
54 Great Facts About Plantae: Change the Way You See Plants
Facts About Plantae
Without plants, life on Earth would not exist as it does today. Moreover, the kingdom plantae forms the foundation of nearly every food chain and sustains countless living things by producing oxygen through photosynthesis. Since plants are often overlooked in daily life, many people remain unaware of the extraordinary characteristics that define them. Therefore, exploring facts about plantae provides not only knowledge but also a deeper appreciation for these essential organisms.
Interestingly, members of the plant kingdom are far more diverse than most realize. From aquatic plants like green algae to massive terrestrial plants such as the giant sequoia, their diversity is staggering. In addition, plants exhibit unique evolutionary relationships with other organisms and have adapted to thrive in different habitats. Thus, learning about these facts about plantae can give insights into their life cycle, reproduction method, cultural significance, and even their distress calls.
The Kingdom Plantae: An Overview
The kingdom plantae consists of eukaryotic cells with rigid cell walls made of cellulose. Since these structures provide support, plants can stand upright and capture light energy efficiently. Additionally, plants produce their own food through photosynthesis by converting light energy into chemical energy.
The Role of Plants in the Food Chain
- Plants act as primary producers.
- They provide food sources for herbivores and indirectly for carnivores.
- Oxygen is released as a by-product of photosynthesis, benefiting all aerobic organisms.
Because members of the plant kingdom are so vital, the well-being of plants directly influences the survival of animals, humans, and many other different organisms.
Evolutionary Facts About Plantae
The fossil record reveals that early land plants appeared during the Devonian period. Furthermore, green algae are considered common ancestors of today’s terrestrial plants. As a result, the transition from an aquatic environment to a terrestrial environment marked one of the most successful evolutionary shifts in history.
The Development of Vascular Tissue
- Vascular tissue allowed water and nutrients to move throughout the plant body.
- This adaptation led to the rise of vascular plants, including ferns, club mosses, and seed plants.
- Vascular systems enabled plants to grow taller and spread into new environments.
Because of these evolutionary advancements, plants became dominant in terrestrial ecosystems, outcompeting lower plants that lacked vascular systems.
Interesting Facts About Plantae
Although most people recognize plants as green, there is much more to their biology. Moreover, fun facts about plantae reveal how diverse and surprising they can be.
- The fastest-growing woody plant is bamboo, which can grow over 30 inches in a single day.
- Carnivorous plants like venus flytraps supplement their nutrient intake by capturing small organisms.
- A giant sequoia can live for thousands of years, ranking among the longest-living organisms on Earth.
- Native plants in certain regions have adapted unique reproductive methods for survival.
Because plant reproduction can occur through seeds, spores, or even asexual reproduction, the plant kingdom demonstrates one of the broadest ranges of reproduction methods among living things.

Life Cycle and Reproduction in Plantae
One of the most fascinating facts about plantae lies in their unique life cycle known as alternation of generations. In this cycle, plants alternate between a haploid multicellular form (gametophyte) and a diploid stage (sporophyte).
Key Stages of Plant Reproduction
- Gametophyte produces haploid sex cells.
- Fertilization leads to the formation of diploid cells.
- Sporophyte of seedless plants produces spores for new plants.
Moreover, pollen grains in seed plants allow reproduction without the need for water. As a result, plants could colonize diverse terrestrial environments.
