38 Great Facts About the Respiratory System You Need to Know
Facts About the Respiratory System
Undoubtedly, the human body depends on many vital systems, but none is as essential to daily survival as the respiratory system. Through its intricate design, this system ensures that every cell receives the oxygen it needs and eliminates the carbon dioxide that could otherwise harm life. When people explore facts about the respiratory system, they uncover a world of tiny air sacs, balloon-like structures, and a network of bronchial tubes that sustain breath.
Interestingly, lungs are the only organs that can float on water, and medical examiners even use a lung float test as part of investigations. Moreover, with each deep breath, the chest cavity expands as the diaphragm contracts, drawing fresh air into the nasal cavity and oral cavity before it travels down to the lower respiratory tract. These processes seem automatic, yet they are tightly controlled by the medulla oblongata, which regulates breathing rate without conscious thought.
Therefore, learning key facts about the respiratory system not only sparks curiosity but also encourages individuals to take better care of their lung function. With respiratory illnesses like chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and respiratory infections on the rise, knowledge becomes an important tool in prevention and awareness.
Vital Role of the Respiratory System
The respiratory system plays a central role in sustaining life. Without it, the human body would be unable to survive more than a few minutes.
Gas Exchange in Action
- Oxygen-rich air enters through the nasal passageways or oral cavity.
- The walls of the trachea guide air down into smaller bronchi.
- Tiny hairs filter out foreign particles, while sticky mucus traps dust.
- In the smaller tubes and smaller air passages, air flows until it reaches bronchioles end.
- Finally, small air sacs, or alveoli, allow the exchange of oxygen and carbon-dioxide waste with tiny blood vessels.
This exchange of oxygen for waste gas keeps red blood cells loaded with oxygen-rich blood, which is then circulated by the circulatory system.
Unique Characteristics of Human Lungs
- The right lung is slightly larger than the left lung because the heart rests on the left side.
- Both lungs together have a surface area of the lungs equal to the size of a tennis court.
- These balloon-like structures are protected by the rib cage and supported by rib muscles and intercostal muscles.
- An average person breathes in around 13 pints (about 6 liters of air) every minute.
According to the International Journal of Legal Medicine, the lungs remain the only organs that can reliably demonstrate buoyancy when filled with air, a fact frequently referenced in forensic studies.
Fun and Interesting Facts About Breathing
Surprisingly, there are countless fun facts and lesser-known truths that reveal just how incredible the respiratory system really is.
Breathing Patterns
- On average, an adult takes about 20,000 breaths each day.
- Residual volume, or the air left in the lungs after a deep breath out, ensures the lungs never fully collapse.
- Even while sleeping, lungs work tirelessly under the command of the medulla oblongata.
The Role of Other Body Parts
- The voice box, or larynx, containing vocal cords, produces sound as air flows through.
- The bottom of the pharynx and small flap of tissue at the bottom end of the throat prevent food from entering the airways.
- Chest wall muscles and a thin sheet of dome-shaped muscle called the diaphragm create chest movement essential for lung function.
Therefore, while it might seem like a simple process, every breath is supported by dozens of body parts working in unison.
Structure of the Respiratory System
When exploring facts about the respiratory system, its structure must be clearly understood. Designed with multiple protective layers and pathways, the system ensures the safe movement of oxygen-rich air.
