55 Fascinating Facts About Rome: Secrets of the Eternal City
Facts About Rome
Rome, often referred to as the Eternal City, is a place where history breathes from every corner. This magnificent city, with its rich tapestry of ancient ruins and modern life, offers a fascinating journey through time. Whether you’re a history enthusiast, a traveler planning your first trip, or simply curious, there are countless facts about Rome that will captivate your imagination. From the grandeur of the Roman Empire to the daily lives of ancient Romans, let’s delve into the most interesting facts about this historic city.
Facts About Rome, The Foundation of Rome
The Mythical Origins
According to Roman mythology, the city of Rome was founded by Romulus and Remus, twin brothers raised by a she-wolf. This tale of the first rulers of Rome is one of the most enduring legends from ancient times.
The Real Foundation
Historically, the city of Rome is believed to have been founded in 753 BC. Situated along the Tiber River, the city quickly grew to become one of the most powerful and influential cities in the ancient world.
Palatine Hill: Where It All Began
The Palatine Hill is considered the birthplace of Rome. Archaeological evidence suggests that this area was inhabited as early as the 10th century BC. Today, visitors can explore the ancient ruins that tell the story of Rome’s early days.
Facts About Rome, The Roman Empire: A Glorious Past

The Expansion Across Continents
At its height, the Roman Empire spanned three different continents: Europe, Asia, and Africa. This vast empire included a diverse array of cultures and languages, all united under Roman rule.
The Power of the Roman Army
The Roman army was known for its discipline, innovative tactics, and engineering prowess. Roman soldiers played a crucial role in expanding and maintaining the empire’s borders. The legacy of the Roman military can still be seen in the remains of fortifications and roads across Europe.
Ancient Romans and Their Innovations
Ancient Romans were pioneers in many fields, from engineering to public health. They developed aqueducts, which supplied water to cities, and public baths, which were centers of social life. The invention of central heating, known as the hypocaust system, showcased their advanced understanding of engineering and comfort.
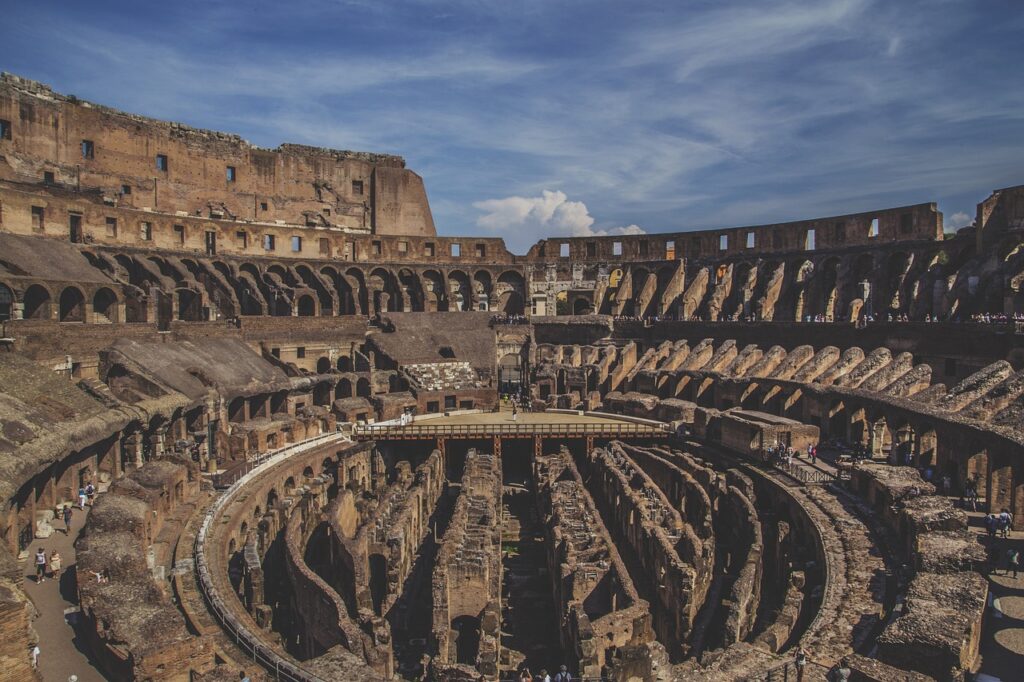
The Grandeur of the Colosseum
The Roman Colosseum, the largest amphitheater ever built, is one of the most iconic symbols of ancient Rome. It hosted gladiator fights, naval battles, and other public spectacles. Despite being damaged by earthquakes and stone robbers, it remains a testament to Roman architectural ingenuity.
Cultural Landmarks: Then and Now
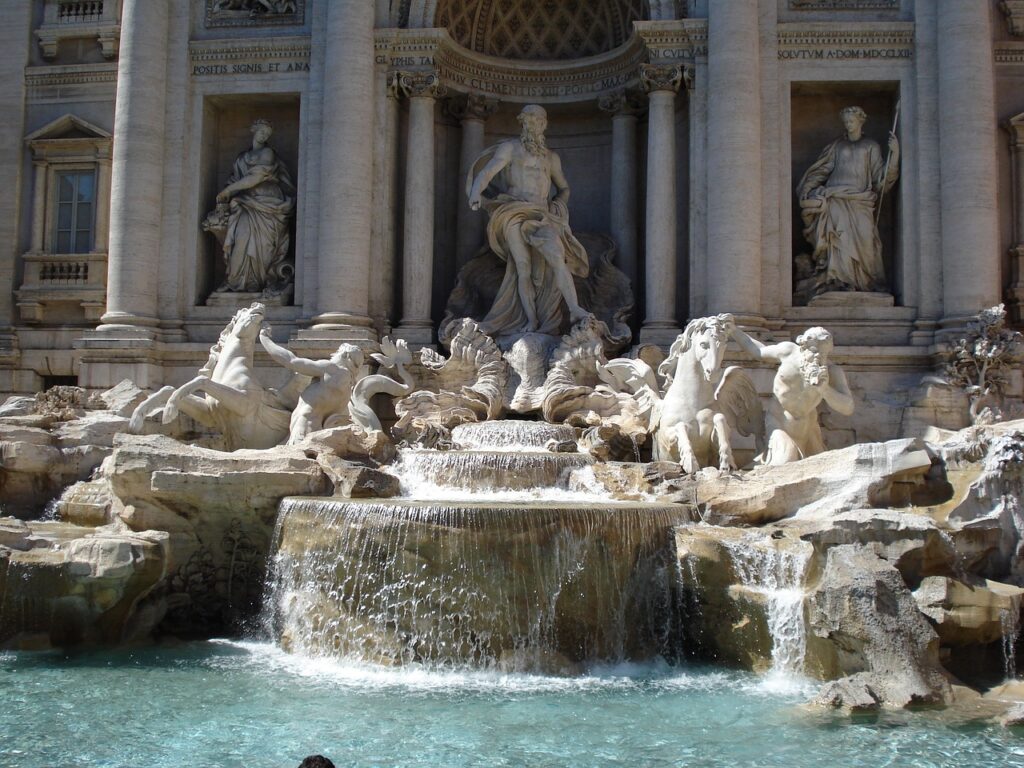

Trevi Fountain: A Baroque Masterpiece
One of the most visited sites in Rome, the Trevi Fountain, is a stunning example of Baroque art. According to popular belief, tossing a coin into the fountain ensures a return to the Eternal City. The tradition attracts millions of visitors each year.
Vatican City: The Heart of Catholicism
An independent country within the city of Rome, Vatican City is the spiritual and administrative center of the Roman Catholic Church. St. Peter’s Basilica and the Sistine Chapel, with its famous ceiling painted by Michelangelo, are must-visit landmarks.
Piazza Navona: From Stadium to Square
Piazza Navona, originally the site of the Stadium of Domitian, is now a vibrant square known for its beautiful fountains and lively atmosphere. It epitomizes Rome’s ability to blend ancient history with modern life.
The Spanish Steps: A Link Between Cultures
The Spanish Steps, connecting the Piazza di Spagna with the Trinità dei Monti church, are a popular meeting spot for both locals and tourists. The steps are named after the nearby Spanish Embassy, symbolizing Rome’s international influence throughout history.
Facts About Rome: Conclusion
Exploring the facts about Rome reveals a city that is much more than its ancient ruins. It is a place where history and modernity coexist, offering endless opportunities for discovery. The city of Rome, with its timeless appeal, continues to enchant visitors from around the world.
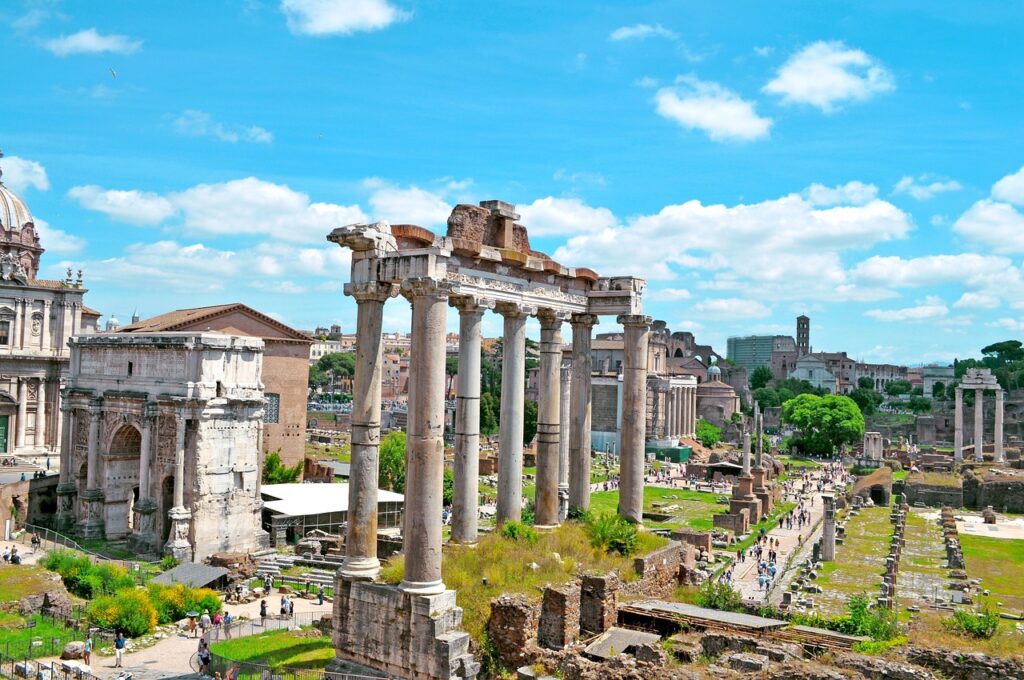

Ancient Rome: A Civilization of Firsts
The First City to Reach a Million Residents
Ancient Rome was the first city in the world to reach a population of one million people. This remarkable achievement underscores the city’s importance as a center of commerce, politics, and culture during ancient times.
Trajan’s Market: The First Shopping Mall
Considered by many to be the world’s first shopping mall, Trajan’s Market was a large complex of shops and offices built during Emperor Trajan’s reign. This architectural marvel showcased the advanced urban planning and commercial sophistication of ancient Rome.
Innovations in Public Infrastructure
Roman society was known for its groundbreaking infrastructure. The extensive network of Roman roads, many of which are still in use today, connected the vast empire. Additionally, the Appian Way, one of the earliest and most important Roman roads, exemplified the engineering prowess of the ancient Romans.
Lesser-Known Facts About Rome
Underground Tunnels: The Hidden City
Beneath the bustling streets of Rome lies a network of underground tunnels and catacombs. These tunnels were used for various purposes, including as burial sites and secret passageways during times of conflict.
The Secret Passage: Passetto di Borgo
The Passetto di Borgo is a hidden passage connecting Vatican City to Castel Sant’Angelo. This secret passage was used by popes to escape danger during sieges and conflicts, highlighting the turbulent history of the city.
Exotic Animals and Gladiator Games
The ancient Roman Colosseum hosted many spectacular events, including gladiator fights and mock naval battles. Exotic animals, such as lions and elephants, were imported from different continents and used in these grand spectacles. These events were not only entertainment but also a demonstration of the empire’s wealth and power.
Flamingo Tongues: A Roman Delicacy
In ancient Roman society, flamingo tongues were considered a delicacy. This unusual food preference reflects the opulence and extravagance of Roman banquets. It’s not just pizzas in Italy.
Public Baths: Centers of Social Life
Public baths were an integral part of daily life in ancient Rome. These baths, such as the Baths of Caracalla, were not only places for bathing but also social and recreational centers. They featured amenities like swimming pools, saunas, and exercise areas, showcasing the Romans’ emphasis on public health and social interaction.
The Eternal City’s Iconic Landmarks
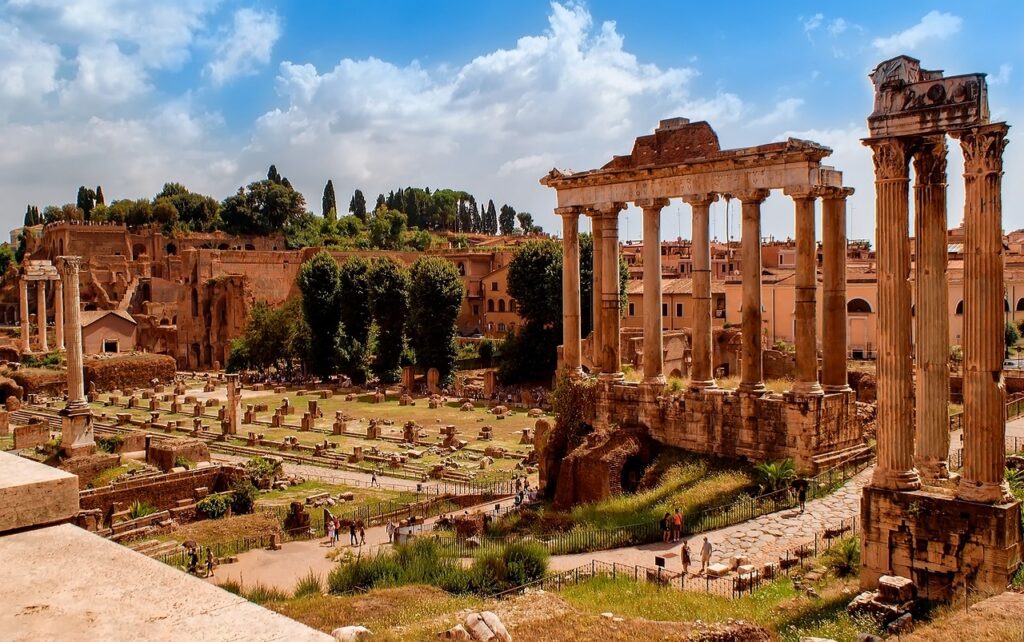

The Roman Forum: Heart of Ancient Rome
Importantly the Roman Forum was the center of public life in ancient Rome. This bustling marketplace and civic center were surrounded by important government buildings, temples, and monuments. Today, the ruins of the forum provide a glimpse into the grandeur of ancient Roman civilization.
The Capitoline Hill: Political and Religious Hub
One of the Seven Hills of Rome, Capitoline Hill was the political and religious heart of the city. It housed significant buildings like the Temple of Jupiter and the Capitoline Museums, which now hold an extensive collection of ancient artifacts.
Circus Maximus: The Great Arena
The Circus Maximus was a massive arena used for chariot races and other public events. Capable of seating over 150,000 spectators, it was one of the largest entertainment venues in the ancient world. Its sheer size and the excitement of the races made it a central part of Roman culture.
Rome’s Influence Through the Ages
The Middle Ages: Transformation and Continuity
During the Middle Ages, Rome underwent significant changes while retaining its importance as a religious and cultural center. The city’s transformation included the construction of medieval churches and the fortification of ancient structures.
The Renaissance: A Rebirth of Art and Culture
The Renaissance period saw a revival of art, architecture, and culture in Rome. Artists like Michelangelo and Raphael left their mark on the city with masterpieces such as the Sistine Chapel and the frescoes in the Vatican. This era of rebirth solidified Rome’s status as a cultural capital.
The 19th Century: Modernization and Preservation
In the 19th century, Rome underwent modernization efforts while preserving its rich historical heritage. The unification of Italy and the designation of Rome as the capital city of Italy brought new infrastructure and development, blending the old with the new.
Fun Facts About Rome
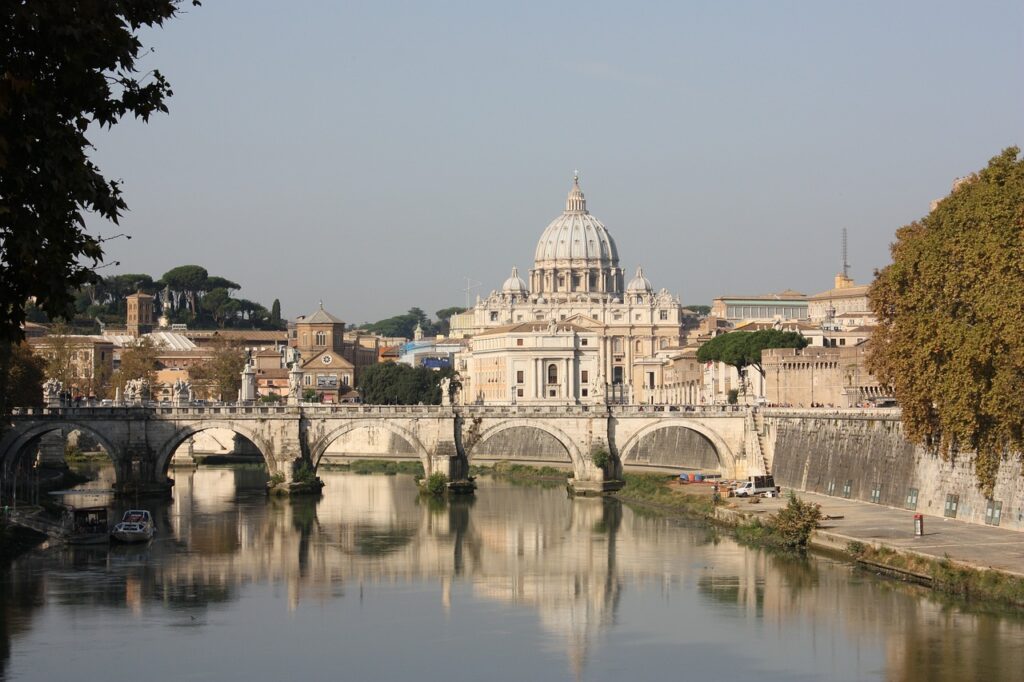

The Tiber River: Lifeline of Rome
Indeed the Tiber River has been the lifeline of Rome since its founding. This river provided water, transportation, and a means of defense, playing a crucial role in the city’s growth and development.
Piazza di Spagna: The Spanish Steps
The Spanish Steps, located at Piazza di Spagna, are a popular tourist attraction. These steps connect the Spanish Embassy with the Trinità dei Monti church and offer a picturesque spot for visitors to relax and enjoy the city’s ambiance.
The Trevi Fountain: A Wish Come True
Tossing a coin into the Trevi Fountain is believed to ensure a return to Rome. This tradition has made the fountain one of the most beloved and visited landmarks in the city.
Cat Lovers’ Paradise
Rome is known for its large population of stray cats. The cats are protected by law and can often be seen lounging among the ancient ruins, adding to the city’s unique charm.
Fascinating Historical Figures of Rome
Emperor Nero: A Controversial Ruler
Emperor Nero is one of the most infamous figures in the history of Rome. Known for his tyrannical rule and extravagant lifestyle, Nero’s reign is often remembered for the Great Fire of Rome, which he reportedly watched while playing his lyre. Despite his negative reputation, Nero’s rule also saw significant cultural contributions, including the construction of the Domus Aurea, a grand palace.
Julius Caesar: A Pivotal Leader
Julius Caesar, a military general and statesman, played a critical role in the demise of the Roman Republic and the rise of the Roman Empire. His conquest of Gaul and subsequent civil war paved the way for his dictatorship. The site of his assassination, the Largo di Torre Argentina, is now a historical landmark and a sanctuary for cats.
Emperor Hadrian: The Builder
Emperor Hadrian is celebrated for his architectural achievements, including the construction of Hadrian’s Wall in Britain and the rebuilding of the Pantheon. His reign marked a period of relative peace and prosperity within the empire.
Emperor Domitian: The Master Planner
Emperor Domitian significantly contributed to the urban development of Rome. His ambitious building projects included the renovation of the Circus Maximus and the construction of the Stadium of Domitian, which is now Piazza Navona. Domitian’s reign left a lasting impact on the architectural landscape of the city.
Rome’s Architectural Wonders
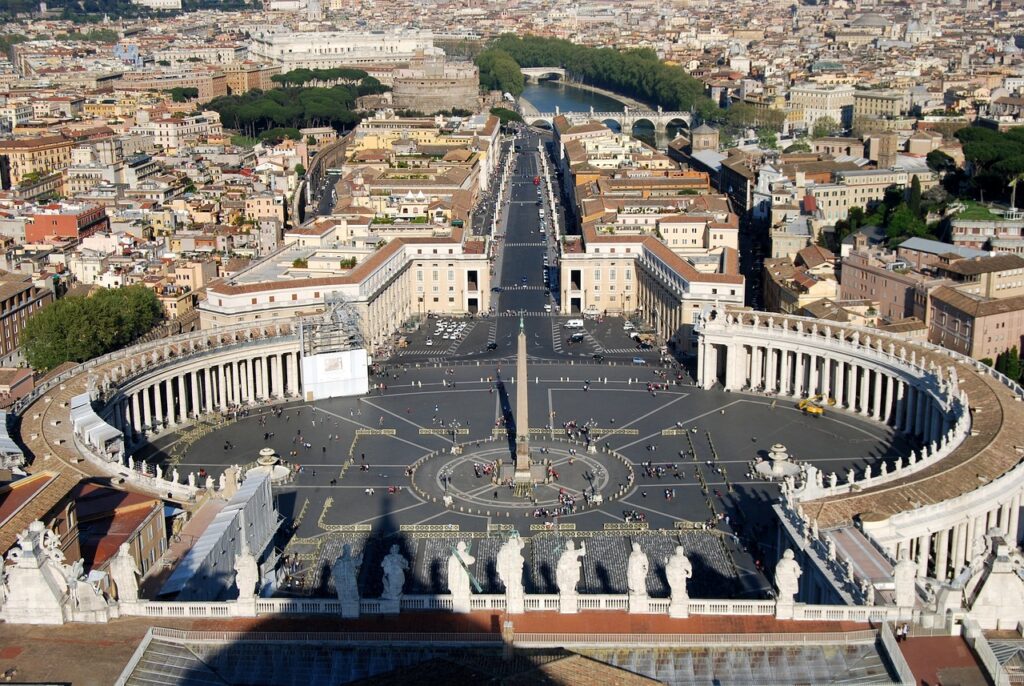

The Vatican: Center of the Catholic Church
The Vatican City, an independent country within Rome, is the epicenter of the Catholic Church. St. Peter’s Basilica, the largest church in the world, stands as a testament to the architectural genius of the Renaissance. The Sistine Chapel, with its ceiling painted by Michelangelo, is a masterpiece that attracts millions of visitors each year.
Castel Sant’Angelo: From Mausoleum to Fortress
Originally built as a mausoleum for Emperor Hadrian, Castel Sant’Angelo has served various purposes throughout history. It was later transformed into a fortress and a papal residence. Today, it is a museum that offers panoramic views of the city.
The Pantheon: A Temple for All Gods
The Pantheon, originally constructed as a temple for all Roman gods, is one of the best-preserved ancient buildings in Rome. Its massive dome, with a central oculus that lets in natural light, is an architectural marvel that continues to inspire awe.
The Roman Colosseum: An Icon of Rome
The Colosseum, also known as the Flavian Amphitheatre, is a symbol of Rome’s grandeur. This colossal structure hosted gladiator fights, public spectacles, and even mock naval battles. Despite the damage it has sustained over centuries, the Colosseum remains a powerful reminder of Rome’s imperial past.
The Everyday Life of Ancient Romans
Public Urinals and Toilet Paper
Ancient Rome was surprisingly advanced in terms of public hygiene. Public urinals were a common sight, and the Romans used sponges on sticks as an early form of toilet paper. These practices reflect the importance of cleanliness in Roman society.
Public Baths: More Than Just Hygiene
Public baths, or thermae, were an essential part of daily life in ancient Rome. These baths were not only places to bathe but also social hubs where people could exercise, relax, and conduct business. The Baths of Caracalla, one of the largest and most luxurious baths, still stand as a testament to this aspect of Roman culture.
The Roman Gladiators: Heroes and Entertainers
Gladiator fights were among the most popular forms of entertainment in ancient Rome. These warriors, who often fought to the death, were admired for their bravery and combat skills. While some gladiators were slaves, others were free men who volunteered for the fame and fortune that came with victory in the arena.
Roman Roads: The Backbone of the Empire
The extensive network of Roman roads was crucial for the administration and control of the vast empire. These roads facilitated the movement of armies, trade goods, and information across different continents. The saying “All roads lead to Rome” highlights the central role of these roads in the empire’s connectivity.

Facts About Rome, Interesting Customs and Traditions
Pagan Temples and Religious Practices
Before the spread of Christianity, the Romans worshipped a pantheon of gods and goddesses. Pagan temples, such as the Temple of Jupiter on Capitoline Hill, were important religious centers. Festivals and rituals were held regularly to honor these deities, reflecting the deeply spiritual nature of Roman society.
The Use of Latin: The Language of Rome
Latin, the language of ancient Rome, has left an indelible mark on many modern languages. Many English words are derived from Latin, and it remains the official language of the Catholic Church. The influence of Latin underscores the cultural legacy of Rome.
Dining Customs: Extravagance and Variety
Dining in ancient Rome was a lavish affair, especially for the wealthy. Roman banquets featured a wide variety of dishes, including exotic foods such as flamingo tongues. These feasts were opportunities for socializing and demonstrating one’s wealth and status.
Facts About Rome: Frequently Asked Questions
What is the most interesting fact about Rome?
One of the most interesting facts about Rome is that it was the first city in the world to reach a population of one million people. This milestone reflects the city’s significance and advanced urban planning during ancient times.
How did ancient Romans build such advanced structures?
Ancient Romans utilized advanced engineering techniques and materials, such as concrete, to construct durable and innovative structures. Their expertise in architecture and engineering allowed them to build iconic landmarks like the Colosseum and the Pantheon.
Why is Rome called the Eternal City?
Rome is called the Eternal City because of its long and continuous history spanning over two millennia. Despite various invasions, political changes, and natural disasters, Rome has remained a significant cultural and historical center.
What is unique about the Trevi Fountain?
The Trevi Fountain is unique for its Baroque design and the tradition of coin tossing. Visitors believe that throwing a coin into the fountain ensures a return to Rome, making it one of the city’s most beloved and visited landmarks.
How did the Roman Empire influence modern society?
The Roman Empire has influenced modern society in numerous ways, including legal systems, engineering, architecture, language, and culture. Many modern institutions and infrastructures trace their origins back to ancient Roman innovations.
The Influence of Rome on Modern Infrastructure
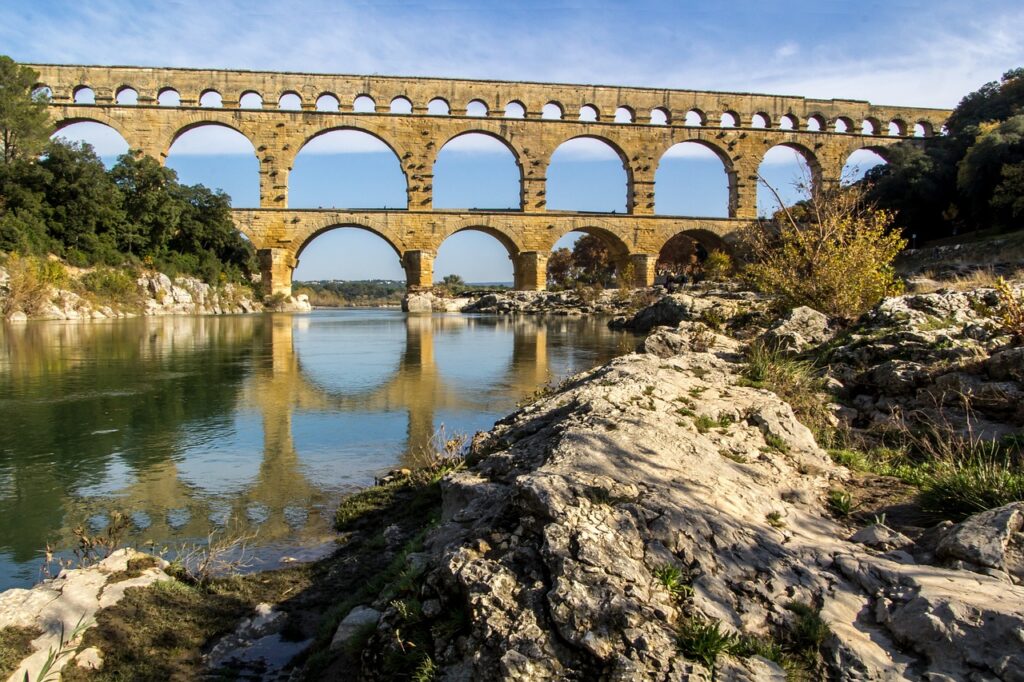

The Roman Roads: Pioneers of Connectivity
Roman roads, renowned for their durability and extensive network, laid the foundation for modern infrastructure. These roads, constructed with multiple layers of materials, were designed to withstand heavy use and weather conditions. They facilitated trade, military movements, and communication across the vast Roman Empire, influencing the design of modern highways and roads.
The Aqueducts: Engineering Marvels
Roman aqueducts were critical in supplying water to urban centers. These engineering marvels transported water over long distances using a system of bridges, tunnels, and pipes. The principles of gravity and precise gradient control applied in Roman aqueducts are still relevant in modern water supply systems.
Public Baths and Social Infrastructure
The concept of public baths in ancient Rome was more than just about hygiene; it was about community and social interaction. Modern public facilities, including sports complexes and recreational centers, draw inspiration from the multifunctional nature of Roman baths.
Rome’s Cultural Legacy
Art and Architecture: Timeless Inspiration
Roman art and architecture have left an enduring legacy, influencing countless artists and architects throughout history. Structures such as the Colosseum and the Pantheon continue to inspire modern architectural designs, emphasizing symmetry, grandeur, and engineering excellence.
Latin: The Lingua Franca of the Past
Latin, the official language of the Roman Empire, has significantly impacted modern languages. Many English words and phrases have Latin roots, and the language remains a crucial part of legal, medical, and scientific terminology. The use of Latin in ecclesiastical contexts further underscores its lasting influence.
Roman Mythology: Stories that Shaped a Civilization
Roman mythology, with its rich pantheon of gods and legendary heroes, has profoundly influenced Western literature, art, and culture. The stories of gods like Jupiter, Mars, and Venus have been retold through the ages, continuing to captivate audiences and inspire creative works.
Rome’s Natural Beauty and Climate

The Mediterranean Climate: An Inviting Atmosphere
Rome enjoys a Mediterranean climate, characterized by hot, dry summers and mild, wet winters. This pleasant climate has made the city an attractive destination for visitors throughout history, contributing to its reputation as the most visited city in the world.
The Tyrrhenian Sea: A Coastal Gem
The Tyrrhenian Sea, bordering the western coast of Italy, enhances Rome’s natural beauty. Its picturesque coastline and proximity to the city offer residents and tourists alike opportunities for relaxation and recreation.
Hidden Gems and Lesser-Known Facts About Rome
The Aventine Hill: A Serene Retreat
The Aventine Hill, one of Rome’s seven hills, is a peaceful retreat from the bustling city center. It offers stunning views of the city and is home to the beautiful Giardino degli Aranci (Orange Garden) and the ancient Basilica of Santa Sabina.
Largo di Torre Argentina: Historical and Feline Sanctuary
Largo di Torre Argentina, the site of Julius Caesar’s assassination, is now a historical landmark and a sanctuary for Rome’s stray cats. This unique blend of history and feline affection makes it a fascinating and endearing spot for visitors.
The Passetto di Borgo: A Hidden Passageway
The Passetto di Borgo, a secret passageway connecting the Vatican to Castel Sant’Angelo, played a crucial role in the history of the papacy. This hidden corridor allowed popes to escape danger during times of conflict, reflecting the tumultuous history of the city.
The Eternal City’s Modern Attractions

Piazza Navona: A Vibrant Hub
Piazza Navona, built on the site of the ancient Stadium of Domitian, is one of Rome’s most vibrant squares. It is known for its stunning fountains, including the famous Fontana dei Quattro Fiumi by Bernini, and its lively atmosphere filled with street performers, cafes, and artisans.
The Spanish Steps: Iconic and Elegant
The Spanish Steps, leading from the Piazza di Spagna to the Trinità dei Monti church, are an iconic symbol of Rome. This elegant staircase, with its picturesque views and bustling crowds, exemplifies the charm and beauty of the city.
Trevi Fountain: A Must-See Masterpiece
The Trevi Fountain, an exquisite example of Baroque art, is a must-see attraction in Rome. Tossing a coin into the fountain is a beloved tradition that promises a return to the Eternal City, making it one of the most iconic landmarks in Rome.
Facts About Rome, The Modern-Day Capital
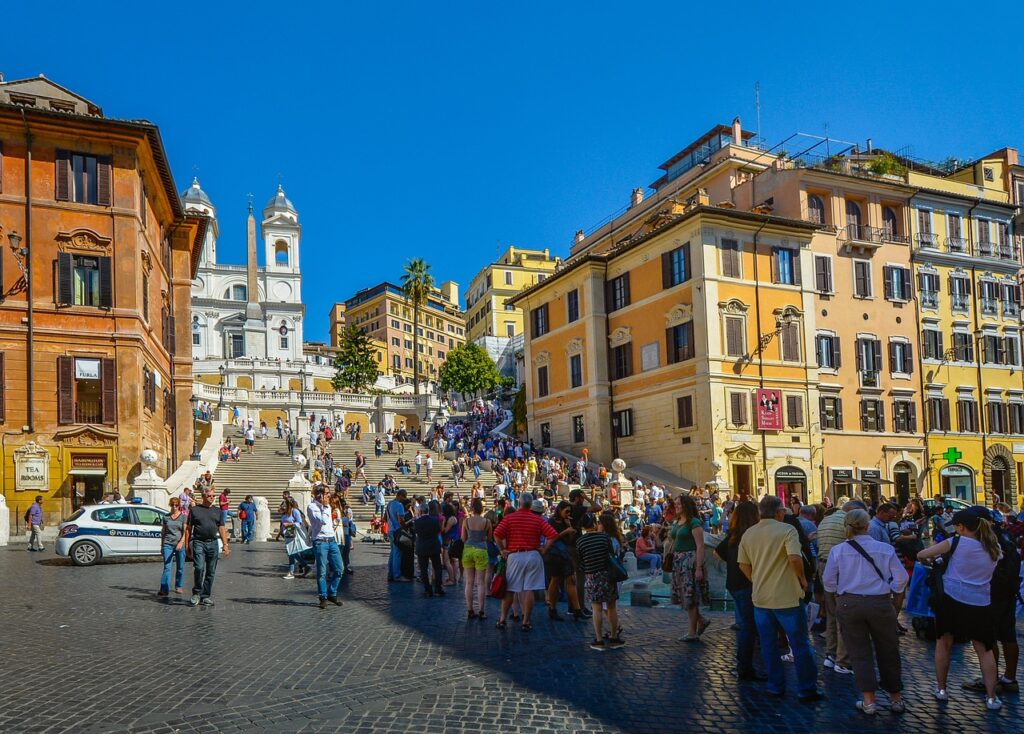

Rome Italy: A City of Contrasts
Rome, the capital city of Italy, is a place of contrasts where ancient history coexists with modernity. The city’s rich history and vibrant contemporary culture make it a unique destination that continues to draw millions of visitors each year.
The Italian Army: Guardians of the Heritage
The Italian army plays a crucial role in preserving and protecting Rome’s historical sites and cultural heritage. Their efforts ensure that the city’s ancient ruins and landmarks are safeguarded for future generations to explore and appreciate.
Facts About Rome: Frequently Asked Questions
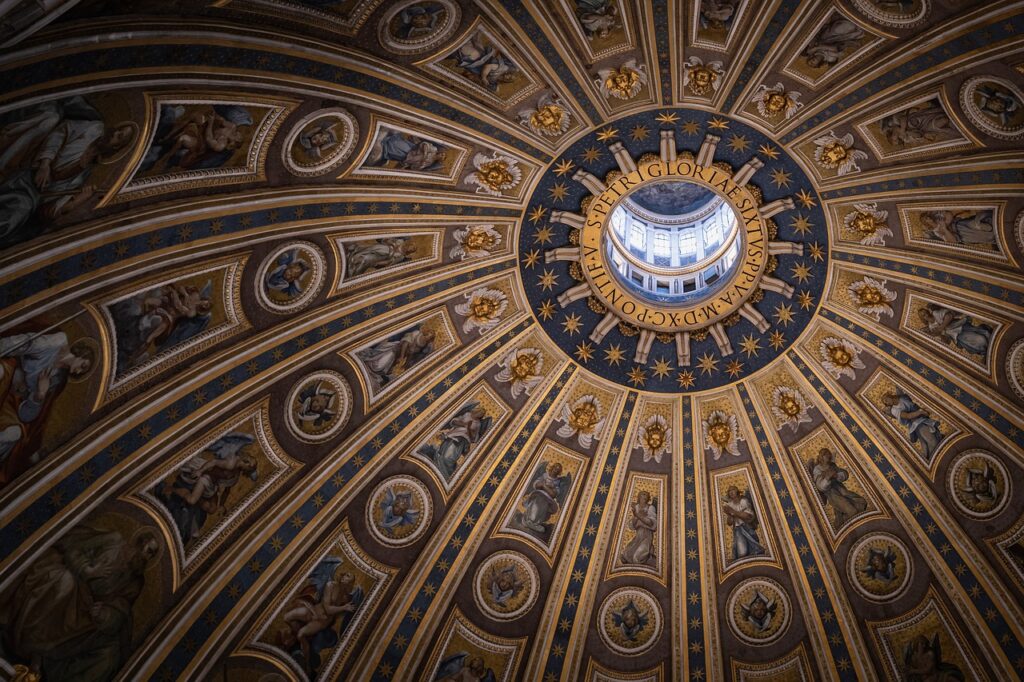

How has Rome managed to preserve its historical sites?
Rome has implemented extensive conservation efforts to preserve its historical sites. The collaboration between local authorities, historians, and international organizations has been crucial in maintaining and restoring ancient structures and landmarks.
What makes the Colosseum a significant landmark?
The Colosseum is significant due to its historical importance as a venue for gladiatorial contests and public spectacles. Its architectural grandeur and enduring presence make it a symbol of Rome’s imperial past.
Why are the Vatican and St. Peter’s Basilica important?
The Vatican and St. Peter’s Basilica are important as the spiritual and administrative centers of the Roman Catholic Church. They hold immense religious, cultural, and historical significance, attracting millions of pilgrims and tourists each year.
What role did the Tiber River play in Rome’s development?
The Tiber River was essential for Rome’s development, providing water, transportation, and defense. Its strategic location facilitated trade and communication, contributing to the city’s growth and prosperity.
How do modern Romans celebrate their rich heritage?
Modern Romans celebrate their rich heritage through festivals, cultural events, and the preservation of historical sites. The city’s vibrant arts scene, culinary traditions, and public celebrations reflect the enduring legacy of its ancient past.
Facts About Rome, The Diverse Aspects of Roman Society
Roman Mythology: The Heart of Belief
Roman mythology played a central role in the lives of ancient Romans. The myths and legends provided explanations for natural phenomena and human behavior, deeply influencing Roman culture and religious practices. Temples dedicated to various gods, such as the ancient temple of Saturn, were common throughout the city, serving as focal points for worship and community gatherings.
Roman Society: Structured and Stratified
Roman society was highly structured, with a clear hierarchy that included emperors, senators, equestrians, plebeians, and slaves. This stratification was evident in various aspects of daily life, from the opulent villas of the elite to the modest homes of the common people. The social structure influenced every aspect of Roman life, including politics, education, and employment.
Entertainment and Leisure in Ancient Rome
Public entertainment was a significant part of Roman life. Gladiator fights, chariot races at the Circus Maximus, and theatrical performances were popular forms of entertainment. These events were often grand spectacles, designed to entertain and distract the masses while demonstrating the power and generosity of the ruling class.
Facts About Rome, Rome’s Rich Historical Timeline

From Republic to Empire
The transition from the Roman Republic to the Roman Empire marked a significant shift in the city’s history. The Republic, characterized by its complex system of checks and balances, gave way to the autocratic rule of the emperors. This transformation was marked by significant events, including Julius Caesar’s assassination and the rise of Augustus as the first emperor.
The Middle Ages and the Papal States
During the Middle Ages, Rome became the center of the Papal States, a series of territories under the direct sovereign rule of the Pope. This period saw the construction of many churches and the fortification of the city. The influence of the Catholic Church shaped Rome’s political and cultural landscape during this time.
The Renaissance and Beyond
The Renaissance brought a renewed interest in art, science, and exploration. Rome, as a major center of this cultural revival, attracted artists, architects, and scholars who contributed to its legacy. The city continued to evolve, incorporating modern developments while preserving its ancient heritage.
Facts About Rome, Modern Rome: A Blend of Old and New
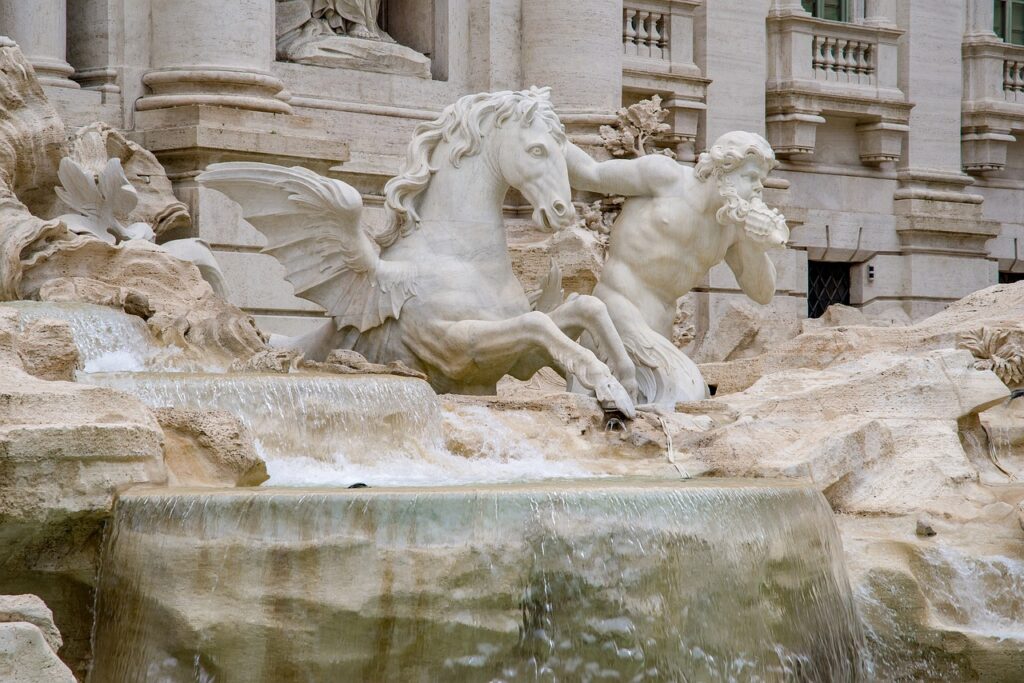

Rome’s City Center: A Living Museum
Walking through the city center of Rome is like walking through a living museum. Ancient ruins, Renaissance palaces, and Baroque fountains coexist with modern shops and cafes. This blend of old and new creates a unique atmosphere that captivates residents and visitors alike.
The Heart of Rome: Cultural and Political Hub
As the capital city of Italy, Rome is not only a historical treasure but also a contemporary cultural and political hub. The city hosts numerous cultural events, political summits, and international conferences, reflecting its ongoing significance on the world stage.
Rome’s Mediterranean Climate: Perfect for Exploration
Rome’s Mediterranean climate, with its warm summers and mild winters, makes it an ideal destination for exploration year-round. The pleasant weather enhances the experience of visiting outdoor landmarks, such as the Roman Forum and Palatine Hill.
Facts About Rome Conclusion
In conclusion, the facts about Rome reveal a city of unparalleled historical and cultural richness. From its mythical origins and the grandeur of the Roman Empire to its status as the Eternal City, Rome’s legacy continues to inspire and fascinate. The city’s architectural marvels, cultural landmarks, and vibrant society reflect a tapestry woven through millennia of human achievement and resilience.
Whether you are exploring ancient ruins, strolling through bustling piazzas, or marveling at Renaissance art, Rome offers an endless array of experiences. The facts about Rome not only highlight its historical significance but also its enduring charm and relevance.
As a visitor or a scholar, the more you learn about Rome, the deeper your appreciation will grow for this remarkable city that truly stands the test of time. One of the fascinating facts about Rome is that gladiators sometimes drank a mixture containing gladiator blood, believed to have healing properties and enhance their strength.