Structure and Parts of a Plant
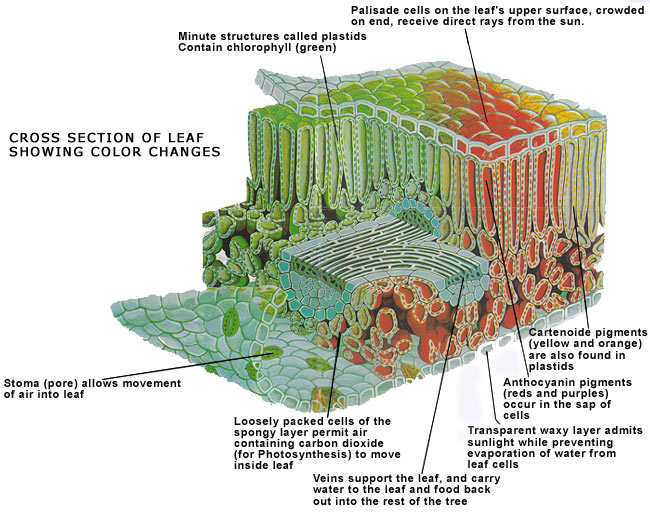
When observing different types of plant species, it becomes clear that each has a specialized plant body. Moreover, the parts of a plant—roots, stems, leaves, flowers, and seeds—each serve a unique role in survival. Since these structures work together, plants can thrive in both aquatic habitats and terrestrial ecosystems.
Roots: The Source of Water and Nutrients
Roots anchor terrestrial plants firmly in the soil. In addition, they absorb small molecules and minerals that fuel growth. Because roots also store food, they provide a backup energy supply during difficult conditions.
Stems: Transport and Support
Stems contain vascular tissue, forming an efficient vascular system that carries water and nutrients upward. Furthermore, the apical meristem tissue at the tips ensures continuous growth. Therefore, the stem acts as both a transport system and a support framework for leaves and reproductive organs.
Leaves: The Powerhouses of Photosynthesis
Leaves contain chlorophyll, which gives them their green color. Moreover, they are designed with small pockets of air that allow the exchange of carbon dioxide and water vapor. Because leaves capture light energy and convert it into chemical energy, they remain the primary producers of energy for the plant and the entire food chain.
Classification: Main Groups of Plantae
The plantae kingdom is divided into several main groups, each with distinct traits. Interestingly, these groups reflect evolutionary relationships that extend back to common ancestors.

Non-Flowering Plants
- Mosses, liverworts, and hornworts represent seedless nonvascular plants.
- These early land plants lack vascular systems, making them dependent on water for reproduction.
- Fun facts about plantae show that these lower plants still thrive in moist environments.
Spore-Producing Plants
Ferns and club mosses belong to this group. Since they reproduce through spores instead of seeds, their reproductive method reflects ancient adaptations from the fossil record.
Seed Plants: Angiosperms and Gymnosperms
- Seeds of angiosperms are enclosed, often inside fruit. Interestingly, the average strawberry contains about 200 tiny seeds on its surface.
- Gymnosperms, such as conifers, bear naked seeds. Because they evolved pollen of seed plants, they were able to dominate many terrestrial environments.
Adaptations of Terrestrial Plants
Plants evolved remarkable adaptations that made them successful land plants. Moreover, these changes allowed them to expand beyond aquatic environments into drier terrestrial ecosystems.
Protective Adaptations
- Rigid cell walls provided structural strength.
- Waxy cuticles reduced water loss.
- Reproductive organs developed that did not depend solely on water.
Because of these traits, plants could withstand the challenges of a terrestrial environment and spread into diverse habitats.
Reproductive Strategies
- Alternation of generations ensured genetic diversity.
- Asexual reproduction in some plants allowed quick propagation of new plants.
- Flowers and pollen grains increased reproductive success in angiosperms.
Unique Reproductive Organs and Features
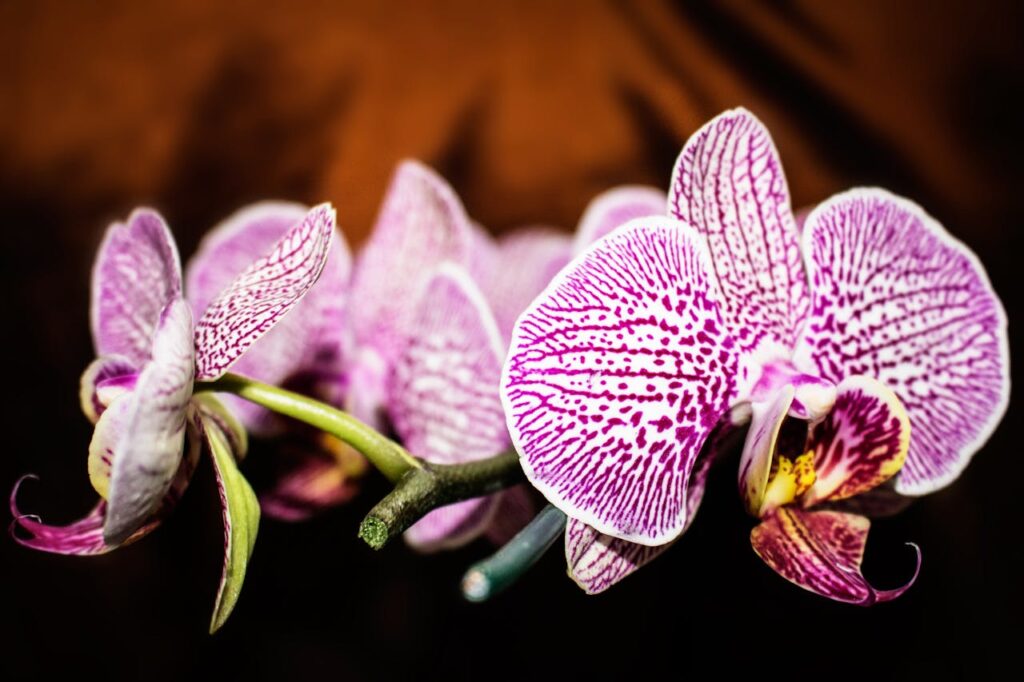

Plants showcase diverse reproductive organs that distinguish them from other groups of organisms. Moreover, these organs ensure continuity across generations.
- The reproductive organ of flowering plants is the flower itself.
- Pollen grains carry haploid cells that fertilize ovules.
- The pod of an orchid contains thousands of dust-like seeds.
- The only fruit with seeds on the outside is the strawberry, a fascinating fact about plantae.
Because of their diversity, the reproductive structures of plants remain one of the most scientifically studied aspects in the scientific study of plants.
I’d really appreciate it if you could read this article Fascinating Facts About Strawberries – The Best 40 when you have a moment. It’s related to what we’ve been discussing.
Photosynthesis: Powering Life on Earth
Without photosynthesis, neither plants nor animals could survive. Moreover, facts about plantae often highlight how plants harness light energy to produce food. Since plants convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose, they sustain themselves while releasing oxygen as a by-product of photosynthesis.
Chemical Energy and Plant Cells
Plant cells contain chloroplasts, where photosynthesis occurs. Furthermore, the rigid cell wall surrounding these eukaryotic cells provides protection and structure. Because of this cellular design, members of the plant kingdom can efficiently capture and store chemical energy.
Importance in the Food Chain
- Plants serve as the base of nearly every terrestrial and aquatic food chain.
- Herbivores rely directly on plant species for energy.
- Carnivores depend indirectly on plants since their prey consumes vegetation.
Therefore, when the well-being of plants is threatened, entire ecosystems face collapse.