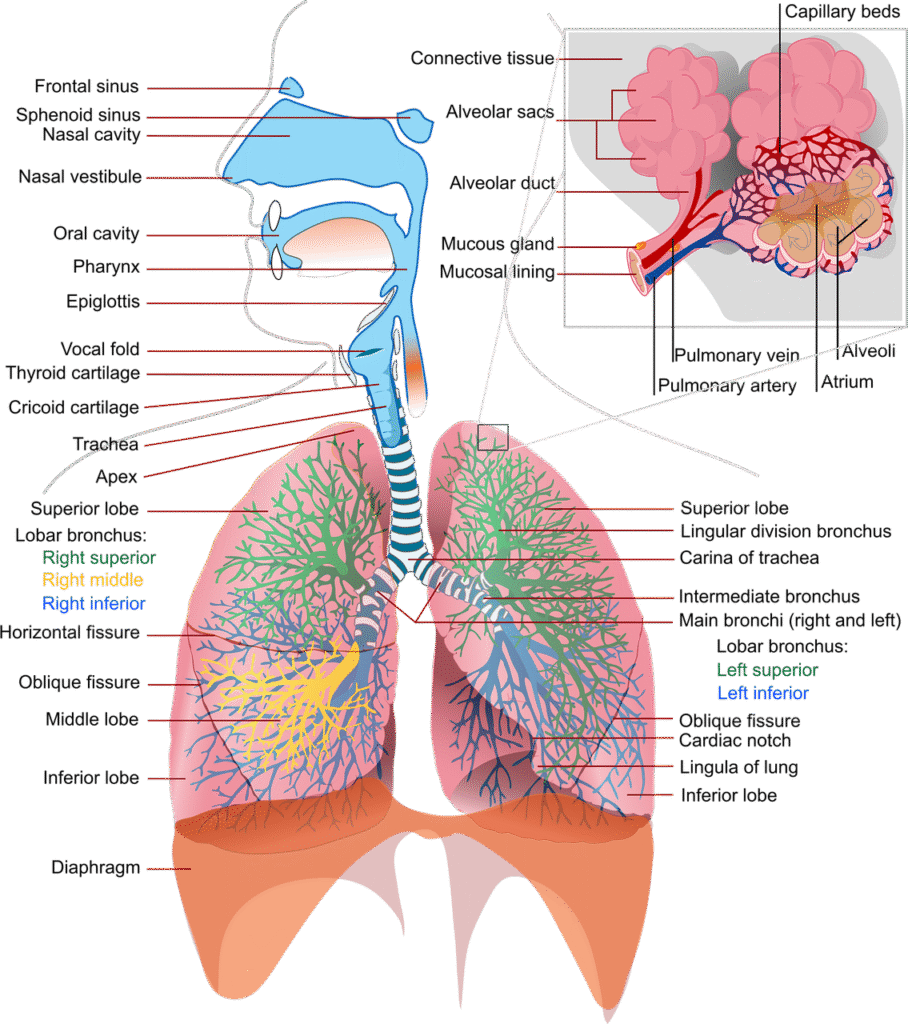
Upper Respiratory Tract
The upper respiratory tract includes the nasal cavity, oral cavity, and the back of your throat.
- The nasal cavity filters incoming air using tiny hairs that trap foreign particles.
- Sticky mucus prevents harmful substances, such as cigarette smoke or secondhand smoke, from reaching the lungs.
- The photic sneeze reflex, an interesting fact, causes some people to sneeze when exposed to bright light.
- Allergic rhinitis, sore throat, and the common cold are among the most common respiratory illnesses affecting this region.
Moreover, the upper respiratory tract plays a vital role in preparing oxygen-rich air before it travels deeper. By warming and moistening the air, body temperature remains balanced.
Lower Respiratory Tract
The lower respiratory tract houses more complex structures.
- The short tube of the trachea branches into smaller bronchi and smaller tubes.
- These passages eventually reach bronchioles end, leading directly into small air sacs.
- At the alveolar walls, the exchange of oxygen for carbon-dioxide waste takes place.
Importantly, these small structures are balloon-like, maximizing surface area of the lungs. The system provides enough room for liters of air while still fitting inside the thoracic cavity.
The Human Lungs in Detail
The human lungs are fascinating organs that reveal numerous facts about the respiratory system.
Left Lung vs. Right Lung
- The right lung has three lobes, making it larger and heavier.
- The left lung, slightly smaller, has only two lobes to make space for the heart.
- This structural difference shows how multiple body parts, including the circulatory system, share the chest cavity.
Additionally, the rib cage surrounds both lungs, providing a protective barrier against injury.
Lung Function and Capacity
- Lung capacity varies depending on physical ability, age, and health.
- An average person has a total lung capacity of about six liters of air.
- Residual volume remains inside the lungs even after full exhalation, keeping them open.
- With training, athletes can increase their lung function, improving oxygen-rich blood flow.
Therefore, the lungs are more than balloon-like structures; they adapt based on lifestyle and health.
Respiratory Conditions and Challenges
Unfortunately, the respiratory system is prone to many respiratory illnesses.
Common Illnesses
- The common cold and respiratory syncytial virus often affect the upper respiratory tract.
- Respiratory infections such as sore throat or allergic reaction can lead to temporary discomfort.
- Chronic illnesses like lung cancer, cystic fibrosis, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease affect the long-term health of human lungs.
The Role of Healthcare Providers
When breathing problems occur, a healthcare provider evaluates lung function through medical exams. In some cases, medical examiners use tests such as the lung float test, often discussed in the Journal of Polish Pneumonology.
