54 Fascinating Facts About the Mayans That Will Amaze You
Facts About the Mayans
Firstly, In this article, a journey will be taken into facts about the Mayans, uncovering the depth of their culture, beliefs, and societal structures. From their impressive pyramid temples to their accurate calendars, the story of the Mayans is one of resilience, creativity, and mystery.
Throughout history, few ancient civilizations have captured the imagination as much as the Maya civilization. Known for its advanced achievements in architecture, astronomy, and writing, the Mayan people left behind a rich legacy that continues to intrigue researchers and history enthusiasts.
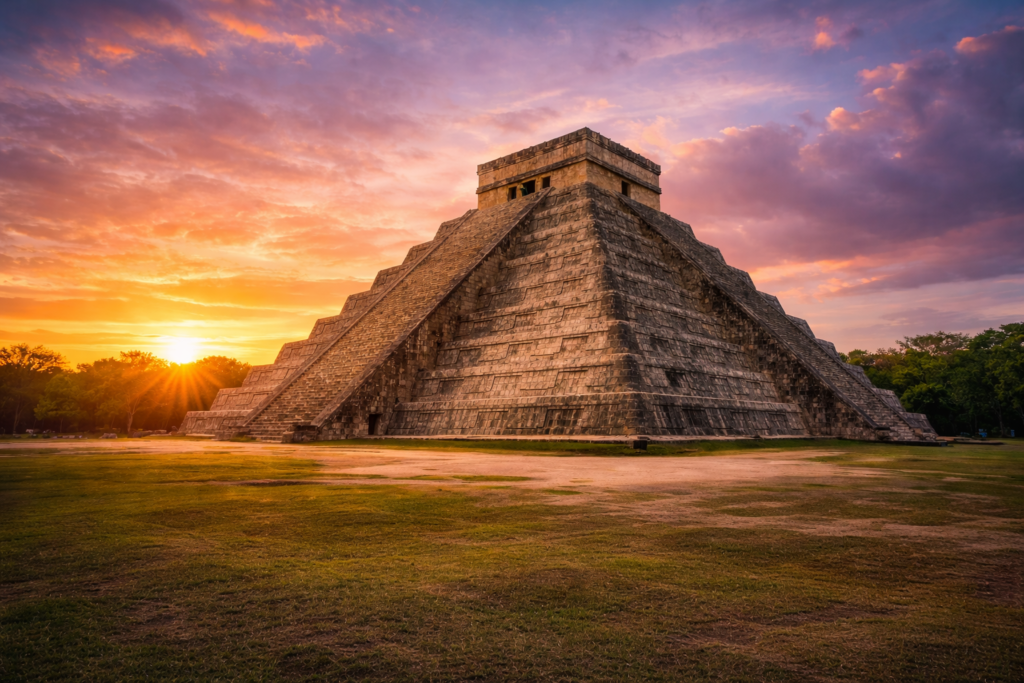
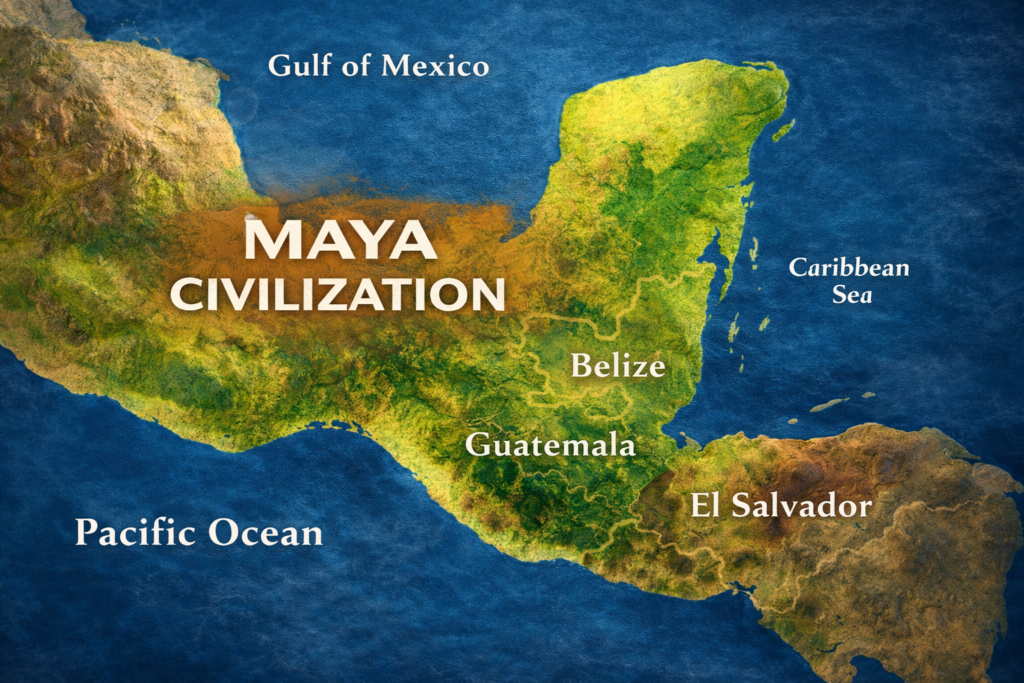
Indeed, the ancient Mayans thrived in Central America, particularly across the Yucatán Peninsula, southern Mexico, northern Belize, El Salvador, and the Guatemalan highlands. With their great cities like Chichén Itzá and Piedras Negras, this advanced civilization demonstrated brilliance in many fields while practicing unique traditions such as religious ceremonies and the Maya ball game.
Quick Facts About the Mayans
- The Maya civilization thrived in Central America, including southern Mexico, Guatemala, El Salvador, and Belize.
- The ancient Mayans developed a unique writing system (maya script) with thousands of glyphs.
- Their long count calendar and solar calendar were highly accurate, even predicting astronomical events.
- Chichén Itzá and other mayan cities feature iconic pyramid temples and ball courts.
- Rituals included religious ceremonies and human sacrifice, often linked to astronomical systems.
- The Popol Vuh recorded their myths and beliefs, while codices like the Dresden Codex preserved knowledge.
- Millions of descendants of the mayan people still live in the Yucatán Peninsula and Guatemalan highlands today.