Fun and Interesting Facts About Plantae
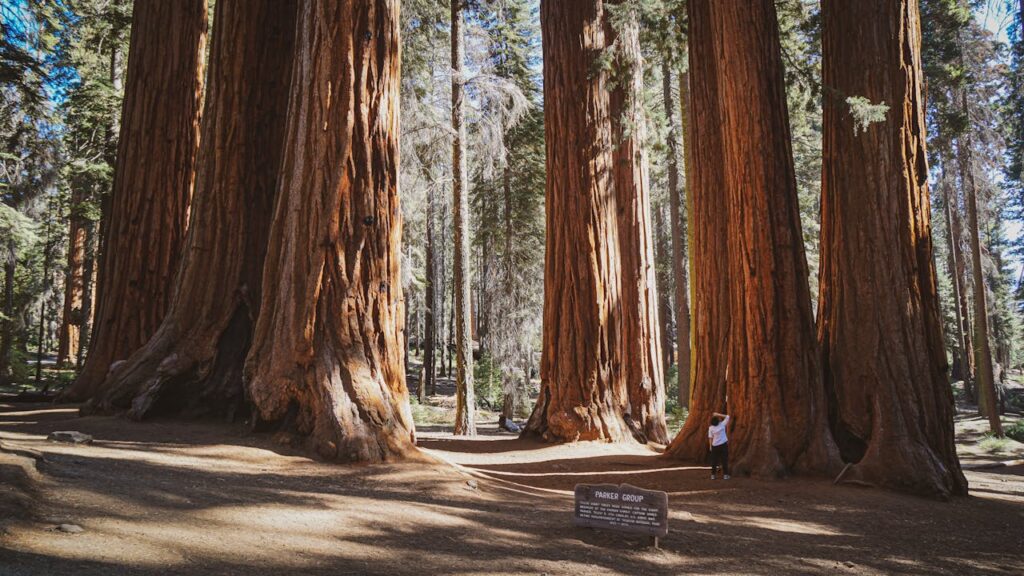

Readers are often surprised by the remarkable adaptations and quirky traits of plants. Moreover, fun facts about plantae show how extraordinary these organisms truly are.
- Venus flytraps can close their leaves in less than one second when triggered.
- Bamboo is recognized as the fastest-growing woody plant, sometimes exceeding three feet of growth in a day.
- Some plants send out a plant distress call using chemical signals when attacked by herbivores.
- The giant sequoia, among the longest-living organisms, can survive for over 3,000 years.
Because such features make plants unique, they spark curiosity and fuel further scientific study of plants.
Evolutionary Relationships and the Fossil Record
The evolutionary history of the plantae kingdom is recorded in fossils. Furthermore, the fossil record confirms that first plants originated from aquatic habitats before moving to land.
From Aquatic Plants to Terrestrial Plants
- Green algae are believed to be the common ancestors of modern green plants.
- Red algae and other aquatic plants highlight the diversity within aquatic environments.
- Early land plants developed adaptations to survive in a terrestrial environment, such as vascular tissue and reproductive strategies not dependent on water.
As a result, the evolution of terrestrial plants represents one of the most significant milestones in Earth’s history.
If you have some free time, it might be helpful to check out this article 18 Fascinating Facts About Algae: Nature’s Unsung Heroes. It covers some relevant points.
Cultural Significance of Plantae
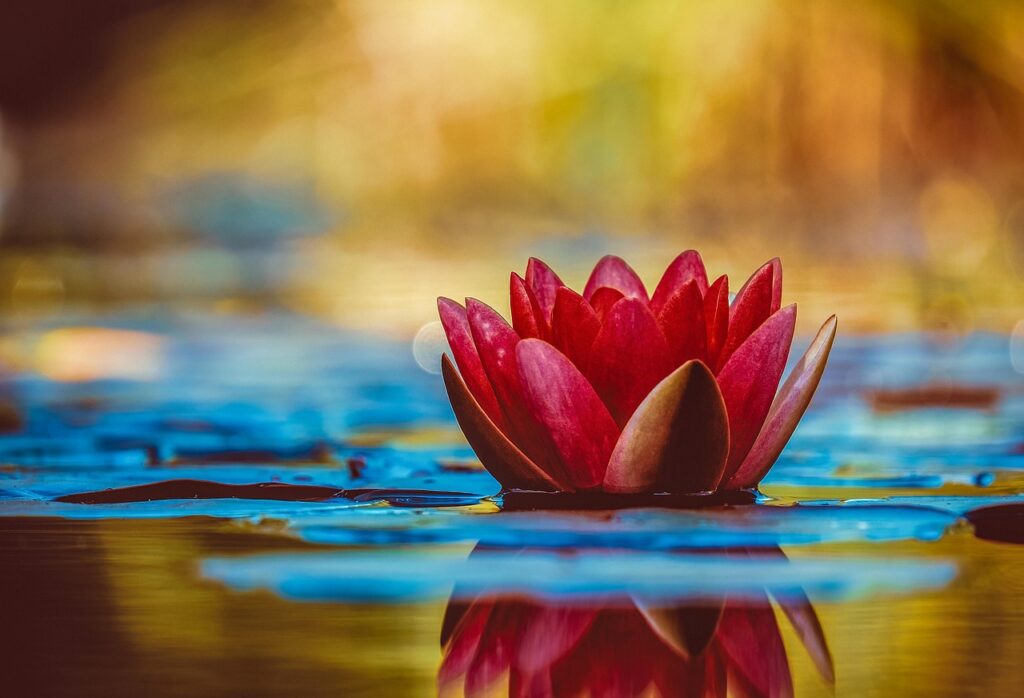

Plants are not only biological marvels but also cultural symbols. Moreover, the cultural significance of plants extends across religions, traditions, and daily life.
