
Essential Facts About the West Region (The Best 33)
From Coast to Mountains: Facts About the West Region
Firstly, the western United States, often simply referred to as the “west region,” is a vast expanse that captures the essence of the American dream, the spirit of exploration, and the wonders of Mother Nature. In this case, from the glistening shores of the Pacific Ocean to the historic pathways of the Oregon Trail. This region brims with tales that have profoundly influenced American history. Whether you’re a local resident, an avid historian, or just someone with a curiosity to learn more, join us as we embark on this enlightening journey filled with interesting facts about the west region.
The Physical Beauty: Nature’s Grand Tapestry
The Majestic Mountain Ranges
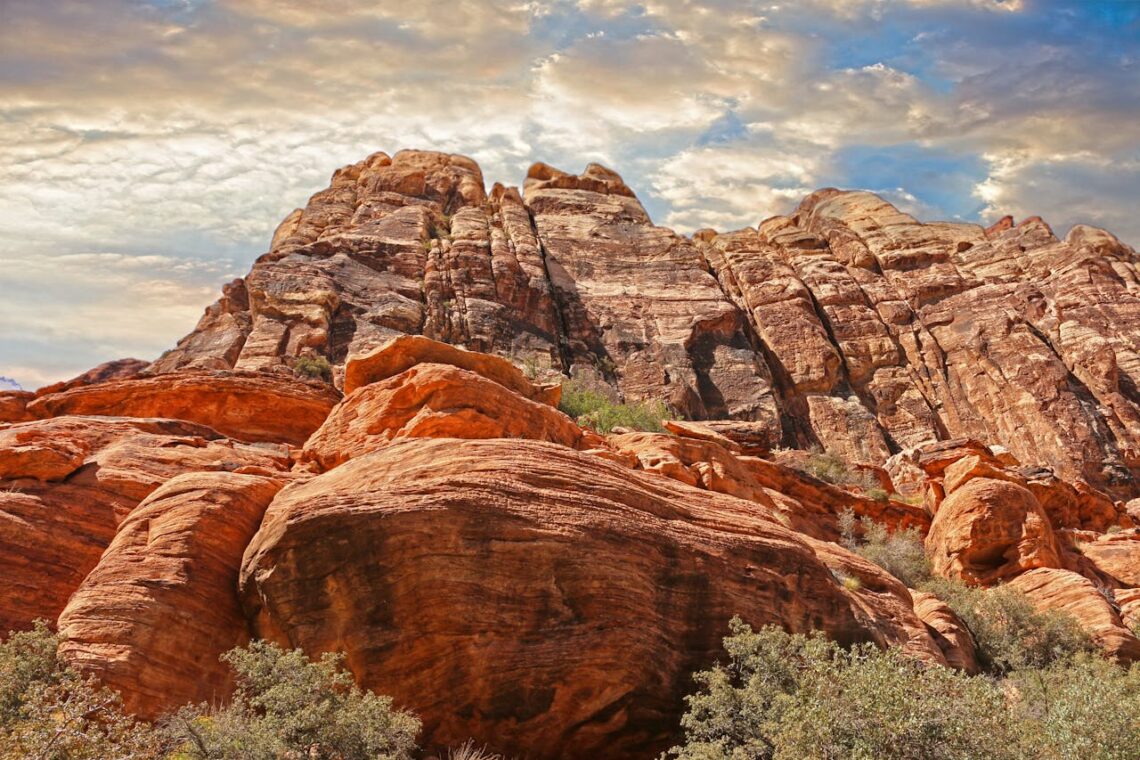
The Rocky Mountains: A dominant feature in the western United States, the Rocky Mountains stretch over 3,000 miles. From British Columbia in Canada to New Mexico in the south. Thus, this impressive mountain range has been a major source of water and natural resources. What’s more it has been providing sustenance to local residents for generations.
The Sierra Nevada Mountains: These iconic mountains have not only defined the topography of the west coast. But also played a significant role in the California Gold Rush. Attracting thousands in the 19th century.