Origins of the Maya Civilization
The beginnings of the ancient Mayan civilization can be traced to the early Maya settlements around 2000 BCE. While evidence suggests influence from other ancient cities in Mesoamerica, the Mayans developed distinctive cultural practices that set them apart.
- The first Maya cities emerged in southeastern Mexico and the ancestral homelands of the Maya people.
- Over time, large mayan cities grew, sustained by sophisticated trade routes and fertile lands enriched with volcanic ash.
- Eventually, the mayan society evolved into a highly stratified system with rulers, nobles, artisans, farmers, and a distinct middle class.
I’d really appreciate it if you could read this article when you have a moment. It’s related to what we’ve been discussing. Interesting Facts About Mexican Culture (Read The Best 88)
Interesting Facts About the Mayans’ Achievements
Advanced Writing System
Indeed one of the most intriguing facts about the Mayans lies in their writing system, considered the most sophisticated in the ancient world.
- The mayan writing, also called the maya script, combined hieroglyphic writing and maya glyphs.
- Scholars like Tatiana Proskouriakoff helped decode this system in recent years, revealing the histories of maya rulers, important events, and daily life.
- Surviving rare books such as the Dresden Codex provide insight into their astronomical systems, sacred calendar, and religious beliefs.
Accurate Calendars and Astronomy
Equally remarkable are the Mayans’ accurate calendars and understanding of astronomical events.
- Their long count calendar, solar calendar, and sacred calendar were used to track celestial bodies, lunar eclipses, and solar eclipses.
- This profound knowledge shaped religious ceremonies and predicted important events with extraordinary precision.