- Sacred groves and native plants hold spiritual meaning in many societies.
- Flowers are used in rituals, celebrations, and healing practices.
- Certain species of plants like the lotus or olive tree carry symbolic associations with peace, purity, and resilience.
Because plants provide food sources, medicine, and cultural meaning, they remain essential not only for survival but also for human identity.
Quick Facts About Plantae
What are some quick facts about plantae?
- Plantae kingdom members are primary producers.
- Plants contain chlorophyll, giving them their green color.
- Plant reproduction alternates between haploid and diploid stages.
- Seeds of angiosperms are enclosed within fruits, unlike naked seeds of gymnosperms.
- The scientific name of plants varies across thousands of plant species worldwide.
Reproduction Methods Across Plant Species
Reproduction in the plantae kingdom demonstrates remarkable diversity. Moreover, facts about plantae reveal that plants can reproduce sexually or asexually, depending on their adaptation and habitat. Since survival depends on reproduction, plants evolved multiple strategies to ensure the spread of new plants.
Sexual Reproduction
- Gametophyte produces haploid sex cells, which fuse to form diploid cells.
- Flowers act as the reproductive organ in angiosperms, producing seeds of angiosperms enclosed in fruit.
- Pollen of seed plants allows fertilization without the need for water, enabling reproduction in terrestrial environments.
Asexual Reproduction
- Many plants can grow from cuttings, tubers, or rhizomes.
- The first potatoes, for instance, propagated through underground stems.
- Asexual reproduction ensures rapid colonization of favorable habitats.
Because of these strategies, the vast majority of plants maintain continuity across generations, ensuring both genetic diversity and population growth.
Special Types of Plants
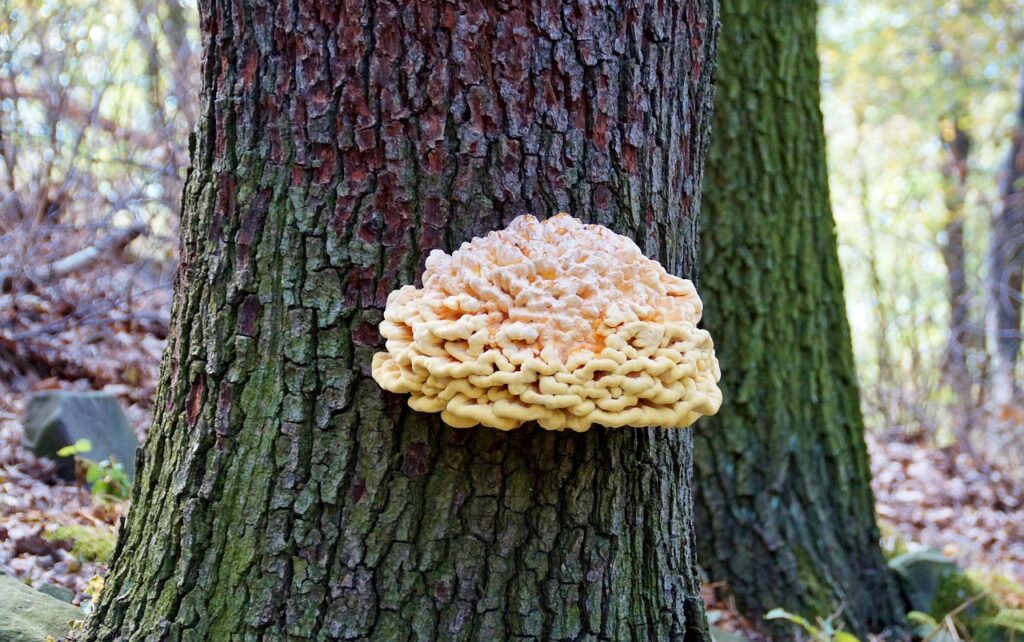

Within the diverse group of organisms in the plantae kingdom, several plant species stand out for their unusual traits. Moreover, fun facts about plantae often highlight these unique members.
Parasitic Plants
- Some plants, unlike typical green plants, cannot make their own food.
- Parasitic plants rely on host organisms to extract nutrients.
- Despite lacking chlorophyll, they play roles in the balance of ecosystems.
Carnivorous Plants
- Venus flytraps and pitcher plants capture insects to supplement nutrient intake.
- These plants often thrive in nutrient-poor soils where survival would otherwise be impossible.
- Their unusual plant body structures, such as traps and sticky leaves, highlight the diversity of plant reproduction and survival methods.
Non-Flowering Plants
- Seedless nonvascular plants, such as mosses, reproduce through spores rather than seeds.
- Spore-producing plants like ferns highlight early evolutionary stages visible in the fossil record.
Because these different forms exist, the scientific study of plants continues to expand, revealing how adaptable and resilient plants can be.

Circadian Rhythm and Plant Behavior
Plants, like animals, follow natural cycles. Moreover, one of the most intriguing facts about plantae is that they exhibit a circadian rhythm. Since plants respond to light and dark cycles, their behaviors align with environmental conditions.
- Flowers may open and close based on the time of day.
- Leaves often shift positions to maximize light energy capture.
- Plant distress calls can be influenced by daily cycles.
Therefore, understanding circadian rhythms offers insights into the well-being of plants and their interactions with different organisms.
Longest-Living and Fastest-Growing Plants
Some of the most fascinating facts about plantae involve their longevity and growth rates. Moreover, plant species demonstrate extremes unmatched in the animal kingdom.
- The giant sequoia ranks among the longest-living organisms, surviving for thousands of years.
- Bamboo, the fastest-growing woody plant, demonstrates exceptional adaptability in many terrestrial ecosystems.
- Certain aquatic plants can double their population in just a few days under ideal conditions.
Because of these extraordinary traits, plants highlight the diversity of strategies life uses to survive on Earth.
Evolutionary Adaptations in Plant Reproduction
Evolutionary relationships shaped the reproduction method of plants over millions of years. Moreover, the alternation of generations remains a defining feature of plant reproduction.
- Haploid multicellular forms ensure genetic recombination.
- Sporophyte of seedless plants continues the cycle by producing spores.
- Seeds of angiosperms and naked seeds of gymnosperms show two successful evolutionary pathways.
As a result, the reproductive adaptations of plants not only ensured their survival but also enabled them to dominate terrestrial environments.
The Role of Plants in Ecosystems
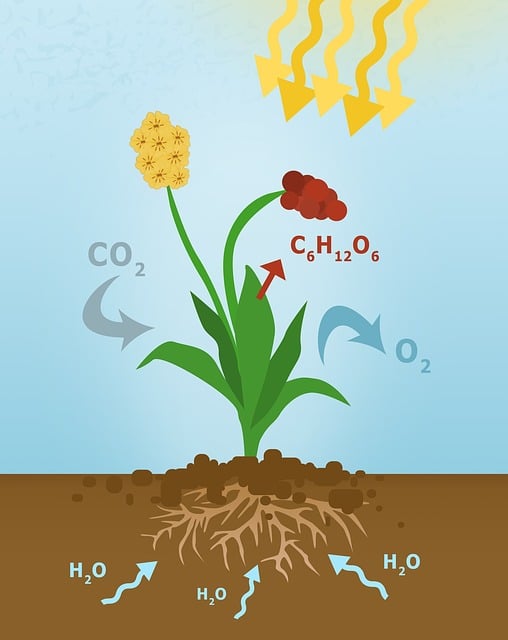
Plants sustain life in both aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems. Moreover, facts about plantae emphasize how plants maintain balance within the natural world. Since they act as primary producers, plants form the foundation for every food chain and energy flow.
Ecosystem Contributions
- Provide oxygen for animals and humans through photosynthesis.
- Serve as food sources for herbivores and omnivores.
- Support soil health by preventing erosion with their root systems.
- Regulate water cycles by releasing water vapor into the atmosphere.
Therefore, the presence and health of plant species determine the stability of entire ecosystems.
Plant Communication and Survival
Modern research reveals fascinating facts about plantae related to communication. Interestingly, plants can release small molecules into the air or soil to signal distress. Moreover, this “plant distress call” warns neighboring plants of threats, such as insect attacks.
- Some species of plants release chemicals to attract predators of herbivores.
- Roots can interact underground, sharing nutrients with neighboring plants.
- The scientific study of plants has uncovered how communication strengthens survival.
Because of these hidden interactions, plants are far more dynamic and interconnected than previously believed.
Plants and Human Life
Plants support humanity in countless ways beyond oxygen and food. Moreover, facts about plantae include cultural, medicinal, and environmental benefits.

Food Sources and Medicine
- Plants supply the majority of human food sources, including grains, fruits, and vegetables.
- Many medicines are derived from plant compounds, such as aspirin from willow bark.
- Cultural traditions worldwide use native plants for healing and rituals.
Economic and Cultural Significance
- Agriculture forms the backbone of global economies.
- Decorative plants enhance human well-being and quality of life.
- Cultural significance is tied to symbols like olive branches, lotus flowers, and bamboo.
Because plants enrich both physical and cultural existence, their importance cannot be overstated.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the kingdom plantae?
The kingdom plantae is a group of organisms that produce their own food through photosynthesis and are essential primary producers in ecosystems.
How do plant cells differ from animal cells?
Plant cells have rigid cell walls and chloroplasts, allowing them to perform photosynthesis, unlike animal cells.
What is alternation of generations in plants?
It is a life cycle where plants alternate between a haploid gametophyte stage and a diploid sporophyte stage.
Which plants are considered lower plants?
Lower plants include mosses and liverworts, which lack vascular tissue and depend on water for reproduction.
What is the fastest-growing woody plant?
Bamboo holds the record, capable of growing more than three feet per day.
Do plants communicate?
Yes, some plants release chemical signals, often described as a plant distress call, to warn others of threats.
Could you give these articles a read when you can? It offers some additional insights on the topic.
Fascinating Facts About Bananas (The Best 42)
The Best 63 Interesting Facts About Apples: Nature’s Delight
Conclusion
Ultimately, the facts about plantae reveal a kingdom of extraordinary complexity, adaptability, and importance. Moreover, plants sustain life on Earth by producing oxygen, storing chemical energy, and serving as food sources for countless living things. Since they evolved from aquatic habitats to dominate terrestrial environments, their story is also the story of survival and growth on our planet.
From the fossil record of early land plants to the cultural significance of flowers in human life, the study of plants offers endless insights. Therefore, by appreciating the fascinating details of the plantae kingdom, we also recognize the intricate connections that keep Earth’s ecosystems thriving.





One Comment
Pingback: