Interesting Facts About X Rays (In B&W)
Interesting Facts About X Rays
What are x-rays?
An x-ray is a type of electromagnetic radiation, just like visible light. X-rays have shorter wavelengths than visible light, so they have more energy. This extra energy makes it possible to take pictures of the inside of your body. So let’s quickly discover more interesting facts about x rays.
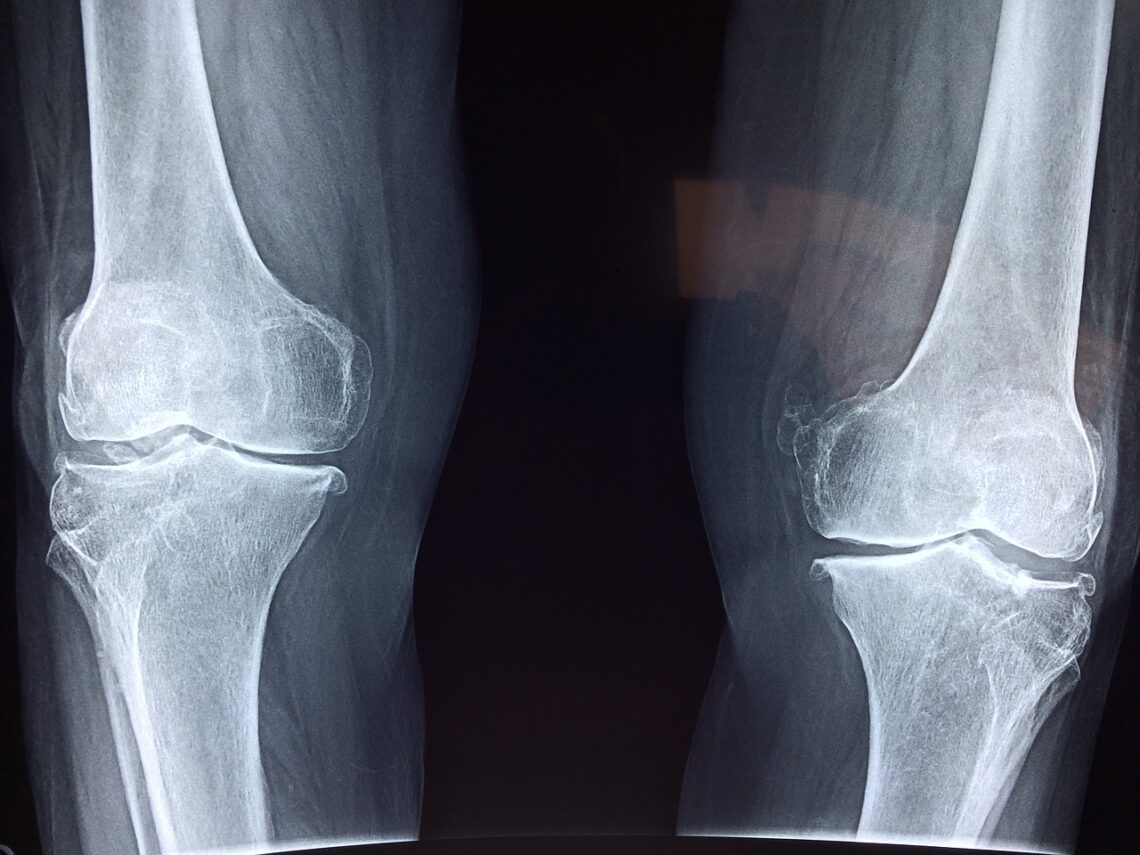
X-rays are made by using a high voltage to shoot electrons through a metal target. The electrons bounce off the target and make x-rays. The x-rays go through your body and hit a piece of film on the other side. The film turns black where the x-rays hit it, and this makes an image of your bones and organs. Doctors use x-rays to look for bone fractures, pneumonia, lung cancer, kidney stones, and tumors.
You might think that all this extra energy would make x-rays dangerous, but our bodies are actually pretty good at dealing with them. X-rays are more dangerous when they are used for medical purposes due to radiation exposure, like looking inside the body.
Doctors use special machines called x-ray machines to make these x-ray images. They have to be careful not to use too much of this extra energy or it can damage the patient’s body. X-rays are harmful to living tissue, so doctors have to be careful when using them. Pregnant women and young children are especially vulnerable to the effects of x-rays. However, the benefits of using x-rays usually outweigh the risks.
The History of X- Rays
In 1895, Wilhelm Röntgen was the first person to discover x-rays while experimenting with electricity. He found that when he placed an electrode near a vacuum tube, a mysterious ray was emitted that could pass through paper and other objects.
He found that when he turned off the lights and placed objects between the cathode rays and photographic plates, shadows of the objects appeared on the plate. He called them “x-rays” because they were an unknown type of radiation. X-rays are a form of electromagnetic radiation, like visible light, microwaves, and radio waves.
They are all made up of waves of electric and magnetic fields that travel through space at the speed of light.
X-rays were originally used for medical purposes, to help doctors see inside the human body. But they have also been used in other ways, such as to help archaeologists study ancient bones and to find hidden weapons in luggage at airports.
Today, x-rays are still used for medical purposes, but there are now more advanced ways of using them, such as computed tomography (CT) scans and x-ray crystallography.
What Are CT Scans

A CT scan is an imaging test that uses X-rays and computer technology to create detailed pictures of the inside of your body. CT scans are more accurate than traditional X-rays because they can show more detail.
CT scans are often used to diagnose cancer, heart disease, lung problems, and other conditions. They can also be used to guide procedures such as biopsies and surgeries. Most people who have a CT scan don’t have any side effects. The most common side effect is feeling tired from lying still during the exam.
X-Ray Crystallography
One of the most interesting things about x-rays is that they can be used to see the inner workings of matter. This process is called x-ray crystallography, and it allows scientists to look at the atoms that make up a material and see how they are arranged. This information can then be used to understand the properties of the material and how it behaves.
X-ray crystallography was first used in the early 1900s, and since then it has been used to study everything from viruses to proteins. It is a powerful tool for understanding the structures of molecules and how they interact with each other.
In recent years, researchers have even used it to create 3D images of individual atoms. X-ray crystallography is an essential tool for many different fields of science, including chemistry, biology, and materials science.
dental x-rays
Dental x-rays are necessary for keeping your teeth and mouth healthy. They help your dentist see what is going on below the surface of your teeth and gums and diagnose problems early. Here are some interesting facts about dental x rays:
- Dental x-rays are more than 100 years old! The first dental x-ray was taken in 1895 by Wilhelm Rontgen, who won the Nobel Prize in Physics for his discovery.
- Dental x-rays are a form of electromagnetic radiation, just like visible light. However, they have a much shorter wavelength and higher energy than visible light, so they can penetrate your teeth and gums to create an image.
- Dental x rays are not harmful to your health when used properly, you would only receive a small radiation dose.
Hard X-Rays
X-rays were first discovered in 1895 by Wilhelm Conrad Roentgen, a German physicist. These high-energy photons are able to penetrate human tissue, making them useful for medical imaging. Here are some interesting facts about hard x-rays:
Hard x-rays have shorter wavelengths and higher energies than soft x-rays. This makes them more penetrating and better at image resolution.
Because they are more energetic, hard x-rays are also more harmful to the body. They can damage DNA and cause cancer. For this reason, they must be used with caution in medical imaging.
Hard x-rays are produced by accelerating electrons with high energies. The most common way to do this is using an X-ray tube.
Soft X-Rays
X-rays are a type of electromagnetic radiation, and they have the ability to penetrate most materials. This makes them useful for medical imaging, as well as security applications. X-rays have a short wavelength, and this gives them high levels of energy.
Soft x-rays are those with a shorter wavelength than visible light. This means that they have more energy than visible light photons. Soft x-rays are used in medical imaging, as they can penetrate the human body without causing too much damage. They are also used in security applications, as they can penetrate many kinds of materials.
One interesting fact about soft x-rays is that they can be used to create images of objects that are too small to be seen with a regular microscope. Another fact is that they can be used to study objects in space, as they can penetrate dust and gas clouds.
Cathode Rays
Cathode rays are a type of electromagnetic radiation. They were first discovered in 1876 by German physicist Eugen Goldstein. Cathode rays are produced when electrons are accelerated in a vacuum.
When they strike a material, they can cause that material to emit X-rays. Cathode rays can also be used to create images on a fluorescent screen. These images are called cathode ray oscillographs. A cathode ray oscillograph is a device used to take pictures of the inside of an object. It is similar to an oscilloscope, which also makes pictures of the inside of objects.
Gamma Rays
Gamma rays are the most energetic form of electromagnetic radiation. They are produced by radioactive decay, nuclear fission, and nuclear fusion. Gamma rays can penetrate through almost anything, including the human body.
They can be used to kill cancer cells and treat other diseases. Gamma radiation can also be used to kill bacteria and germs. X-rays are a form of gamma-rays.
Types of Electromagnetic Radiation Light is the most common form of electromagnetic radiation. It has many uses, such as lighting buildings and streets, signaling, and communication.
Chest X-Rays
A chest x-ray is a diagnostic test that uses ionizing radiation to produce images of the structures inside the chest. The images are used to evaluate the lungs, heart, and bones of the chest. A chest x-ray is typically performed as part of a routine physical examination or when a person has symptoms that suggest a problem with the lungs, heart, or bones.
The test is quick and easy to perform, and it is usually painless. There are some risks associated with exposure to ionizing radiation, but these risks are generally considered to be small compared to the benefits of the test.
How X-rays Work

An x-ray is a type of high-energy radiation that can pass through the body, making images of the inside of the body on film. X-rays are used to look for problems such as broken bones, tumors, and foreign objects in the body.
The x-rays are produced by an x-ray machine. The machine has two parts: an x-ray tube and a computer that processes the images. The x-ray tube contains electrons.
When the electrons collide with atoms in the tube, they produce x-rays. The x-rays travel through the body and are picked up by a special film or plate placed on the other side of the body. The film or plate is then sent to a computer for interpretation by a radiologist (a doctor who specializes in reading medical images).
How X-rays Are Used
X-rays are a type of electromagnetic radiation, just like visible light. They were first discovered in 1895 by German physicist Wilhelm Roentgen. X-rays are used in many different ways, including:
-To take pictures of the inside of the human body (medical x-rays)
-To detect luggage at airports (security x-rays)
-To inspect the welds on metal objects (industrial x-rays)
Medical x-rays are the most common type of x-ray. They are used to take pictures of the inside of the human body to look for broken bones, cancers, and other problems.
Security x-rays are used to detect guns, knives, and other dangerous objects in luggage at airports. Industrial x-rays are used to inspect the welds on metal objects like pipelines and bridges.
Thomas Edison and x-rays
Few people know that the x-ray was actually developed by Thomas Edison in 1878. He was experimenting with electricity and noticed that when he placed a piece of paper over an electrified wire, it would create a shadow image of the wire on the paper.
He realized that he could use this same principle to create images of objects inside the human body. However, it wasn’t until 1895 that Wilhelm Röntgen discovered how to produce x-rays, which led to their widespread use in medicine.
Thomas Edison, an American inventor, and businessman was born on February 11, 1847. He is best known for his development of the incandescent light bulb and his work with electricity. Here are some interesting facts about Thomas Edison:
-He was home-schooled by his mother until he was 12 years old.
-Edison worked as a telegraph operator after he was forced to leave school.
-He developed the incandescent light bulb in 1879 after years of experimentation.
-Edison held 1,093 patents in his lifetime, including for the phonograph and motion picture camera.
-He founded the Edison General Electric Company in 1890.
-Edison died on October 18, 1931, at the age of 84.
Clarence Dally
Clarence Dally was an interesting character. Here are some facts about him:
He was Thomas Edison’s assistant, and he was the one who developed x-ray machines.
Dally was also known for being a heavy drinker and gambler. He would often spend his evenings in bars and gambling halls.
In 1904, Dally died of cancer after years of working with x-rays. It is believed that his cancer was caused by exposure to radiation.
Nikola Tesla and The Use of X-Rays
Nikola Tesla was one of the first scientists to investigate the use of x-rays. He began experimenting with them in 1884, and by 1886 he had developed a way to use them for medical purposes. Tesla’s x-ray experiments led to the development of radiography, which is now used extensively in medicine.
Tesla’s work with x-rays was not without its dangers, however. In 1896, he suffered a debilitating injury to his left hand when an x-ray tube exploded. Despite this setback, Tesla continued to work with x-rays and other forms of electromagnetic radiation. He is credited with many important discoveries in the field of radioactivity.
Who Was John Hall-Edwards
John Hall-Edwards was the first person to ever be successfully photographed using x-rays. He was a medical student at the time and was experimenting with x-ray technology. The photo was taken in 1896 and showed his hand and bones.
This was a major breakthrough in medical technology at the time and paved the way for future advances in x-ray imaging. The X-Ray Machine The first mobile x-ray machine was developed by Dr. John Hall-Edwards who also helped develop the first x-ray pictures of bones.
He took his x-ray machine to the battlefields of World War I to help doctors treat wounded soldiers.
X-Rays in the United States
In the United States, x-rays are one of the most commonly used diagnostic tools. They are painless and quick and can be used to image many different parts of the body.
X-rays work by passing through the body and being absorbed in different amounts by different tissues. This allows a doctor to see inside the body without having to make an incision.
X-rays are a form of ionizing radiation, which means that they can damage cells and soft tissues. However, the risks posed by x-rays are low when compared to the benefits of using them for diagnosis and treatment.
There are some simple precautions that can be taken to minimize the risks posed by x-rays. For example, pregnant women or young children should only have x-rays if absolutely necessary, as their bodies are more sensitive to radiation.
X-Rays and Space
Though x-rays were first discovered in the late 1800s, it wasn’t until 1895 that German physicist Wilhelm Conrad Roentgen realized their potential for investigating the universe. X-rays are a type of electromagnetic radiation, like visible light, but with much shorter wavelengths and higher energies.
When x-rays strike an object, they cause it to emit x-rays of its own. By studying this secondary emission, astronomers can learn about the composition, temperature, and other properties of distant astronomical objects. If you’re interested in technology then you may find my Interesting Facts About Technology article a fun read.
In 1963, NASA’s Mariner 2 spacecraft made history when it became the first manmade object to fly by another planet–Venus. As Mariner 2 approached Venus, it detected x-radiation emanating from the planet’s hot surface.
This was the first direct evidence that other worlds in our solar system can be quite different from Earth. NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory is one of the most powerful x-ray telescopes ever launched into space. It was designed to detect some of the highest-energy forms of light, including x-rays from the hottest and most energetic objects in the universe.
Black holes and x-rays
A black hole is an object with a gravitational field so strong that nothing, not even light, can escape from it. X-rays are a type of electromagnetic radiation with a very short wavelength.
Black holes are interesting objects to study because they are so massive and have such a strong gravitational force. One way to study black holes is by looking at the x-rays that they emit.
When matter falls into a black hole, it gets heated up and emits x-rays. By studying the x-rays emitted by black holes, scientists can learn about the structure of these fascinating objects.
Neutron stars and x-rays
Neutron stars are the ultra-dense cores of dead stars that have collapsed under their own gravity. These incredibly dense objects are incredibly fascinating to astronomers, and they’re also responsible for some of the most energetic phenomena in the Universe.
One of the most interesting things about neutron stars is that they emit X-rays. This is because the extremely strong gravitational field of a neutron star can accelerate particles to high energies. These high-energy particles then collide with other particles near the surface of the star, resulting in X-ray emission.
Interestingly, while most X-ray sources in the Universe are transient (they come and go over time), neutron stars are relatively stable X-ray emitters. This means that astronomers can study them in great detail, providing us with valuable insights into these strange and exotic objects.





One Comment
Pingback: