
The Basics of E.coli
E.coli, belonging to the family Enterobacteriaceae, is a gram-negative bacterium found in the intestines of humans and animals.
This bacterium encompasses a wide range of strains, some of which are pathogenic and capable of causing various infections.
The most well-known strain is Shiga toxin-producing E. coli (STEC), responsible for numerous outbreaks and severe cases of illness.
Shiga Toxin-Producing E. coli (STEC)

Shiga toxin-producing E. coli (STEC) is a highly virulent strain of E. coli that has garnered significant attention.
Due to its association with outbreaks and severe cases of illness, particularly in the United States.
This strain produces toxins known as Shiga toxins, which can cause damage to the lining of the small intestine and red blood cells.
STEC infections are commonly associated with consuming contaminated food or water. Such as undercooked ground beef, unpasteurized milk, or raw vegetables.
Additionally, person-to-person transmission can occur in settings like day care centers, where young children are more vulnerable to infection.
Symptoms and Complications of STEC Infections
The symptoms of STEC infections can vary from mild to severe. Depending on the individual and the specific strain involved.
Common symptoms include severe stomach cramps, diarrhea (often bloody), and vomiting.
In some cases, individuals may also experience fever and headache.
While most individuals recover from STEC infections within a week, some may develop complications.
Especially in young children and older adults.
One of the most severe complications is hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS). A condition characterized by kidney damage and the breakdown of red blood cells.
HUS can lead to serious problems, including acute kidney failure. Requiring intensive care, and potentially kidney dialysis.
Preventing STEC Infections

Preventing STEC infections involves practicing good hygiene and adopting safe food handling practices.
Here are some important measures to consider:
Properly Cook Meat: Ensure that ground beef, particularly hamburgers, is cooked to a safe internal temperature to eliminate any potential E. coli bacteria present.
Using a food thermometer can help ensure thorough cooking.
Avoid Unpasteurized Products: To minimize the risk of infection, avoid consuming unpasteurized milk and other dairy products. Which can be a potential source of E. coli bacteria.
Choose pasteurized versions instead.
Practice Good Hygiene: Wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water before handling food, after using the restroom, and after contact with animals.
This helps prevent the spread of harmful bacteria.
Fresh Fruits and Vegetables: Wash fresh fruits and vegetables thoroughly before consumption, especially those that are consumed raw.
This helps remove any potential contamination present on the surface.
Different Strains of E. coli and Their Impact
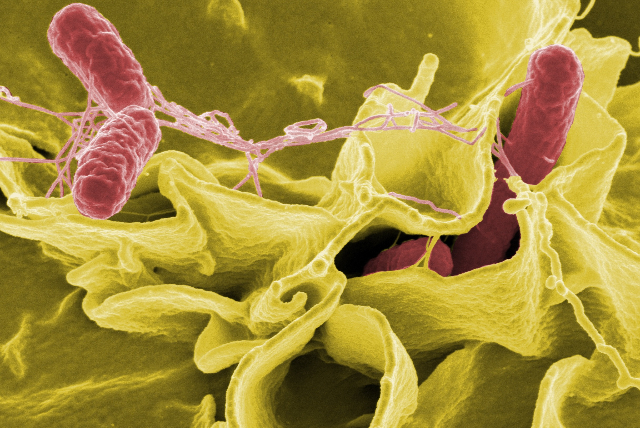
E.coli encompasses a diverse range of strains, each with its unique characteristics and potential for causing illness.
While some strains, like the pathogenic STEC, can lead to severe symptoms and complications, others are harmless.
They play an important role in digestion and nutrient absorption within the gastrointestinal tract.
Understanding the different types of E. coli is essential for identifying and addressing the specific challenges associated with each strain.
Public health agencies and researchers continually monitor the presence of E. coli in various settings. Such as food production, to prevent outbreaks and reduce the risk of infectious diseases.
Fact: Hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS) is a serious complication of STEC infections, particularly in young children and older adults.
Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2021). Escherichia coli (E. coli). Source
Let’s delve deeper into the intriguing facts about E.coli:
E.coli Strains and Pathogenicity
Diverse Group of Bacteria: E.coli comprises numerous strains, each with its distinct genetic makeup and characteristics.
While most strains are harmless and contribute to the normal functioning of our digestive system, pathogenic strains can cause severe illness.
Serious Infection: Pathogenic E.coli infections can manifest in different ways, such as urinary tract infections, respiratory illness, and bloody diarrhea.
In severe cases, these infections can lead to a condition called hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS). Which can cause kidney damage and acute kidney failure.
Transmission and Risk Factors
Contaminated Water and Food Products: One of the most common ways of contracting an E.coli infection is through the consumption of contaminated water or food products.
This can include raw vegetables, raw meat, unpasteurized dairy products, and even fresh produce.
Person-to-Person Contact: E.coli can be easily transmitted from infected people to others through close contact, especially in settings like daycare centers.
Good personal hygiene, such as proper handwashing, is crucial in preventing the spread of the bacteria.
Symptoms and Complications

Gastrointestinal Distress: The symptoms of an E.coli infection typically include abdominal pain, severe diarrhea, and abdominal cramps.
In some cases, the diarrhea may become bloody, indicating a more severe infection.
Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome (HUS): HUS is a severe complication that can occur in a small percentage of E.coli-infected individuals.
Particularly young children, and older adults. It can lead to kidney damage and, in rare cases, even death.
Prevention and Treatment
Food Safety Practices: To reduce the risk of E.coli infections, it is essential to follow proper food safety practices.
This includes thorough cooking of ground beef, avoiding consumption of raw milk or unpasteurized dairy products. Plus practicing good hygiene when handling food.
Hydration and Rest: If infected, it is crucial to stay hydrated by consuming plenty of fluids to prevent dehydration. Resting and allowing the body to recover are equally important.
Seeking Medical Attention: If you experience severe symptoms such as persistent diarrhea, high fever, or signs of dehydration, it is crucial to seek medical attention promptly.
A healthcare professional can provide a specific treatment plan based on the severity of the infection.
Antibiotic Treatment: It’s important to note that antibiotic treatment is not recommended for all E.coli infections.
In fact, certain strains of E.coli can become more virulent in the presence of antibiotics. Therefore, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any antibiotic treatment.
5 Frequently Asked Questions About E.coli
To further enhance your understanding of E.coli and address common concerns, we’ve compiled a list of frequently asked questions:
What are the different types of E.coli?
E.coli strains can vary in their characteristics and pathogenicity. Some well-known types include enterotoxigenic E.coli (ETEC), enteropathogenic E.coli (EPEC), and enterohemorrhagic E.coli (EHEC).
How does E.coli spread?
E.coli can spread through various routes, including contaminated food and water, person-to-person contact, and contact with animal feces.
Who is at a higher risk of developing severe complications from E.coli infections?
Young children, older adults, and individuals with weakened immune systems are at a higher risk of experiencing severe illness and complications from E.coli infections.
What are the symptoms of an E.coli infection?
Symptoms may include abdominal pain, severe diarrhea (sometimes bloody), abdominal cramps, and in severe cases, hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS) with kidney damage.
How can E.coli infections be prevented?
Practicing good food safety, such as proper cooking and handling of food, avoiding unpasteurized dairy products, and maintaining good personal hygiene, can help prevent E.coli infections.
Facts About E.coli Conclusion
E.coli, an intriguing and diverse group of bacteria, has both benign and pathogenic strains.
While certain strains can cause severe illness and complications, many are harmless and even beneficial.
Understanding the transmission routes, symptoms, and preventive measures can help reduce the risk of contracting an E.coli infection.
Remember, maintaining good hygiene, practicing safe food handling and preparation, and being aware of potential sources of contamination are essential.
Especially in safeguarding your health and the well-being of your loved ones.
If you experience severe symptoms or suspect an E.coli infection, it is crucial to seek medical attention promptly.
As we continue to expand our knowledge of this microbial world, ongoing research and advancements in disease control and food safety will play a vital role in minimizing the impact of E.coli outbreaks.
By staying informed and taking necessary precautions, we can navigate this microbial landscape with confidence and ensure a healthier future for all.
Fact: Hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS) can be a severe complication of E.coli infection.
Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). (2021). Escherichia coli (E. coli).