- Scholars often cite their calculations of the solar year as more accurate than those of Europe at the time.
Maya Architecture and Great Cities
Another set of fascinating facts revolves around Maya pyramid temples and ball courts.
- The towering maya pyramid structures in Chichén Itzá remain among the most iconic archaeological sites in the ancient world.
- Many mayan cities, including different cities across the Yucatán Peninsula and northern Belize, displayed unique urban layouts reflecting maya culture and social status.
- Stone carvings and inscriptions inside pyramid temples reveal details of maya society, including religious ceremonies, social class distinctions, and the ultimate goal of reaching the afterlife.
Religion, Rituals, and Human Sacrifice
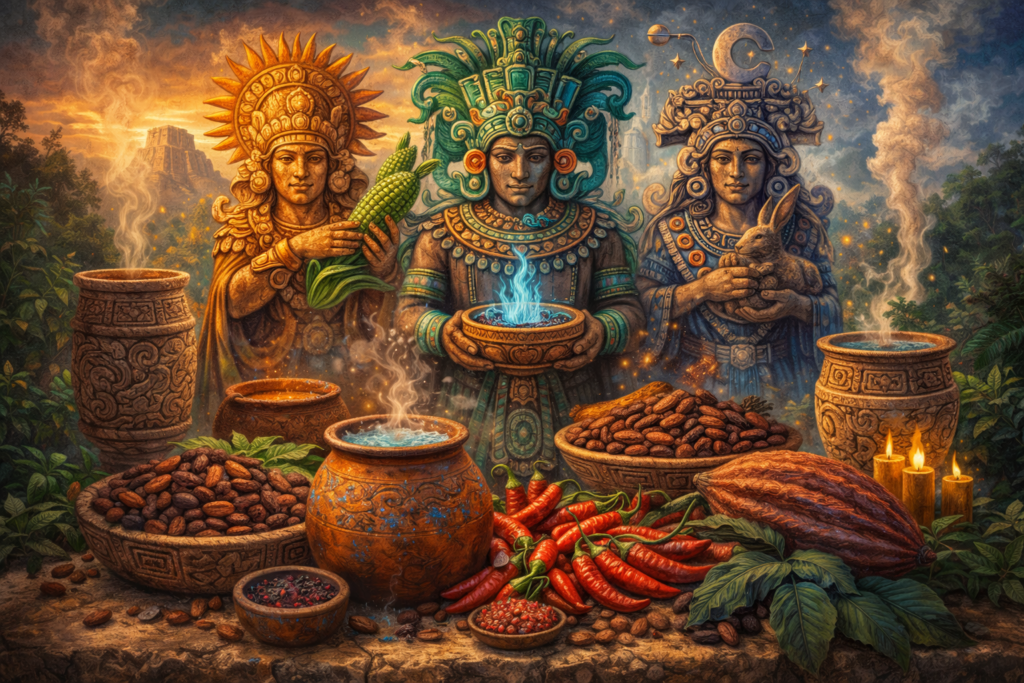

Beliefs in Various Gods
A central element in mayan culture was religion, with worship dedicated to various gods representing nature, fertility, and celestial bodies.
- The mayan people believed their ultimate goal was to maintain cosmic balance.
- Offerings included food, chili peppers, cacao beans, and even spicy drinks flavored with maya blue pigment.
Human Sacrifice and Religious Ceremonies
However, one of the darker facts about the Mayans involves human sacrifice during religious ceremonies.
- Such rituals were conducted to appease gods and ensure agricultural fertility.
- Victims, often prisoners of war or slaves, were offered during astronomical events like solar eclipses.
- While shocking by today’s standards, these practices reflected deeply held spiritual convictions of the mayan civilisation.
Maya Society and Daily Life
Social Structure and Middle Class
When exploring facts about the Mayans, attention must be given to the complexity of maya society. Unlike many other ancient civilizations, the Mayans had a well-defined social hierarchy.
- At the top were the maya rulers, considered divine intermediaries between gods and people.
- Nobles and priests followed, holding power in both religious ceremonies and political affairs.
- A unique middle class of artisans, scribes, and traders existed, highlighting the diversity of the mayan culture.
- At the base were farmers, laborers, and slaves who ensured the sustenance of large populations across mayan cities.
Daily Life of the Maya People
Equally captivating are the details of daily life among the mayan people.
- Homes were often simple, made of wood, thatch, and mud, especially in rural areas of the Yucatán Peninsula and southern Mexico.
- Diets were rich in maize, beans, squash, and chili peppers, while cacao beans were not only consumed but also used as currency.
- Clothing and adornments reflected social status, with nobles displaying elaborate costumes and jewelry.
- Music and dance were essential parts of festivals, often performed with musical instruments like drums, flutes, and rattles.
Maya Cities and Architecture
The Great Cities of the Mayan Civilization
Among the most impressive facts about the Mayans are their great cities, which remain standing as awe-inspiring archaeological sites.
- Chichén Itzá, perhaps the most famous, houses the iconic maya pyramid known as El Castillo, which served as a temple and an astronomical marker.
- Other ancient cities such as Piedras Negras and the sites in northern Belize highlight the widespread reach of the mayan civilisation.
- These cities were not merely urban centers but also religious and cultural hubs.
Pyramid Temples and Ball Courts
Further evidence of Mayan ingenuity can be seen in pyramid temples and ball courts.
- Temples stood as monuments to gods, often aligned with astronomical systems to mark important events such as solstices.
- The ball game, played in large ball courts, was more than entertainment—it was a ritual tied to mythological themes described in the Popol Vuh, the sacred text of the yucatec maya.
- Sometimes, the losing team’s captain was sacrificed, symbolizing a cosmic victory for the gods.
The Mayan Calendar and Astronomical Knowledge

The Famous Calendar Systems
Another widely discussed topic in facts about the Mayans involves their famous calendar.
- The maya calendar works through various combinations of the sacred calendar and the solar calendar.
- The long count calendar tracked longer periods, often tied to creation myths and important events.
- Misinterpretations of this calendar fueled myths about the end of the world, especially in recent years.
Knowledge of Celestial Bodies
Moreover, the ancient mayans demonstrated deep knowledge of celestial bodies.
- Observatories were constructed to study astronomical events, including solar eclipses and lunar eclipses.
- The alignment of temples and pyramids with the stars shows how astronomy influenced architecture and religious ceremonies.
- Their accurate calendars remain one of the greatest intellectual achievements of the ancient mayan civilization.
Literature and Knowledge
The Popol Vuh and Maya Blue
Literature also offers remarkable fascinating facts about the Mayans.
- The Popol Vuh, written in the yucatec maya language, tells of creation myths, gods, and heroic adventures.
- Another marvel, maya blue, a pigment used in art and ritual, has puzzled scientists due to its durability and unique composition involving volcanic ash.
Rare Books and Codices
Unfortunately, much of Mayan literature was destroyed during the Spanish conquest, particularly by Spanish missionaries like Diego de Landa.
- A few rare books, including the Dresden Codex, survive, offering insights into astronomical systems, rituals, and daily life.
- These works serve as a bridge between the ancient world and recent years, helping modern researchers unlock the secrets of mayan civilisation.
Trade Routes and Economy
Extensive Trade Networks
Among the most compelling facts about the Mayans is the complexity of their trade. The mayan people were not isolated but instead built vast trade routes connecting different cities across southern Mexico, the Yucatán Peninsula, and into El Salvador and beyond.
- Goods such as obsidian, jade, salt, textiles, and feathers moved along these networks.
- Cacao beans often functioned as currency, further illustrating their economic significance.
- Coastal trade included canoe routes, linking ancient cities by sea and allowing access to distant resources.
Agricultural Foundations
Meanwhile, agriculture provided the backbone of mayan society.
- Farmers cultivated maize, beans, and squash using techniques like raised fields and terracing.
- Chili peppers, cacao beans, and other staples enriched their diets and rituals.
- The fertile soils, often replenished by volcanic ash, supported large populations across the lowlands and highlands.
Warfare and Expansion
Military Strategies and Conquests
When studying facts about the Mayans, attention must also be given to their frequent conflicts.
- City-states often engaged in warfare for dominance, resources, and captives.
- Victories ensured tribute and labor, while captives were used in human sacrifice or enslaved.
- Warfare was not only political but also spiritual, tied to religious ceremonies and the ultimate goal of cosmic balance.
Fall of Great Cities
Eventually, conflict and overpopulation contributed to the collapse of great cities.
- By the end of the post-classic period, many mayan cities in the lowlands were abandoned.
- Scholars point to factors such as environmental stress, prolonged droughts, and strained trade routes.
- Despite this decline, mayan culture and mayan languages persisted among the indigenous people of the region.
The Spanish Conquest and Cultural Suppression
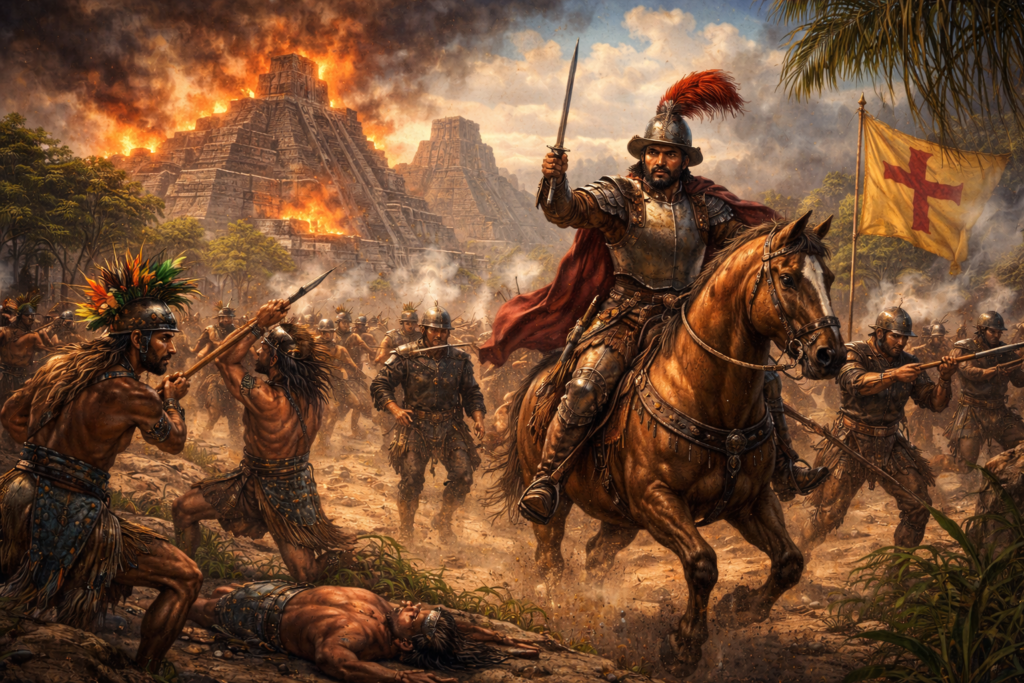

Arrival of the Spanish
Another key chapter in facts about the Mayans involves the Spanish conquest.
- Beginning in the 16th century, Spanish forces entered central America, bringing warfare, disease, and cultural suppression.
- Despite fierce resistance, the ancient mayan civilization was gradually subdued.
- Cities across the Yucatán Peninsula and guatemalan highlands fell to foreign rule.
Role of Spanish Missionaries
Equally significant were the actions of Spanish missionaries like Diego de Landa, who sought to convert the mayan people.
- Many rare books and codices were destroyed, leading to a devastating loss of cultural knowledge.
- Yet paradoxically, some missionaries documented elements of maya script and mayan writing, preserving fragments of history.
- The suppression of mayan culture did not erase it, as traditions, mayan languages, and customs survived among descendants.
End of the World Myths
Misinterpretation of the Mayan Calendar
In recent years, myths about the end of the world have fueled public curiosity.
- The long count calendar ended a major cycle in 2012, leading to widespread speculation about doomsday.
- Scholars emphasized that this marked the start of a new era, not the destruction of the earth.
- Such misunderstandings illustrate how modern fascination sometimes distorts authentic facts about the Mayans.
The True Meaning of the Calendar
Instead, the mayan calendar reflected cycles of renewal, tied to astronomical events and important events in maya civilisation.
- Its structure highlighted the interconnectedness of time, nature, and divine order.
- Far from a warning of disaster, it symbolized the continuity of life and the resilience of mayan society.
Art, Culture, and Creativity
Artistic Expression in Maya Civilization
Among the most remarkable facts about the Mayans is their vibrant artistic tradition. Art was not merely decorative but deeply connected to religion, politics, and daily life.
- Murals, pottery, and carvings illustrated myths, important events, and the deeds of maya rulers.
- The use of maya blue, a pigment made with indigo and volcanic ash, gave their art unique brilliance and durability.
- Stone stelae and monuments displayed hieroglyphic writing, commemorating battles and dynastic successions.
Musical Instruments and Performance
In addition to visual art, music held a central place in maya culture.
- Drums, trumpets, rattles, and flutes were among the musical instruments played during religious ceremonies and festivals.
- Dance, accompanied by rhythm, became a spiritual act, often reflecting cosmic cycles and the relationship between humans and gods.
- Even today, echoes of these traditions survive among the descendants of the mayan people.
Sports and Recreation
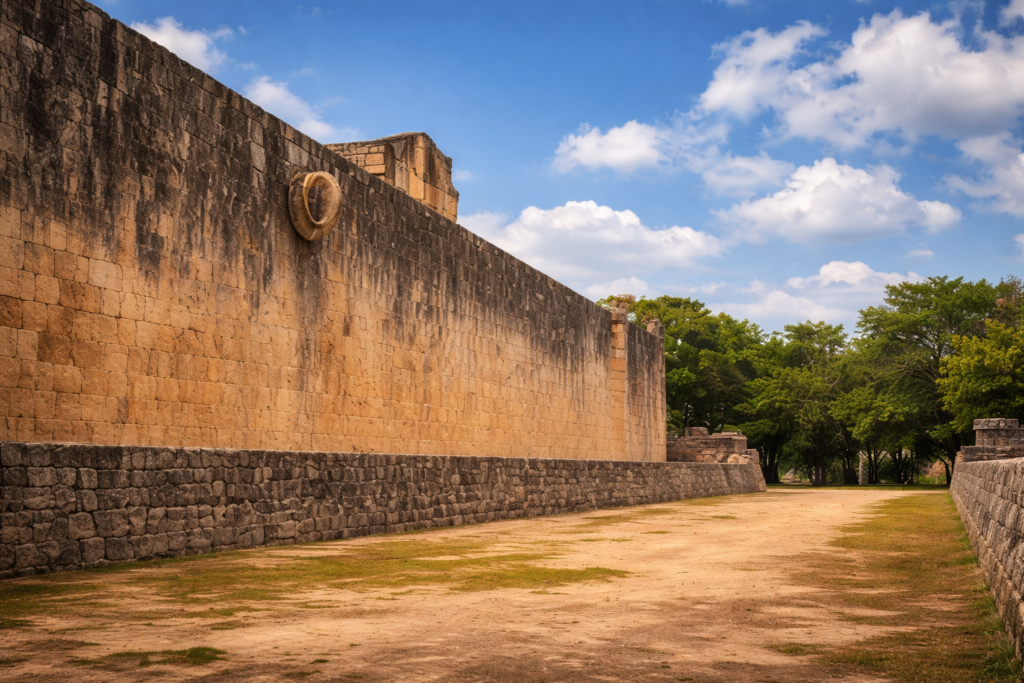

The Maya Ball Game
One of the most fascinating and widely discussed facts about the Mayans is their unique ball game, played in vast ball courts throughout mayan cities.
- The game involved propelling a heavy rubber ball through stone hoops using hips, knees, and elbows.
- Matches were charged with ritual meaning, often tied to themes of life, death, and the cosmos as described in the Popol Vuh.
- Archaeological evidence suggests that the outcome sometimes determined whether captains or players faced human sacrifice, symbolizing victory for the gods.
Extreme Sports of the Ancient World
Interestingly, some modern scholars have likened the ball game to extreme sports because of its intensity and high stakes. With games often deciding matters of honor, religion, and even life or death, it became one of the most symbolic cultural practices of the ancient mayan civilization.
Archaeological Evidence and Discoveries
Rediscovery of Maya Civilization
For centuries, the great mayan cities lay hidden beneath dense jungle, forgotten by much of the world. Then, in the 19th and 20th centuries, explorers uncovered ruins that revealed the brilliance of the ancient mayans.
- Sites like Chichén Itzá, Piedras Negras, and others on the Yucatán Peninsula were rediscovered, offering insight into mayan society.
- Scholars like Tatiana Proskouriakoff made breakthroughs in deciphering maya script, changing the way history understood the maya calendar works and their dynastic records.
- Modern technology such as LIDAR has revealed ancient cities and complex infrastructure, showing large populations once thrived in regions previously thought to be sparsely inhabited.
Codices and Surviving Texts
Equally crucial to understanding the Mayans are their surviving texts.
- The Dresden Codex, one of the few rare books to escape destruction, provides invaluable knowledge of astronomical systems, solar year calculations, and religious ceremonies.
- Together with stone inscriptions and stelae, these documents form a bridge between the ancient world and modern scholarship.
- According to the Smithsonian Institution, the Dresden Codex is believed to be one of the earliest uses of a paper-like material made from bark, demonstrating advanced techniques in record-keeping.
Fascinating Facts That Still Amaze Scholars
Finally, many fascinating facts about the Mayans continue to intrigue researchers.
- They were one of the first advanced civilisations in the Americas to develop a full writing system.
- Their accurate calendars tracked celestial bodies and predicted astronomical events with remarkable precision.
- The mayan culture produced innovations in agriculture, architecture, and literature that influenced the ancient world and beyond.
The Legacy of the Mayan People
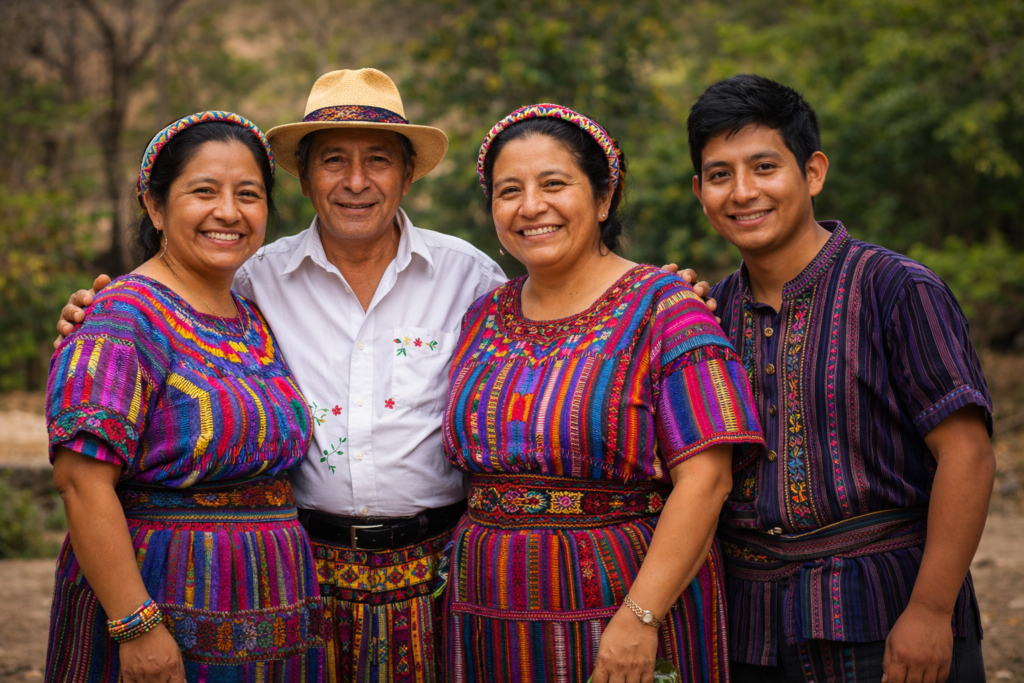

Modern Descendants and Culture
Despite the collapse of many great cities and the impact of the Spanish conquest, the legacy of the mayan people has not vanished. Today, millions of descendants live across southern Mexico, Guatemala, northern Belize, and El Salvador.
- Many communities still speak mayan languages, including yucatec maya.
- Traditional practices, from weaving to farming, remain part of daily life in these regions.
- Festivals often blend ancient religious ceremonies with Catholic influences, reflecting centuries of adaptation.
Preservation of Mayan Heritage
In fact efforts to preserve mayan culture continue through archaeology, anthropology, and cultural revival.
- Excavation of archaeological sites has revealed lost ancient cities, pyramid complexes, and ball courts.
- Museums and cultural centers highlight mayan writing, codices, and the brilliance of maya glyphs.
- Indigenous activists promote the survival of mayan society and advocate for recognition of their ancestral knowledge.
Facts About the Mayans FAQs
What are some of the most interesting facts about the Mayans?
Some of the most interesting facts include their creation of accurate calendars, their advanced writing system, and their practice of the ritual ball game.
Did the Mayans really predict the end of the world?
No, the belief that the Mayans predicted the end of the world in 2012 was a misinterpretation of the long count calendar. It marked the end of a cycle, not the earth itself.
Why did the Mayan civilization decline?
The decline was influenced by warfare, environmental stress, overpopulation, and shifting trade routes, leading to the abandonment of many mayan cities.
What role did human sacrifice play in Mayan culture?
Human sacrifice was part of religious ceremonies, often conducted during astronomical events to honor gods and ensure fertility.
What is the Popol Vuh?
The Popol Vuh is a sacred text of the Mayans, written in mayan script, that records creation myths, heroic tales, and spiritual beliefs.
How many people speak Mayan languages today?
Millions still speak mayan languages, particularly in the guatemalan highlands and the Yucatán Peninsula.
What foods did the Mayans eat?
Staple foods included maize, beans, squash, chili peppers, and cacao beans, often consumed in the form of drinks or used as trade currency.
What are some famous Mayan archaeological sites?
Sites like Chichén Itzá, Piedras Negras, and ruins in northern Belize are among the most famous, showcasing maya pyramids and inscriptions.
Facts About the Mayans Conclusion
Finally, in the end, exploring facts about the Mayans reveals a civilization that shaped history through its advanced civilisation, famous calendar, and enduring culture. Thus their mastery of astronomical systems, hieroglyphic writing, and monumental architecture continues to astonish scholars and inspire wonder.
Although the spanish conquest altered the course of their society, the resilience of the mayan people ensures that their traditions remain alive today. The story of the Mayans is not only one of past glory but also of survival, identity, and heritage passed down through generations.
Indeed, the Mayans stand as a reminder that even in the face of conquest and decline, a people’s wisdom, spirit, and culture can endure the test of time.
If it’s not too much trouble, I’d recommend reading this article 30+ Amazing Facts About the Incas and Their Lost Empire. You’ll love it.