Moreover, respiratory conditions can affect physical ability, reduce lung capacity, and alter breathing rate. Prevention, early detection, and management are crucial.
How Breathing Works Step by Step
Among the most fascinating facts about the respiratory system is how breathing occurs seamlessly, without conscious effort most of the time.
The Inhalation Process
- First, the diaphragm contracts, flattening downward.
- Then, chest wall muscles and rib muscles expand the rib cage, creating more room inside the thoracic cavity.
- As pressure decreases, fresh air flows into the nasal passageways or oral cavity.
- Finally, oxygen-rich air travels down the walls of the trachea and into the smaller bronchi and smaller air passages.
This careful sequence allows balloon-like structures to fill with oxygen-rich air.
The Exhalation Process
- When the diaphragm relaxes, chest movement reverses.
- The rib cage contracts slightly, pushing air back out.
- Carbon dioxide, a waste product, exits through the nasal cavity or oral cavity.
Therefore, every deep breath involves the coordination of body parts designed to manage airflow and maintain proper gas exchange.
Connection Between Respiratory and Circulatory Systems
The circulatory system works hand in hand with the respiratory system. Both systems form a vital partnership that sustains the human body.
Oxygen Transport
- Tiny blood vessels, known as capillaries, surround small air sacs in the lungs.
- Oxygen-rich air crosses alveolar walls into red blood cells.
- These cells carry oxygen-rich blood throughout the body.
Removal of Waste Gas
- Simultaneously, carbon-dioxide waste leaves the bloodstream.
- This waste gas then moves into the alveoli and is exhaled.
In short, the exchange of oxygen and removal of carbon-dioxide waste proves essential for every part of the respiratory system and circulatory system.
Could you give this article Intriguing Facts About the Circulatory System (The Best 23) a read when you can? It offers some additional insights on the topic.
Protective Features of the Respiratory System
Interestingly, several natural defenses exist to shield human lungs from foreign particles and respiratory conditions.
Mechanical Defenses
- Tiny hairs in the nasal cavity act as the first line of defense.
- Sticky mucus traps dust, allergens, and even small microbes.
- A small flap of tissue at the bottom end of the throat ensures food enters the digestive system instead of airways.
Reflexive Defenses
- Sneezing clears irritants from nasal passageways.
- Coughing expels sticky mucus and foreign particles from the chest cavity.
- The photic sneeze reflex, though less common, demonstrates how sensitive the nasal cavity can be.
Therefore, the respiratory system not only brings in oxygen-rich air but also protects against harmful substances.
Fun Facts About the Respiratory System

Exploring fun facts about the respiratory system makes it clear how remarkable it really is.
- Human lungs are the only organs that can float on water.
- The size of a tennis court equals the surface area of the lungs.
- Breathing rate changes depending on body temperature, physical activity, or emotional state.
- A deep breath can hold several liters of air, depending on lung capacity.
- Some people experience respiratory illnesses triggered by allergic reaction to foreign particles.
These fun facts emphasize both the complexity and uniqueness of lung function.
Diseases and Disorders Affecting the Respiratory System
While many interesting facts about the respiratory system highlight its strength, it is also highly vulnerable. Numerous diseases and disorders can disrupt lung function, limit physical ability, and endanger life.
Acute and Common Conditions
- The common cold frequently affects the upper respiratory tract, causing sore throat, coughing, and congestion.
- Respiratory syncytial virus is a leading cause of illness in children and elderly adults.
- Allergic rhinitis develops as an allergic reaction, often triggered by pollen, dust, or cigarette smoke.
Because these conditions are widespread, prevention through clean environments and fresh air intake becomes important.
Chronic Respiratory Diseases
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) restricts airflow, making breathing extremely difficult.
- Cystic fibrosis is a genetic disorder that leads to sticky mucus clogging the bronchial tubes and smaller air passages.
- Lung cancer, one of the deadliest forms of cancer, often results from long-term exposure to cigarette smoke or secondhand smoke.
I’d really appreciate it if you could read this article Facts About Cancers: Key Information You Need to Know when you have a moment. It’s related to what we’ve been discussing.
Moreover, these chronic diseases often require long-term care from a healthcare provider, who may order breathing tests or imaging scans to assess lung capacity.
The Role of Breathing in Daily Life
Survival depends on many body parts working together, but none is as essential as the respiratory system.
Physical Activity and Breathing
- During exercise, the body requires more oxygen-rich air.
- Intercostal muscles, rib muscles, and the diaphragm contract harder to increase breathing rate.
