
21 Facts About Geothermal Energy: A Constant Energy Supply
Facts About Geothermal Energy
Facts About Geothermal Energy: Geothermal energy has been around for centuries, but its potential as a renewable energy source is often overshadowed by solar and wind power.
Interestingly, geothermal energy harnesses the natural heat produced beneath the Earth’s surface to generate electricity, heat buildings, and even cool them.
This makes it one of the most reliable and efficient energy sources available today. However, many people are unaware of the various facts about geothermal energy and how it plays a crucial role in reducing the use of fossil fuels and minimizing the environmental impact of energy consumption.
In recent years, geothermal energy has gained recognition due to its ability to provide a constant energy supply. The Earth’s heat is virtually inexhaustible, unlike other energy sources such as natural gas or coal.
Geothermal systems are increasingly being adopted in many regions, including the United States. Where geothermal power plants and geothermal heat pumps are becoming more prevalent.
As more people recognize the benefits of geothermal energy, it’s essential to understand the facts about geothermal energy that make it such a promising alternative.
What is Geothermal Energy?
Geothermal energy is heat that comes from the Earth’s interior. The heat originates from the Earth’s core and is brought to the surface through various geothermal sources. Like hot springs, volcanic activity, and underground reservoirs.
As this heat escapes from the Earth’s crust, it can be tapped for different uses. Such as geothermal electricity generation and direct-use applications like space heating and district heating systems.
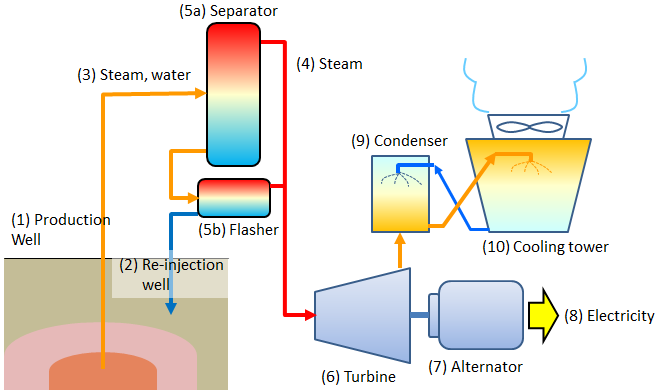
How Geothermal Power Plants Work
Geothermal power plants are designed to convert geothermal energy into electricity. Typically, these plants are located in areas with high geothermal activity. Such as near active volcanoes or hot rocks beneath the Earth’s surface.
One of the main types of geothermal plants is the dry steam plant, which directly uses steam from geothermal reservoirs to turn turbines that generate electricity.
Moreover, flash steam plants and binary cycle power plants are two other common types of geothermal power stations that provide clean energy.
Flash steam plants convert high-pressure geothermal hot water into steam. Binary cycle plants use a heat exchanger to transfer heat from the geothermal water to a secondary fluid. Which then vaporizes and drives a turbine.
Geothermal Heat Pumps: An Efficient Solution for Homes
Geothermal heat pumps are becoming an increasingly popular way to heat and cool buildings. These systems utilize the constant temperature found just below the surface of the Earth.
By installing ground loops, a series of pipes buried underground, geothermal heat pump systems can transfer heat from the Earth’s surface to the building during the winter months, and in the summer, they can cool the building by drawing heat away.
Direct Use of Geothermal Energy
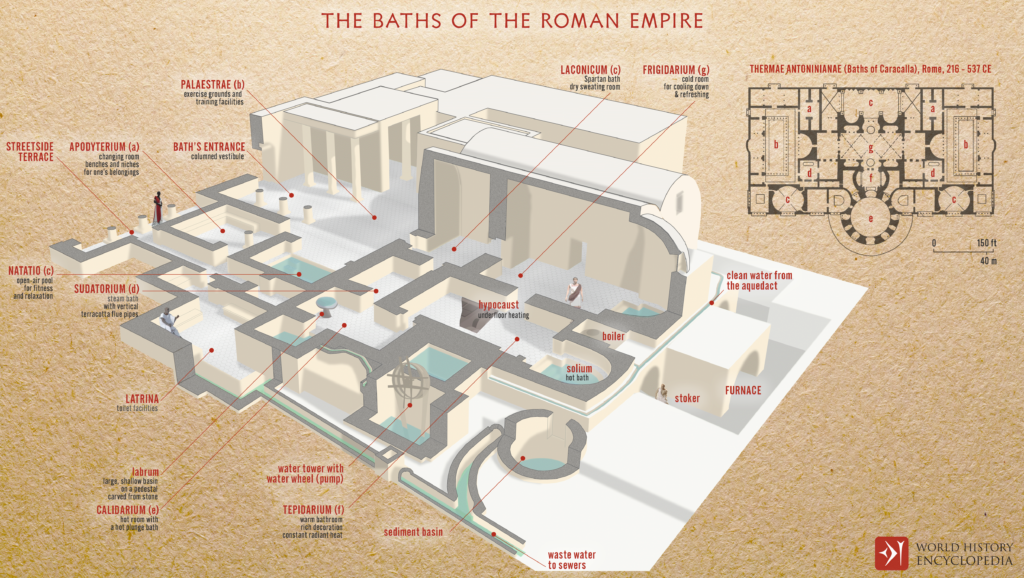
Geothermal energy is not only used for power generation; it has been applied directly in various industrial processes and heating systems for centuries.
Ancient Roman times saw the use of geothermal hot water for baths, and today, it is used for space heating, drying crops, and even melting snow on roads.
By harnessing these natural geothermal resources, communities can benefit from an affordable source of alternative energy that minimizes the carbon footprint.
Geothermal Energy’s Environmental Impact
One of the most appealing facts about geothermal energy is its minimal environmental impact compared to conventional fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas.
Geothermal plants have a significantly smaller carbon footprint, producing far fewer greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide.
In contrast to fossil fuels, geothermal energy is a renewable energy source that can be continuously replenished by the Earth’s natural heat.
This means that geothermal energy production is sustainable. And can help mitigate climate change by reducing the reliance on polluting energy sources.
Although geothermal energy is considered green energy, it is not entirely without environmental concerns.
The release of trace amounts of gases like hydrogen sulfide, which smells like rotten eggs, is a main concern in some geothermal sites.
However, advancements in geothermal technology have made it possible to capture and manage these emissions effectively.
Furthermore, geothermal systems can help reduce the environmental impact of energy production by lowering the overall consumption of natural resources.
Facts About Geothermal Energy
Types of Geothermal Power Plants
There are three main types of geothermal power plants used to generate electricity. They are dry steam plants, flash steam plants, and binary cycle power plants.
Each of these technologies operates slightly differently. But all are efficient ways to tap into the Earth’s natural heat and convert it into usable energy.
- Dry Steam Plants: As mentioned earlier, dry steam plants directly use steam from geothermal reservoirs to turn turbines. This is the simplest form of geothermal power generation and has been used for over a century. One of the most famous dry steam plants is located in Yellowstone National Park, where underground steam powers turbines to generate electricity.
2. Flash Steam Plants: These plants are the most common type of geothermal power stations. They work by pulling up hot water from the geothermal reservoirs, which is under high pressure.
When the pressure is reduced, the hot water flashes into steam, which is then used to power turbines.
3. Binary Cycle Power Plants: In binary cycle power plants, geothermal hot water is used to heat a secondary fluid. With a lower boiling point than water.
This secondary fluid vaporizes and drives the turbines. Binary cycle plants are capable of operating in areas where geothermal resources have lower temperatures, expanding the geographic range where geothermal energy can be harnessed.
Geothermal Energy Applications
In addition to electricity generation, there are various direct-use applications of geothermal energy that can benefit households, businesses, and communities.
One interesting fact is that geothermal water has been used since ancient Roman times for heating baths and buildings.
Today, it’s applied in more advanced ways, including space heating, greenhouse heating, and even industrial processes like drying food and heating fish farms.
In many areas, geothermal energy is also used for district heating systems, which distribute heat from geothermal resources to multiple buildings.
This method is highly efficient and helps reduce the need for fossil fuel-based heating methods.
In colder climates, geothermal energy is used to cool buildings during the summer by taking advantage of the constant temperature found in shallow ground just below the Earth’s surface.
The Global Reach of Geothermal Energy
Globally, geothermal energy is gaining traction as an affordable source of alternative energy.
Countries such as New Zealand, Iceland, and parts of the Western United States have abundant geothermal resources, which have been harnessed for decades.
In the United States, California is the leading producer of geothermal electricity, with areas like San Francisco and other regions tapping into underground reservoirs.
Countries like New Zealand utilize geothermal energy extensively due to their volcanic activity.
In fact, regions with active volcanoes often have rich geothermal resources that make them ideal locations for geothermal energy production.

Benefits of Geothermal Energy
When discussing the facts about geothermal energy, it is crucial to highlight the numerous benefits that come with its use.
One of the most significant advantages is that geothermal energy is a renewable resource, meaning it is derived from the Earth’s heat, which is continuously replenished. Unlike fossil fuels.
Which are finite and contribute to pollution, geothermal energy offers a cleaner, more sustainable alternative.
Furthermore, geothermal power generation is highly reliable. Unlike solar and wind power, which are dependent on weather conditions, geothermal plants can operate 24/7.
This consistency makes geothermal energy an excellent choice for base-load power generation, ensuring a steady supply of electricity to the electrical grid.
Another side benefit of geothermal energy is its relatively low land footprint. Geothermal wells and power plants occupy much less space than solar farms or wind turbines.
This makes them an attractive option for regions where land availability is limited. Additionally, since most geothermal infrastructure is located underground, the visual and environmental impact on the landscape is minimal.
Geothermal Systems for Heating and Cooling
Another essential aspect of geothermal energy use is its application in heating and cooling systems.
Geothermal heat pumps and geothermal heating systems are increasingly being adopted in residential, commercial, and industrial buildings as a means of providing energy-efficient climate control.
These systems work by taking advantage of the constant temperature found beneath the Earth’s surface, which remains stable year-round.
Geothermal Heat Pump System: These systems use a network of underground pipes known as a ground loop to circulate fluid and transfer heat between the ground and a building.
In the winter, heat is drawn from the ground to warm the building. In the summer, the system removes heat from the building and releases it into the Earth, providing cooling.
Space Heating: Geothermal energy is particularly effective for space heating. Buildings equipped with geothermal heating systems can enjoy consistent warmth during colder months.
This is especially beneficial in regions with colder climates, where heating costs are typically higher.
Cooling Systems: In addition to heating, geothermal systems can also cool buildings.
The process of drawing heat away from the building and dispersing it underground is much more efficient than conventional air conditioning systems, reducing both energy consumption and costs.
Facts About Geothermal Energy
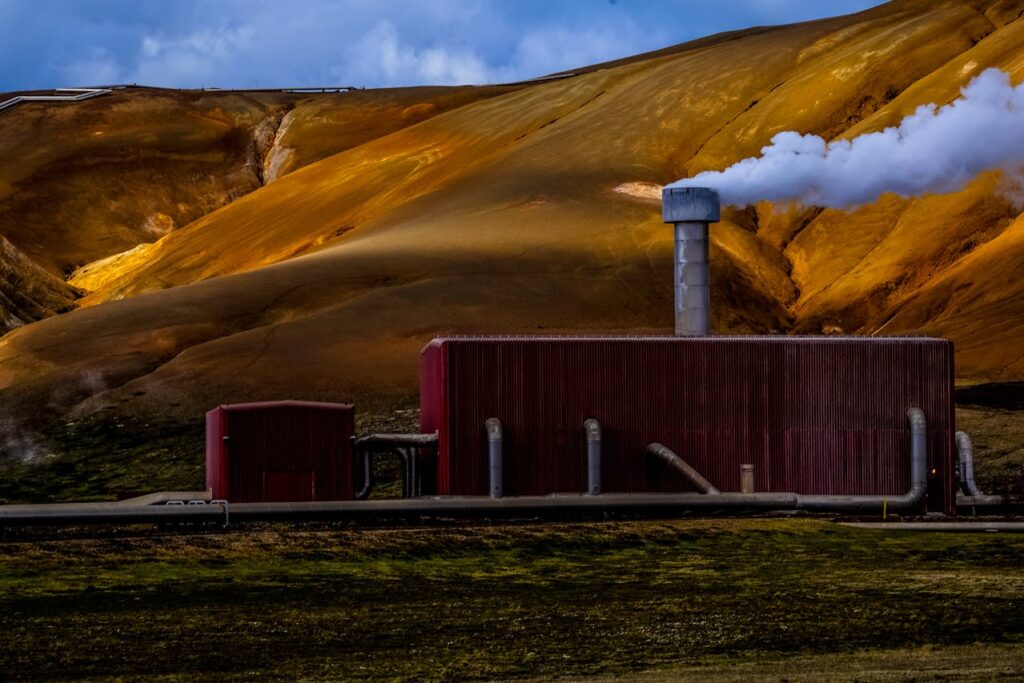

The Potential of Geothermal Energy
One of the most interesting facts about geothermal energy is its untapped potential.
While geothermal energy is currently used in specific regions, there is still a vast amount of geothermal resources around the world that have not yet been fully exploited.
For instance, the U.S. Department of Energy estimates that geothermal energy could supply up to 10% of the nation’s electricity needs if fully developed.
Globally, countries such as Iceland, the Philippines, and Indonesia have already embraced geothermal energy as a significant part of their energy mix.
In these countries, geothermal power plays a critical role in meeting energy demand while reducing dependence on imported fossil fuels.
The potential of geothermal energy to provide a stable and sustainable energy source continues to attract attention from policymakers and investors looking for long-term solutions to energy challenges.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its many advantages, geothermal energy is not without challenges. One of the main concerns is that geothermal sites must be located near geothermal reservoirs.
This restricts the geographic regions where geothermal energy can be harnessed efficiently. While advancements in geothermal technology have allowed power plants to operate in areas with lower geothermal activity, the availability of high-temperature geothermal sources remains a limiting factor.
Additionally, the initial costs of developing geothermal power plants can be high. Drilling deep into the Earth’s crust to access geothermal energy requires significant investment in infrastructure and technology.
However, these upfront costs are often offset by the long-term savings and reduced operating costs, making geothermal energy a cost-effective option in the long run.
Related Article: Interesting Facts about Thermal Energy
Facts About Geothermal Energy: Frequently Asked Questions

What are the main types of geothermal energy systems?
There are three main types of geothermal energy systems: dry steam plants, flash steam plants, and binary cycle power plants. These systems use geothermal reservoirs to convert heat into electricity.
How does geothermal energy impact the environment?
Geothermal energy has a low environmental impact. It produces significantly fewer greenhouse gases, like carbon dioxide, compared to fossil fuels. Additionally, geothermal plants have a smaller land footprint, preserving natural landscapes.
Is geothermal energy renewable?
Yes, geothermal energy is a renewable resource. The Earth continuously produces heat from its core, making geothermal energy an inexhaustible source of power.
Where is geothermal energy used most?
Geothermal energy is used extensively in countries like Iceland, New Zealand, Indonesia, and the Western United States. In the United States, California is a leader in geothermal electricity generation, with areas around San Francisco being key producers.
What is the lifespan of geothermal power plants?
Geothermal power plants can operate for decades, with some plants running for over 50 years. The heat source remains constant, making it a long-lasting form of energy production.
Can geothermal energy be used for cooling?
Yes, geothermal energy can be used for cooling. Geothermal heat pumps use the stable temperatures underground to cool buildings in the summer by removing heat from the structure and transferring it back to the Earth.
What are the applications of geothermal energy?
Geothermal energy has a wide range of applications, from generating electricity to providing space heating, district heating systems, and even direct-use applications like greenhouse heating and fish farming.
Geothermal Energy and the Future of Clean Energy
As the world transitions towards more sustainable energy sources, geothermal energy is poised to play a vital role in reducing carbon emissions and reliance on fossil fuels.
The environmental impact of geothermal energy is minimal compared to traditional power generation methods, making it an attractive option for countries seeking to reduce their carbon footprint.
Moreover, as the demand for clean energy increases, geothermal technology continues to advance.
Researchers are exploring new ways to tap into lower-temperature geothermal sources, which could expand the geographical areas where geothermal energy can be used.
These innovations could make geothermal energy even more accessible and cost-effective in the future.

Facts About Geothermal Energy Conclusion
In conclusion, geothermal energy offers a reliable, sustainable, and eco-friendly alternative to traditional energy sources.
By harnessing the heat of the Earth, geothermal systems provide consistent power generation and heating solutions with minimal environmental impact.
From the direct use of geothermal water to large-scale electricity generation in geothermal power plants, the potential of geothermal energy is vast. With its renewable nature, low emissions, and long-term cost savings, geothermal energy is becoming an integral part of the global shift towards greener energy solutions.
By understanding these facts about geothermal energy, individuals and governments alike can make informed decisions about the future of energy.
As more countries recognize the value of geothermal resources, this affordable source of alternative energy will continue to grow, playing a critical role in the fight against climate change and ensuring a cleaner, more sustainable future for all.