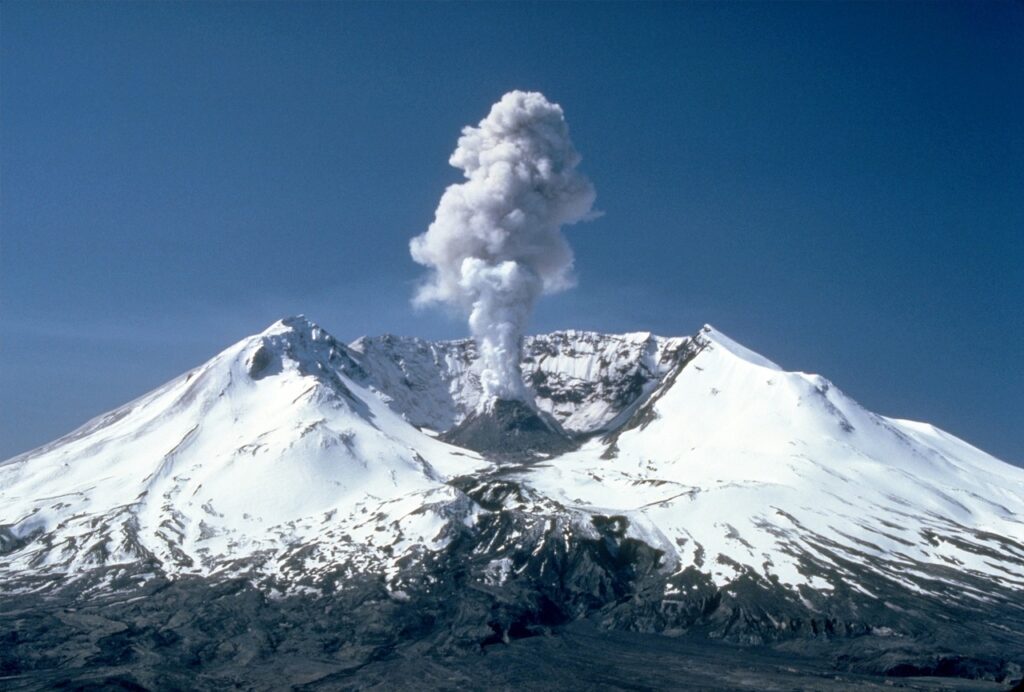
The Cascade Range: East of the Coast Ranges, this mountain range is among the most geologically active areas in North America. In fact, Mount St. Helens and Mount Rainier, part of the Cascade Range, have witnessed major volcanic eruptions, with the former erupting as recently as 1980.
Deserts and Valleys: The Dry Heartbeat of the West

The Mojave Desert: Spanning parts of California, Nevada, Utah, and Arizona, this desert is home to the famous Death Valley. The hottest and driest place in North America.
Interesting fact: The highest point in the contiguous U.S., Mount Whitney. And the lowest point, Death Valley, are less than 100 miles apart!
The Great Basin: Lying between the Rocky Mountains and the Sierra Nevada, this region comprises wide areas of salt flats, rugged mountain ranges, and the famous Salt Lake City.
The Sonoran Desert: Stretching from California to Arizona, this desert boasts unique flora and fauna and played a crucial role during the westward expansion. Thus, influencing major events like the Louisiana Purchase.
Waterways: The Lifelines of the West
The Mighty Mississippi: Serving as a natural boundary for the West, the Mississippi River has long been a major source of water, transportation, and commercial activities. Hence, its confluence with the Missouri River stands as a testament to the interconnectedness of the Western region with other parts of North America.
The Columbia River: Originating in British Columbia and flowing into the Pacific Ocean. This river has been central to the Pacific Northwest’s economy and culture.
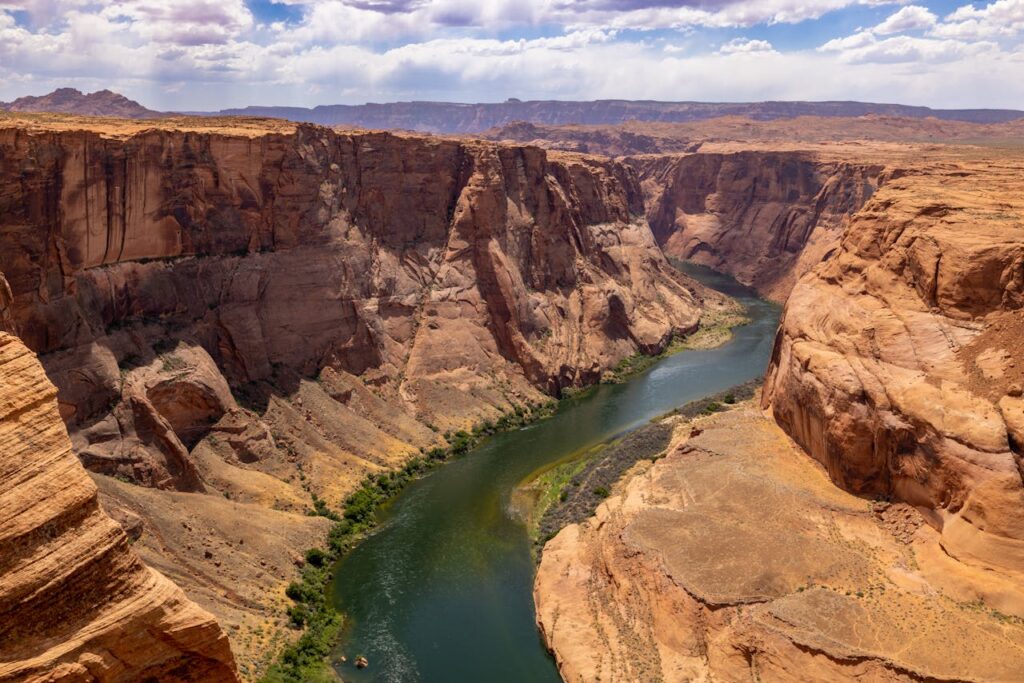
The Colorado River: Carving its way through the Grand Canyon, this river has been pivotal for both Native Americans and white settlers. Influencing trade, agriculture, and the very definition of the west.

FAQs about the West Region:
What defines the “west region” in terms of geography?
The “west region” of the United States is broadly defined by the U.S. Census Bureau and encompasses a vast area that includes the westernmost states of the United States. Also, this region is characterized by diverse landscapes ranging from the Pacific coastline to mountain ranges like the Rockies. Vast deserts like the Mojave and Sonoran, fertile plains, and significant river systems. The region stretches from the Pacific Ocean in the west to the Rocky Mountains in the east. And from the Canadian border in the north to the Mexican border in the south.
How has the Pacific Ocean influenced the culture of the West Coast?
The Pacific Ocean has played a significant role in shaping the culture of the west coast. Additionally, it has been a source of livelihood, recreation, and inspiration for the coastal communities. Also, the ocean has influenced culinary traditions, with seafood being a staple in the West Coast diet.
The coastal areas have also embraced a laid-back beach culture, promoting surfing, beach volleyball, and other ocean-centric activities. Additionally, the Pacific has facilitated trade and migration. Therefore, leading to diverse, multicultural communities that are a hallmark of the West Coast.
What role did San Francisco play in the gold rush era?
San Francisco was a pivotal city during the California Gold Rush, which began in 1848. With the discovery of gold at Sutter’s Mill, San Francisco rapidly transformed from a small settlement to a booming metropolis. Additionally, it became the primary port and gateway for thousands of gold seekers. Known as ’49ers, arriving from around the world.
The city’s population, economy, and infrastructure grew exponentially. Additionally, San Francisco became a melting pot of cultures as people from diverse backgrounds converged in the city. Hoping to strike it rich. The Gold Rush also led to significant commercial and banking establishments in San Francisco. Cementing its position as a major economic hub of the West.
How have national parks like Yellowstone contributed to the west region’s identity?
National parks like Yellowstone are emblematic of the West region’s majestic natural beauty and its commitment to conservation. But Yellowstone, the first national park in the world, established in 1872, showcases the region’s unique geothermal features, diverse wildlife, and pristine landscapes.
Indeed, such parks have been instrumental in promoting tourism, outdoor recreation, and environmental awareness. Moreover, they symbolize the West’s pioneering spirit in preserving natural wonders for future generations.
Thus, over the years, these parks have become deeply intertwined with the cultural and environmental identity of the West. Therefore, reminding residents and visitors alike of the profound beauty and fragility of the natural world.
Conclusion for this segment:
The Western region, with its diverse landscapes and rich history, is undeniably a treasure trove of stories, facts, and wonders. Thus, as we continue our exploration, we’ll delve deeper into its cultural nuances, major cities like San Francisco and Los Angeles. And the significant events that have shaped this iconic region.
Note: The aforementioned fact about Mount Whitney and Death Valley is sourced from the U.S. Geological Survey.
Urban Legends and Iconic Cities of the West

San Francisco: The Golden Gateway
Nestled by the Pacific Ocean and defined by its steep rolling hills, San Francisco remains one of the west region’s most iconic cities. What’s more, often heralded as the birthplace of the tech boom, Silicon Valley, located in its southern part, stands as a testament to innovation and entrepreneurship. Obviously, beyond technology, San Francisco offers a rich tapestry of history. Indeed, from the Gold Rush days at the bustling piers to the resilient spirit showcased after the devastating 1906 earthquake.
Los Angeles: The Starlit Dream
Firstly, Los Angeles, the second-largest city in the U.S., is not just about Hollywood and the motion-picture industry. While it’s undeniably the epicenter of global entertainment, the city is also steeped in culture. Such as the vibrant murals of East LA to the historic Olvera Street, reflecting its deep-rooted Mexican heritage. Moreover, the diverse population, including a significant number of Asian Americans, adds a unique flavor to this melting pot of cultures.
Las Vegas: The Desert Mirage
While traditionally known for its glitzy casinos and never-ending nightlife, Las Vegas has evolved over recent years. Still, beyond the Strip, the city boasts world-class museums, art districts, and a burgeoning local food scene. Moreover, its proximity to natural wonders, such as the Grand Canyon and the Mojave Desert, makes it a perfect blend of urban charm and natural beauty.
The Great Outdoors: National Parks and Protected Wonders
Yellowstone National Park: Nature’s Theater
Surprisingly, established in 1872 and managed by the National Park Service, Yellowstone is the U.S.’s first national park. Indeed, it’s home to the famous Old Faithful geyser and a plethora of wildlife, it remains a popular destination for nature lovers.
Interesting fact: Yellowstone sits atop one of the world’s largest active volcanic systems!
Death Valley: The Land of Extremes
Despite its ominous name, Death Valley offers stunning vistas, unique geological formations, and a rare glimpse into the resilience of life in extreme conditions. Managed by the National Park Service, it stands as a testament to the west region’s diverse topography.
Grand Canyon: The Majestic Rift
Carved by the Colorado River, the Grand Canyon is a breathtaking natural wonder that has inspired poets, artists, and travelers for generations. Also, its layered bands of red rock reveal millions of years of geological history. Thus, making it a living museum and a must-visit in the west region.
The Legacy of Exploration and Migration
The Oregon Trail: Pathway to the West
Firstly, one of the most significant migration routes in American history, the Oregon Trail, saw over 400,000 settlers, miners, and traders traverse from the Midwest to the western United States. In fact, starting near the Missouri River, this 2,000-mile-long route was instrumental in the westward expansion. And the subsequent development of cities like Portland and Salt Lake City.
The California Gold Rush: The Lure of Fortune
Post the 1848 discovery of gold at Sutter’s Mill, thousands flocked to California, dreaming of riches. Moreover, this massive migration, often fraught with perils and challenges, indelibly shaped the state’s demographic, economic, and cultural landscape. Towns sprang up overnight, and San Francisco, in particular, experienced a population explosion.

FAQs about the West Region’s Cities and Parks:
How has the Pacific Northwest, including places like Seattle, contributed to the West region’s identity?
The Pacific Northwest, with cities like Seattle at its heart, has played a pivotal role in defining the west region’s identity. This area is known for its lush landscapes, innovative tech industries, vibrant arts scenes, and rich indigenous cultures.
Seattle, in particular, has been a hub for music. Birthing the grunge movement in the 1990s with bands like Nirvana and Pearl Jam. The city is also home to tech giants like Microsoft and Amazon. Solidifying the region’s reputation as a nexus of technology and innovation.
Additionally, the Pacific Northwest’s emphasis on sustainability, its coffee culture epitomized by brands like Starbucks. And its unique blend of urban and natural beauty have significantly contributed to the broader identity of the West.
What are some lesser-known national parks in the West that are worth visiting?
While parks like Yellowstone and the Grand Canyon often steal the limelight, the western region boasts several hidden gems that deserve attention:
Great Basin National Park, Nevada: Known for its ancient bristlecone pines, vast caves, and starlit skies, this park offers a serene desert landscape.
Lassen Volcanic National Park, California: A geothermal wonderland with boiling springs, fumaroles, and an active volcano.
Channel Islands National Park, California: A collection of five rugged islands that offer a glimpse into the rich biodiversity and archaeological resources.
North Cascades National Park, Washington: Often referred to as the “American Alps,” it features stunning mountain vistas, glaciers, and azure lakes.
Black Canyon of Gunnison, Colorado: Known for its steep, dramatic canyons and the Gunnison River, this park is a haven for rock climbing and scenic drives.
How has the motion-picture industry in Los Angeles influenced global cinema?
The motion picture industry in Los Angeles, centered in Hollywood, has had a profound impact on global cinema. Hollywood has set industry standards, popularized genres, and introduced groundbreaking storytelling and technical methodologies.
Over the decades, films produced in Hollywood have reached global audiences, shaping perceptions, influencing cultures, and promoting cross-cultural understanding. The Oscars, hosted by the Academy of Motion Picture Arts and Sciences based in LA, is a testament to the city’s significance. As it’s one of the most prestigious and internationally recognized film awards.
Furthermore, Los Angeles has been a hub for film schools, attracting budding filmmakers from around the world. Fostering innovation, and ensuring the legacy of global cinematic influence continues.

Conclusion for this segment:
The cities and natural wonders of the western region, each with its unique story and charm, together paint a vivid picture of a land of dreams, challenges, and breathtaking beauty. As we journey further, we will uncover more about the native communities. The impact of the West on popular culture, and the ongoing evolution of this vibrant region.
Native Roots: The Indigenous Cultures of the West Region
The First Settlers: Native American Tribes
Before the waves of explorers and settlers, the western region was home to numerous Native American tribes. These communities, with their rich traditions and deep-rooted histories, have played a crucial role in shaping the identity of the region. From the Navajo in the Great Plains to the Haida in the Pacific Northwest. Their stories are integral to the fabric of the West.
Impact of European Exploration
The Lewis and Clark Expedition, also known as the Corps of Discovery Expedition, was a transformative journey that had significant implications for Native Americans. Their interactions, sometimes friendly and at times conflict-ridden. With tribes like the Shoshone and the Nez Perce, paved the way for subsequent settlers. Moreover, events such as the Louisiana Purchase expanded European-American territories, often at the expense of Native American lands.
Modern Forms of Recognition
In recent years, there has been a concerted effort to recognize and respect the contributions and rights of Native Americans. From federal land rights to cultural preservation initiatives, the journey towards justice, while ongoing, has seen notable milestones. Notably, the establishment of Native American Heritage Month has helped bring their stories to the forefront.
The West and Popular Culture
The Wild West: More Than Just a Legend
The term “Wild West” conjures up images of cowboys, cattle drives, outlaws, and gunfights. While these stories have been romanticized in movies and literature, they are rooted in the real challenges and adventures of the 19th-century West region. The cattle drive, for instance, was an economic necessity before the advent of railroads. Shaping places like Texas and the Great Plains.
Hollywood: The West’s Gift to the World
Los Angeles, specifically Hollywood, has been instrumental in broadcasting the myths, tales, and truths of the West to a global audience. The motion-picture industry, with its captivating storytelling, has turned regional narratives into worldwide sensations.
Music and Art: Echoes of the West’s Soul
Genres like Country and Western, inspired by the landscapes and stories of the West, have touched hearts globally. Additionally, artists and writers, captivated by the West’s beauty and complexity, have contributed significantly to global arts. Offering perspectives ranging from the Gold Rush days to modern urban challenges.
Environmental Challenges and Conservation Efforts
The Delicate Balance of Natural Resources
The western region, rich in natural resources, faces challenges related to conservation and utilization. Places like the Mojave Desert, while appearing barren, house delicate ecosystems that can be easily disrupted. Similarly, the Colorado River, a lifeline for many states, has seen debates over water rights and usage.
National Issue: Conservation vs. Commercial Activities
National parks and protected areas in the west region, managed by the National Park Service, often find themselves at the crossroads of conservation and commercial interests. Places like Yellowstone have seen debates on wildlife management. While areas rich in minerals face the pressures of mining and drilling.
Modern Initiatives for a Sustainable West
Acknowledging these challenges, there have been efforts both at the federal government level and among local communities to ensure a sustainable future for the west. From green energy projects to eco-tourism, the shift towards sustainability is palpable.
FAQs about the Culture and Environment of the West Region:

How are modern Western cities addressing environmental challenges?
Modern Western cities are at the forefront of implementing sustainable and environmentally-friendly practices. Some measures include:
Renewable Energy: Cities like Portland and San Francisco are increasing their use of renewable energy sources. Such as solar and wind, to reduce carbon footprints.
Water Conservation: Given the drought challenges, cities like Los Angeles have introduced strict water usage regulations. And promote xeriscaping — landscaping with drought-resistant plants.
Public Transportation: Many cities, such as Seattle, have invested in expanding and modernizing public transportation systems to reduce car emissions.
Waste Management: Cities are emphasizing recycling, composting, and waste reduction programs to minimize landfill usage.
Green Building Standards: There’s a push for new constructions to adhere to green building standards. Ensuring energy efficiency and reduced environmental impact.
What roles have Asian Americans played in the West’s cultural landscape?
Asian Americans have had a significant influence on the West’s cultural landscape, given the region’s history of Asian immigration:
Culinary Influence: Asian American communities have introduced and popularized many Asian cuisines. From Chinese and Japanese to Filipino and Vietnamese, enriching the west’s culinary scene.
Arts & Entertainment: Asian American artists, filmmakers, and musicians have contributed immensely to the region’s arts scene, bringing unique perspectives and narratives.
Technology: Many Asian Americans have played crucial roles in the tech industry. Especially in places like Silicon Valley, driving innovation and establishing startups.
Cultural Festivals: Events like San Francisco’s Chinese New Year Parade or Los Angeles’s Nisei Week showcase the blend of traditional Asian cultures with American influences.
Social Activism: Asian Americans in the West have been active in advocating for civil rights, social justice, and community development, shaping the broader social landscape.
Are there contemporary movies or books that accurately depict the West’s history and challenges?
The West Region Movies:
There Will Be Blood portrays the early 20th-century oil boom in California.
Brokeback Mountain provides a poignant look into the lives of two cowboys. Challenging the stereotypical views of masculinity and life in the American West.
The Joy Luck Club, based on the novel by Amy Tan, delves into the experiences of Chinese-American women in San Francisco.
The West Region Books:
The Overstory by Richard Powers touches on the environmental and conservation challenges faced by the Pacific Northwest. Particularly regarding its old-growth forests.
Where the Crawdads Sing by Delia Owens, while set in the marshes of North Carolina, echoes many environmental and social themes relevant to the west.
The Great Alone by Kristin Hannah provides insights into the challenging and isolating beauty of Alaska’s wilderness.
Both mediums have a rich tapestry of works that capture various facets of the West’s history. Its evolving identity, and the challenges it grapples with.
Conclusion for this segment:
The Western region, while often seen through the lens of its stunning landscapes and iconic cities, has a depth that goes beyond the obvious. Its indigenous roots, cultural contributions, and the environmental challenges it faces make it a microcosm of broader global issues. As we journey ahead, we’ll delve into the economic dimensions, technological innovations, and the future aspirations of this ever-evolving region.
Economic Powerhouses: The West’s Contribution to Growth

Silicon Valley: The Tech Capital
Nestled in the heart of California, Silicon Valley stands as a beacon of innovation and technological advancement. Home to global giants like Google, Apple, and Facebook, this hub has transformed the digital landscape. Making the West region pivotal in the 21st-century economy. Interestingly, this area, now synonymous with startups and venture capital, started its journey with the silicon-based integrated circuits, giving it its iconic name.
Los Angeles and The Entertainment Industry
Beyond its cultural significance, Los Angeles’ entertainment industry is a massive economic contributor. With film studios, music production houses, and television networks, it offers employment to thousands and generates significant revenue, further underscoring the economic importance of the Western region.
The Agriculture Backbone: From Wheat Belt to Vineyards
Despite its urban centers and tech hubs, vast stretches of the western region remain agrarian. The Great Plains, often referred to as the Wheat Belt, are pivotal for grain production. Meanwhile, regions like Napa Valley in California are globally renowned for their exquisite wines, highlighting the West’s agricultural diversity.
The Natural Wonders: Tourism and its Economic Impact
Attracting Global Tourists
Places like the Grand Canyon, Mount Rainier, and the Pacific Coast make the west region a popular destination for tourists from across the globe. This influx not only adds to the region’s cultural richness but also significantly boosts its economy. National parks, in particular, managed by the National Park Service, have seen a steady increase in visitors, leading to both opportunities and challenges.
Ski Resorts and Mountain Getaways
The Rocky Mountains, with their majestic peaks, offer more than just scenic beauty. Towns like Aspen and Vail have become synonymous with winter sports, drawing in enthusiasts and contributing to the tourism-driven economy.
Looking Ahead: The Future of the West Region
Rising Urban Centers: Beyond LA and San Francisco
Cities like Seattle, home to tech behemoth Amazon, and San Diego, with its biotech hub, are emerging as new economic powerhouses. These cities, while retaining their unique identities, are evolving rapidly, promising a vibrant future for the West region.
Addressing Environmental Concerns
With increasing urbanization and industrial growth, the West region faces environmental challenges. However, there’s a growing consciousness about sustainable development. Investments in renewable energy sources, water conservation efforts in places like Salt Lake City, and initiatives to protect natural habitats signify a promising way forward.
Embracing Cultural Diversity
The West region, historically a melting pot of cultures, continues to welcome people from all over the world. This influx promises not only economic growth but also a rich tapestry of cultural experiences, further solidifying the west’s position as a global hub.
FAQs about the West Region’s Economy and Future:

How are small towns in the West adapting to the globalized economy?
Small towns in the West have been implementing several strategies to adapt to the globalized economy:
Diversification: Many towns that rely on single industries, such as mining or agriculture, are diversifying their economies, often promoting tourism or local arts and crafts.
Digital Transition: Several towns are investing in broadband infrastructure to support online businesses and remote work, making them attractive to professionals who wish to live in smaller communities.
Educational Initiatives: Partnering with local colleges or online education platforms to offer residents training in new skills to compete in the global market.
Local Entrepreneurship: Encouraging local startups and businesses through incentives, grants, and resources, aiming to keep wealth within the community.
Agricultural Shift: Some agricultural towns are shifting to organic farming or specialty crops that cater to global tastes and demands.
With Silicon Valley’s dominance, what are the prospects for tech startups in other parts of the West?
While Silicon Valley remains a hub for tech innovation, other parts of the West are emerging as promising destinations for tech startups:
Regional Hubs: Cities like Seattle (home to Amazon and Microsoft), Portland, Denver, and Salt Lake City are becoming recognized tech hubs, offering a blend of skilled labor, infrastructure, and lower living costs compared to Silicon Valley.
Incentives and Support: Many states and cities offer tax incentives, grants, and incubator programs to attract startups and tech companies.
Quality of Life: Some regions, particularly in the Pacific Northwest, are marketing their quality of life, natural beauty, and recreational opportunities to attract tech professionals and entrepreneurs.