- This improved airflow boosts oxygen-rich blood circulation, enhancing physical ability.
Therefore, athletes often practice breathing techniques to maximize lung function and performance.
If you have some free time, it might be helpful to check out this article The Best 22 Interesting Facts About Muscle in the Human Body. It covers some relevant points.
Breathing and Emotions
- Stress can change chest movement, leading to rapid or shallow breaths.
- A deep breath often calms the nervous system, showing the vital role of controlled breathing.
- Interestingly, meditation practices focus heavily on regulating breathing rate for mental clarity.
In short, the act of breathing affects both body and mind in remarkable ways.
Snippet-Worthy Section: Quick Facts About the Respiratory System
Here are some quick and fascinating facts about the respiratory system that summarize its importance:
- Human lungs contain about 480 million small air sacs.
- The left lung is smaller than the right lung to fit the heart.
- The exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide happens across alveolar walls.
- On average, a person breathes about 20,000 times daily.
- The surface area of the lungs is roughly the size of a tennis court.
- Residual volume keeps lungs from collapsing after exhalation.
- Voice box and vocal cords create sound as air passes through.
The Complexity of Airflow
Another fascinating aspect of respiratory anatomy lies in the airflow journey.
- Air begins in nasal passageways, where tiny hairs capture foreign particles.
- Then, it passes down the short tube of the trachea into smaller bronchi.
- Smaller tubes and bronchioles end at balloon-like alveoli.
- Finally, oxygen enters red blood cells while carbon dioxide leaves as waste gas.
This journey emphasizes how many body parts are required to keep lungs working seamlessly.
Advanced Insights Into the Respiratory System
Among the most advanced facts about the respiratory system is how finely it is controlled by the brain.
Role of the Medulla Oblongata
- The medulla oblongata monitors carbon-dioxide waste levels in the blood.
- When waste gas rises, breathing rate automatically increases.
- This process ensures stable oxygen-rich blood supply throughout the human body.
Therefore, even while asleep, the respiratory system functions without conscious control.
Interactions With Other Body Systems
- The digestive system shares the oral cavity and bottom of the pharynx with the respiratory system.
- A small flap of tissue prevents food from entering the lungs during swallowing.
- Body temperature regulation also depends on breathing, as exhaled air releases heat and moisture.
This constant interaction highlights the respiratory system as more than just a set of balloon-like structures—it is interconnected with nearly all body systems.
Medical and Scientific Perspectives
Scientific studies continually reveal fascinating facts about the respiratory system.
- According to the Journal of Polish Pneumonology, chronic lung disease rates are increasing worldwide, largely due to pollution and cigarette smoke.
- Medical examiners use the lung float test to determine if a newborn ever took a breath.
- Healthcare providers recommend regular checkups and lung function tests for those at risk of respiratory conditions.
These medical insights demonstrate the ongoing importance of research in understanding human lungs.
FAQs: Facts About the Respiratory System
What are the main parts of the respiratory system?
The respiratory system includes the nasal cavity, oral cavity, voice box, trachea, bronchial tubes, bronchioles, and small air sacs in the lungs.
Why is the left lung smaller than the right lung?
The left lung is smaller because the heart occupies space on the left side of the chest cavity.
How much air can the human lungs hold?
An average person has a lung capacity of about six liters of air, though lung function varies with physical ability and health.
What protects the lungs from injury?
The rib cage, rib muscles, and chest wall muscles shield the lungs from damage while supporting chest movement.
Which diseases affect the respiratory system?
Common respiratory conditions include asthma, lung cancer, cystic fibrosis, COPD, and respiratory infections such as the common cold.
What makes human lungs unique compared to other organs?
Human lungs are the only organs that float on water, making them distinct during medical examinations.
Facts About the Respiratory System Conclusion
In conclusion, countless fascinating facts about the respiratory system highlight its complexity and importance. From the exchange of oxygen in tiny air sacs to the rib cage’s protection of balloon-like lungs, the system sustains life every second. Moreover, fun facts—such as lungs having the surface area of a tennis court—make clear how extraordinary the design truly is.
However, because respiratory illnesses such as lung disease, respiratory infections, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease remain widespread, awareness and preventive care must be prioritized. By understanding these interesting facts and consulting a healthcare provider when needed, individuals can safeguard lung function and improve overall well-being.
Ultimately, the respiratory system represents not just a vital role in survival but also a marvel of the human body. Every deep breath taken is a reminder of this remarkable design.
I’d recommend reading this article The Best 15 Interesting Facts About E.coli next.