Educational Institutions: Cities with major universities, such as Boulder (University of Colorado) or Austin (University of Texas), are fostering innovation ecosystems by bridging academia, industry, and entrepreneurship.
How is the West region addressing the challenges of climate change?
The western region, facing tangible threats from climate change, such as wildfires, droughts, and rising sea levels, is taking proactive measures:
Renewable Energy Transition: Many states are pushing for a transition from fossil fuels to renewable energy sources, such as wind, solar, and hydroelectric power, to reduce carbon emissions.
Water Conservation: Given the West’s susceptibility to droughts, states are implementing stringent water conservation measures, from regulating agriculture to encouraging residential conservation practices.
Forest Management: In response to the increasing frequency and intensity of wildfires, there are concerted efforts to manage forests better, including controlled burns and clearing of dry vegetation.
Infrastructure Improvements: Cities along the coast, like San Francisco and San Diego, are investing in infrastructure to mitigate the effects of rising sea levels, such as seawalls and improved drainage systems.
Research and Innovation: In fact, many Western universities and research institutions are at the forefront of studying climate change and developing solutions, from drought-resistant crops to innovative water desalination techniques.
Conclusion for this segment:
The Western region’s economic contributions, from tech innovations to its agrarian roots, underscore its multifaceted identity. As we peer into the future, it’s evident that while challenges exist, the spirit of innovation, the richness of its natural resources, and the diversity of its people position the West for continued growth and evolution. So as we conclude this exploration, we will reflect on the west’s indomitable spirit, its lessons for the world, and its enduring allure.
Next read my 24 Interesting Facts About Alaska: Unveiling the Great Land
A Reflection on the West’s Indomitable Spirit

Embracing Change While Honoring the Past
Of course, the Western region’s history is a tapestry of change. From the times of the native populations to the influx of settlers during the California Gold Rush, and now to its transformation into a tech and cultural powerhouse, the West has always been in flux. Yet, it has managed to honor its roots, whether it’s in the preservation of historic trails like the Oregon Trail or in the homage paid to its indigenous cultures.
Lessons in Resilience
From the major volcanic eruption of Mount St. Helens to the challenges faced by local residents in desert areas, the West has showcased resilience. Hence, this is evident in the rebuilding efforts after natural calamities and in the community-driven initiatives to address water scarcity in areas like the Mojave Desert. Indeed, the region teaches us that with community, adaptability, and respect for nature, challenges can be overcome.
The West Region Fun Facts: Adding Color to the West’s Landscape
- Highest and Lowest: The west region boasts both the highest point in the contiguous U.S., Mount Whitney, and the lowest, Death Valley.
- Cinema’s Birthplace: The motion picture industry began its global journey from the lanes of Hollywood, making Los Angeles the movie capital of the world.
- Geological Wonders: The west has some of the most geologically active areas in North America, from the bubbling geysers of Yellowstone National Park to the dormant volcanoes of the Cascade Range.
- Diverse Population: Asian Americans, especially in cities like San Francisco and Los Angeles, have made significant contributions, from tech innovations to culinary delights.
The West’s Message to the World
Unity in Diversity
Obviously, the west region, with its mix of terrains, from the Pacific Ocean shores to the mountain ranges and the Great Plains, mirrors its diverse population. Therefore this blend of cultures, backgrounds, and histories creates a message of unity, showcasing that differences can coexist harmoniously.
Innovation with Empathy
Silicon Valley’s tech innovations and Hollywood’s storytelling prowess have global implications. But these advancements are coupled with an understanding of responsibilities, whether it’s in sustainable practices or in the portrayal of diverse narratives.
Read next: Astonishing Facts About Mt. Rushmore (The Best 53)
FAQs about the West’s Spirit and Contributions:
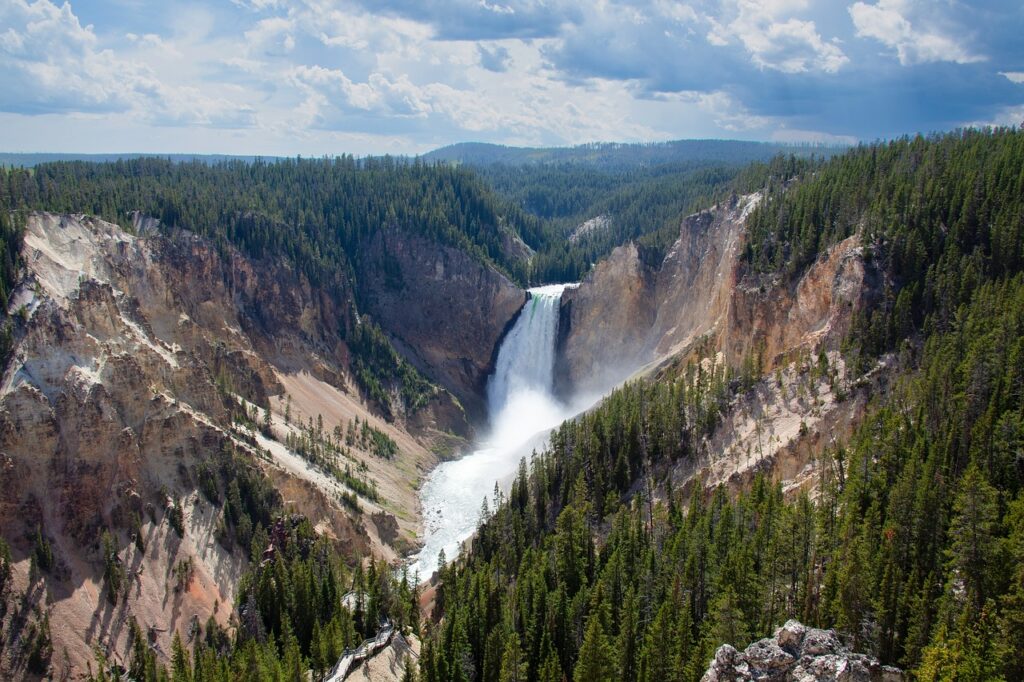

How do national parks like Yellowstone contribute to the West’s identity?
Yellowstone, along with other national parks, contributes profoundly to the West’s identity by:
Natural Beauty & Conservation: These parks represent the rugged and diverse landscapes of the West, from geysers and canyons to vast forests, showcasing a commitment to conservation and appreciation of untouched nature.
Cultural Significance: National parks, with their rich indigenous histories and tales of pioneers and explorers, embody the spirit of the American West. They stand as symbols of adventure, exploration, and resilience.
Tourism & Economy: Drawing millions of visitors annually, parks like Yellowstone have spurred tourism-based economies, helping surrounding communities thrive.
Educational Value: These parks serve as living classrooms, educating visitors about geology, ecology, and history, reinforcing the West’s role as a custodian of natural wonders and cultural stories.
What role have the Mississippi and Missouri rivers played in shaping the west’s history?
The Mississippi and Missouri rivers have been pivotal in the west’s development:
Trade & Transportation: Historically, these rivers served as major trade routes, enabling the movement of goods, people, and ideas. They significantly impacted the region’s economic growth.
Settlement & Expansion: As gateways to the west, the rivers guided pioneers and settlers in their westward journeys, leading to the establishment of numerous towns and cities along their banks.
Agriculture: The fertile lands around these rivers have been crucial for agriculture, making the region the country’s breadbasket.
Cultural Influence: These rivers have inspired countless stories, songs, and artworks, embedding themselves deeply into the cultural fabric of the West and the nation at large.
How have cities like Las Vegas, known for entertainment, diversified their economies in recent years?
Las Vegas, traditionally synonymous with casinos and entertainment, has been diversifying its economy:
Tech & Startups: The city is actively courting tech companies and startups with tax incentives and the promise of a lower cost of living than traditional tech hubs.
Conventions & Business Tourism: Beyond leisure tourism, Las Vegas has positioned itself as a premier destination for conventions, trade shows, and business meetings.
Education & Research: Institutions like the University of Nevada, Las Vegas (UNLV) are driving research and offering educational opportunities, drawing students and professionals.
Health & Medical Tourism: With state-of-the-art facilities, Las Vegas is venturing into health and medical tourism, offering high-quality care and treatments.
Real Estate & Residential Development: With its appeal as a city with ample amenities and comparatively lower housing costs, many people are choosing to relocate to Las Vegas, spurring real estate growth and community development.
Sports & Recreation: The city has expanded into the sports arena, with teams like the Las Vegas Raiders (NFL) and the Vegas Golden Knights (NHL) calling it home, drawing sports enthusiasts and contributing to a diversified local economy.

The West Region Concluding Thoughts
The western region of the United States stands as a testament to the human spirit’s capacity for growth, adaptation, and reverence for its surroundings. From its majestic Rocky Mountains to its bustling cities, it’s a land of contrasts, yet it weaves a singular story. A story of exploration, of dreams realized, of challenges met, and of looking to the horizon with hope.
Whether you’re drawn to the West for its tales from the Wild West, its technological marvels, or its natural wonders, there’s one thing certain – it promises an experience like no other. Subsequently, as we reflect on the “facts about the west region,” it becomes clear that this region is not just a geographical entity; it’s an embodiment of the American experience, one that continues to inspire and beckon.
I hope that you found this article The West Region interesting? If so please share it with your friends or on Social Media, Thank you.
Looking for another interesting read? the try this article: The Best 25 Interesting Facts About Georgia Colony




One Comment
Pingback: