
Surprising And Interesting Facts About El Salvador
Interesting Facts About El Salvador
El Salvador is a vibrant Central American country that is home to a unique and diverse culture. From its beautiful beaches to its delicious cuisine, El Salvador has something for everyone. But what about the less obvious facts about this amazing nation? In this article, we’ll explore some interesting facts about El Salvador that you may not know.
From its incredible biodiversity to the sites of its most famous battles, there are plenty of surprises and fun facts in store for inquisitive minds.
For instance, did you know that El Salvador is the smallest and most densely populated country in Central America and that the official name of the country is the Republic of El Salvador? , there is much more to this vibrant nation than meets the eye.
With a long and fascinating history stretching back to before European contact, El Salvador has many interesting facts that are worth knowing.
El Salvador is a country with plenty of surprises in store for visitors and locals alike. The name El Salvador is a derivative of its ancient Aztec name, Cuzcatlán, which means “the place of the cacao trees.”
It has been recorded that Mayan settlers from South America arrived in Central America around 1200 BC.
What is the capital of El Salvador?
San Salvador is the capital of El Salvador, located in the central part of the country. It is a bustling metropolis with a population of approximately 2.2 million people spread out over an area of 11 square miles.
The city was established in 1525 and quickly became a major economic hub for Central America during colonial times.
San Salvador is home to many cultural centers, parks, museums, and other attractions, making it one of the most visited cities in El Salvador.
The city has an average temperature year-round that ranges from 64°F (18°C) to 90°F (32°C).
Although Spanish is the official language spoken by locals, English can be found throughout much of San Salvador as well due to its high rate of tourism.
Coffee beans of San Salvador
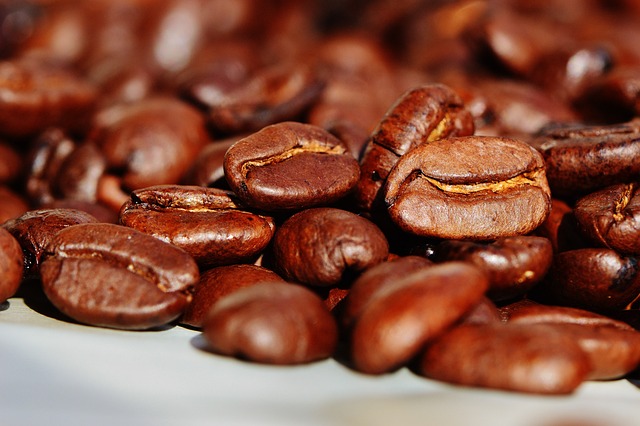

Due to its location near two volcanoes and fertile volcanic soil, San Salvador produces some of the best coffee beans in all of Latin America which are exported around the world.
San Salvador is the most populous city in El Salvador, with an estimated population of nearly 2.2 million people as of 2019.
It serves as the nation’s economic and cultural center, home to a variety of industries such as tourism, manufacturing, trade, and banking.
The city is also home to many historic attractions like the Monumento de la Divina Misericordia and La Asuncion Cathedral.
San Salvador has a rich history dating back to pre-Columbian times when it was inhabited by the Pipil tribe who called it Cuzcatlan.
After Spanish colonization in 1525, the city was founded under its current name in 1528. Over time it grew into an important commercial center for Central America before becoming El Salvador’s capital in 1841.
In recent years, San Salvador has become a popular vacation destination due to its tropical climate and vibrant culture.
From lively nightlife spots and beautiful beaches to delicious local cuisine and historical landmarks like Plaza Barrios or National Theater Ruben Dario – there’s something for everyone in this vibrant metropolis!
What is the population of El Salvador?
El Salvador is the smallest country in Central America, covering an area of 8,124 square miles. It has a population of 6.42 million people as of 2020.
Nearly half (48%) of El Salvador’s population is under 24 years old, making it one of the youngest countries in the Americas.
The majority (86%) of El Salvador’s population is made up of mestizos, meaning individuals who are a mix between Native American and European ancestry.
Hispanics account for about 90% of El Salvador’s population; Indigenous peoples make up 9%, and people from other ethnic backgrounds comprise 1%.
Approximately half (51%) of El Salvadoreans live in urban areas such as San Salvador city, Santa Ana, and San Miguel.
Migration has profoundly impacted El Salvador’s demographics and culture; over 2 million people have left the country since 1980 due to civil war and economic hardship—nearly a third (30%) of its current population living abroad today primarily in the United States, Mexico, Canada, and Spain.
Western El Salvador
Western El Salvador is home to several volcanoes, including the San Miguel volcano, one of the most active in Central America.
It is believed to be over 20,000 years old and has erupted more than 50 times since 1576.
El Salvador also boasts some of the best beaches in Central America on its western coast. Such beaches include Playa El Espino, La Barra de Santiago, and Las Flores.
These beaches are popular among tourists for their pristine white sand and clear blue waters.
Much like other parts of El Salvador, they are known for their excellent surfing conditions as well.
In addition to its natural beauty, Western El Salvador is home to the nation’s capital – San Salvador – where visitors can experience unique local culture and explore many historical sites such as its famous cathedral or art galleries like MARTE (Museo de Arte de El Salvador).
This region also offers plenty of outdoor activities such as hiking trails around Cerro Verde National Park or bird watching at Laguna de Olomega Wildlife Refuge.
What are the major religions in El Salvador?

El Salvador is a predominantly Catholic country, with nearly 80% of its population identifying as Roman Catholic.
Other Christian denominations present in El Salvador include Protestantism, Jehovah’s Witnesses, and Mormonism.
A small percentage of the population (1%) identifies with the Jewish faith, and another 1% follow indigenous religious beliefs.
The remaining 18% of the population either has no religion or follows non-Christian religious beliefs like Islam and Buddhism.
The religion most commonly practiced by Indigenous peoples in El Salvador is called Nahuat-Pipil religion.
This belief system combines traditional Mayan worship practices with Catholicism to create a unique set of religious practices that blend both worlds.
This practice has been observed since pre-Columbian times and continues to be an important part of El Salvador’s cultural identity today.
Additionally, some Afro-Salvadorans practice folk religions that combine African spiritual traditions with Christianity.
These religions are collectively known as “Afro-Salvadoran Religions” and involve elements like Santeria and Voodoo rituals which have become more popular in recent years due to increased immigration from Central America’s Caribbean region.
El Salvador’s traditional dishes
Pupusas are a traditional dish from El Salvador. They are thick, handmade corn tortillas that are stuffed with ingredients such as cheese, pork, and beans.
The pupusa is then either fried or grilled and served warm with a variety of accompaniments such as curtido (a cabbage slaw) and salsa roja (a spicy tomato sauce).
Pupusas can be found in nearly every restaurant throughout El Salvador.
El Salvador has its version of tamales, known as “paches”. These are large tamales filled with pork or beef and potatoes, wrapped in plantain leaves before being boiled until cooked through.
They are usually served accompanied by cream or salad on the side. Paches can often be seen sold by street vendors around El Salvador’s cities during the holiday season.
Pasteles de pollo is another classic dish of El Salvador which consists of chicken wrapped in banana leaves along with carrots and potatoes, then steamed for several hours until it becomes soft and flavorful.
It is usually served alongside rice, beans, sour cream, and avocado slices for extra flavor. This hearty dish is popular among all generations throughout the country due to its delicious taste!
Plus, dishes such as pupusas (stuffed corn tortillas), yuca con chicharrón (fried cassava with pork cracklings), and caldo de res (beef soup).
One unique aspect of El Salvadorean cuisine is its use of spices to give an extra punch to dishes like tamales or tacos.
What are the major industries in El Salvador?

El Salvador is a small Central-American nation with a population of 6.2 million people, making it the smallest and most densely populated country in Central America.
The country has an industrial base that creates significant economic activity. Two of the major industries in El Salvador are agriculture and manufacturing.
Agriculture is El Salvador’s main source of income, accounting for 25% of its GDP, and employs 35% of its labor force. Major products include coffee, beef, cotton, sugarcane, corn, rice, beans, and bananas.
Manufacturing also contributes to the economy with apparel being one of its leading exports.
El Salvador is part of CAFTA-DR (the Dominican Republic-Central American Free Trade Agreement), which has opened up new opportunities for foreign investment in the sector.
The services sector also makes an important contribution to the economy as tourism continues to grow as a major industry in El Salvador due to its beautiful beaches and rich cultural attractions such as Mayan ruins and colonial towns like San Miguel.
Construction also plays a role in stimulating economic growth due to government infrastructure projects such as road construction and public buildings like schools or hospitals being built across the country as well as private housing developments driven by foreign investment or remittances from abroad.
What is the GDP of El Salvador?
El Salvador’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is estimated to be around $25.3 billion USD (united states dollars) in 2018, a slight decrease from 2017 when it was estimated at $26.1 billion USD.
This places El Salvador with the second smallest GDP in Central America, only larger than that of Belize ($2.25 billion USD). It is also one of the lowest GDPs per capita in Latin America at $3,296 USD per person.
Compared to other Central American countries like Costa Rica and Panama which have an average GDP per capita of nearly double El Salvador’s at around $6,500 and 8,400 respectively.
The main factor contributing to El Salvador’s low GDP is its economy’s reliance on remittances from abroad for income rather than domestic production and exports; greater than 20% of its annual income comes from remittances alone.
Additionally, the country has suffered from large budget deficits due to rising public debt and limited sources of revenue-taxes make up just 15% of total revenue compared to the 35% average for most Latin American countries.
What are the most popular Interesting Facts About El Salvador?
El Salvador is the smallest country in Central America, but it holds many interesting facts. It is a primarily Spanish-speaking country and has one of the highest population densities in Latin America.
Here are some of the most popular and interesting facts about El Salvador.
The official language of El Salvador is Spanish and is spoken by more than ninety percent of its population.
It also has several indigenous languages such as Nawat, Lenca, and Pipil which are still spoken by some communities. Additionally, Nahuatl is also spoken by some people who have migrated from Mexico to El Salvador.
Surprisingly, El Salvador has been home to two Nobel Prize winners: Oscar Arias Sanchez (1987) and Rigoberta Menchu (1992).
Both were awarded for their work on human rights initiatives during the civil war period in El Salvador.
The currency used in the country since 2001 has been the united states dollar, making it one of only two countries worldwide that use foreign currency as its legal tender.
What are the most interesting facts about El Salvador’s culture and history?
El Salvador is a small Central American country with an interesting history and culture. While the country has only been independent since 1841, it has a long and varied past.
Here are some of the most interesting facts about El Salvador’s culture and history:
The official language in El Salvador is Spanish, but many indigenous languages are still spoken by some in the country.
The majority of people living in El Salvador are Mestizo, meaning they have both European and Indigenous ancestry.
There is also a large Afro-Salvadoran population due to African slaves being brought to the region centuries ago.
The national sport in El Salvador is soccer and it’s very popular throughout the country. Soccer games often draw huge crowds of passionate fans who cheer on their favorite teams enthusiastically.
Additionally, music plays an important role in El Salvador’s culture – genres like salsa, merengue, cumbia, reggaeton, and bachata can be heard all over the country!
What are the most interesting facts about El Salvador’s natural resources and environment?
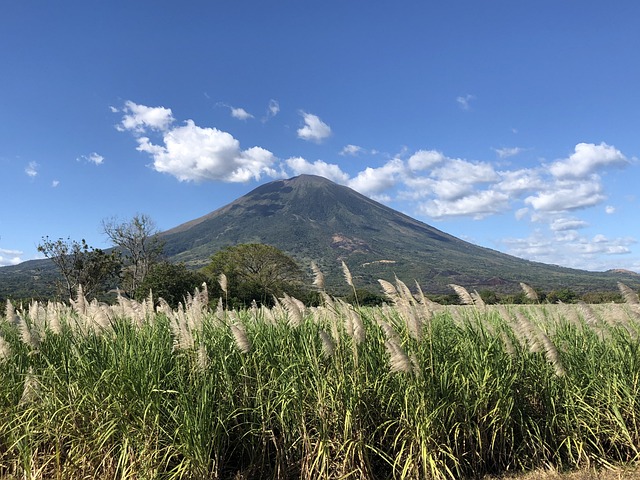

El Salvador is home to a diverse range of natural resources and environments. The country is divided into four zones, each with its distinct characteristics.
One of the most notable facts about El Salvador’s natural resources and environment is that it has some of the richest biodiversity in Central America, with a variety of both terrestrial and aquatic species to explore.
This includes unique wildlife such as the endangered jaguar, giant anteater, mountain tapir, and ocelot.
El Salvador also boasts some impressive geography — including over 20 volcanic peaks and three major rivers — making it an ideal destination for hiking or rafting.
El Salvador is known as the Land of Volcanoes due to its many active and inactive volcanoes. Plus, El Salvador has over 20 volcanic cones, making it one of the most volcanically active countries in Central America.
One of the most notable volcanoes is Izalco, which was formerly known as “The Lighthouse of the Pacific” due to its frequent volcanic eruptions that illuminated much of Central America for centuries.
El Boquerón is another popular volcano in El Salvador, located near San Salvador. It erupted for days straight in 1917, causing massive destruction and loss of life.
Its crater lake remains a popular tourist destination today. Cerro Verde National Park also contains two large stratovolcanoes – Santa Ana and Izalco – that are both popular hiking destinations for visitors to El Salvador.
The park’s awe-inspiring views make it a must-see destination when visiting El Salvador’s Land of Volcanos.
In addition to its stunning landscapes, El Salvador has several national parks such as Montecristo National Park where visitors can experience nature in all its glory.
Furthermore, there are multiple reserves dedicated to protecting threatened species from deforestation or other harm caused by humans.
Interesting facts about El Salvador

Did you know El Salvador is the only country in Central America that does not have a coastline on the Caribbean Sea?
Finally, El Salvador’s climate ranges from tropical wet-dry in the north to subtropical dry forests in the south; this makes for great conditions for growing coffee beans which are one of the country’s largest exports!
Overall, El Salvador offers much more than just beaches — offering unique natural beauty that is worth exploring!
El Salvador’s most famous battles
The Battle of El Porvenir, fought in 1932, was an important battle in El Salvador’s history and one of its most famous.
It marked the beginning of a civil war between the government forces and peasant rebels that lasted several years.
The battle began when a group of peasants attempted to march on the capital city to demand better wages and working conditions.
Government forces met them at a small town called El Porvenir where they were defeated by the rebels after three days of fighting.
The victory gave the peasants confidence that their cause could be won and set the stage for other battles during the civil war.
The Slaughter
Another famous battle in El Salvador’s history is known as “La Matanza” or “The Slaughter”.
This took place in 1932, shortly after The Battle of El Porvenir, when government troops massacred thousands of unarmed protesters who had gathered to demand better wages and rights for workers.
This event sparked outrage around the world and led to international pressure on El Salvador’s government to end its oppressive regime.
As a result, reforms were made which eventually put an end to La Matanza as well as prevented similar atrocities from occurring again in El Salvador’s future.
What are the top 5 most spoken languages in El Salvador?

Spanish is the official language of El Salvador, and it is spoken by 97% of the population. Due to Spanish being so widely spoken, other languages are not as prevalent in El Salvador.
However, there are still five other languages that are commonly spoken in El Salvador.
These include Nahuatl, which is a language originating from Mexico that’s primarily used by Indigenous people living in the western part of the country;
Mam, which is an indigenous Mayan language mainly used in Western and Southwestern areas of El Salvador;
Garifuna, an Arawakan-based dialect found along parts of the Caribbean coast; Xinca, another indigenous language mostly spoken around eastern parts of El Salvador;
And lastly Kaqchikel, a Maya language mainly spoken by K’iche’ people who inhabit central and southeastern regions.
These five languages make up less than 3% of the entire population combined but they still hold importance as they represent some of El Salvador’s many cultures.
The government has taken measures to protect these minority languages through educational initiatives such as creating bilingual schools where both English and Spanish can be taught alongside one of these lesser-known languages.
This ensures that all citizens will have access to education regardless of their native tongue.
What is El Salvador’s highest point?
Cerro El Pital is the highest peak in El Salvador, located near the Honduran border. It stands at 8,725 feet above sea level and attracts tourists and locals alike to marvel at its majestic beauty.
The area has a rich history of indigenous peoples and colonial influences that have shaped the region over time.
First settled by the Lenca people more than 500 years ago, Cerro El Pital was later occupied by Spanish colonists after they arrived in 1524.
During this period, coffee plantations were developed in the region with coffee production reaching its peak in 1865 when exports to Europe began from nearby Santa Ana City.
Today, visitors can still explore these coffee plantations on guided tours around Cerro El Pital National Park.
The national park itself is home to an impressive array of flora and fauna; several species of birds including hummingbirds and toucans are known to inhabit the area alongside wildcats, monkeys, boars, and deer amongst other creatures.
There are also several trails for hikers or mountain bikers who wish to explore further into this picturesque landscape which offers stunning views of both Honduras and El Salvador’s valleys below.
What is Joya de Ceren
Joya de Ceren is an archaeological site located in the El Salvadoran district of La Libertad. It is believed to have been inhabited by the Pipil people, part of the larger Mesoamerican culture, between 600-800 AD.
This pre-Columbian village is considered to be one of the most important archaeological sites in Central America.
Joya de Ceren was discovered in 1976 and recognized as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1993 for its importance to Pre-Columbian culture.
The ruins were well preserved due to their being buried under layers of volcanic ash from eruptions of the nearby Loma Caldera volcano.
This allowed researchers to uncover artifacts from everyday life such as tools, utensils, furniture, and other materials that give insight into how these people lived during this period.
The ruins are made up of several structures including dwellings, temples, and a sweat house which all remain remarkably intact giving visitors a peek into what life was like for these early civilizations.
It has become an important tourist destination offering guided tours and educational programs which help tell its story and preserve its rich cultural heritage for future generations.
When is the rainy season in El Salvador?

The rainy season in El Salvador usually begins in May and ends in October. The rainiest months are June, September, and October when the country receives most of its average annual precipitation.
During this time of year, temperatures are slightly cooler while rainfall is quite heavy.
Not only do these rains replenish soil moisture and groundwater levels but they also bring with them a feeling of renewal as plants come alive again after months of dryness.
El Salvador’s mountainous terrain makes for a unique experience during the rainy season since you can experience both rainforest-like conditions at higher altitudes and savannah-like conditions near sea level.
The country also has an extensive network of rivers that swell to their fullest capacity during this period, providing wonderful opportunities for rafting or kayaking adventures.
The dry season usually runs from late November to May, and the wet season typically falls between May and November.
During the dry season, average temperatures can range from 70-90°F (21-32°C). It’s also the sunniest time of year with an average of 8 hours of sunshine a day.
In contrast, the wetter months bring more rain, increased humidity levels, and cooler temperatures ranging from 65-85°F (18-29°C).
El Salvador’s dry season
The dry season is El Salvador’s most popular tourist season as it offers optimal conditions for outdoor activities such as hiking, biking, and exploring Mayan ruins.
As well as offering great weather for sightseeing, this period is also advantageous for agricultural production since crops require less water during this time of year.
The cooler temperatures during the night make it ideal for growing coffee beans which are one of El Salvador’s main exports.
The lack of rainfall may cause water shortages in some parts of the country during these months so it’s important to be aware that resources may become limited during this period.
This is especially true in rural areas where access to clean water is scarce as reservoirs run low or dry out altogether due to inefficient irrigation systems or extreme heat waves caused by global warming.
Interesting facts about El Salvador

El Salvadoreans love soccer; it’s considered one of their national pastimes.
Also, El Salvador was the first Central American team to qualify for the FIFA World Cup in 1970. They made their debut against Belgium and surprised everyone by holding them to a 0-0 draw, despite being huge underdogs.
El Salvador reached the quarterfinals of the CONCACAF Championship in 1967, their best performance in international competitions before qualifying for the World Cup.
They scored their only goal in the tournament against Mexico which they won 1-0, making it one of El Salvador’s greatest football moments ever.
Unfortunately, they were knocked out in the group stages after failing to advance with just one point from three games played.
It was an impressive achievement considering that El Salvador had never qualified for a major international tournament before this competition.
Despite not having much success at subsequent editions of the World Cup, El Salvador remains a proud nation and its people take great pride in this historic accomplishment.
Thank you for reading this far, if you have found this article interesting or helpful then discover Interesting Facts About Nicaragua
The Football War
Football war, or the Football War, is an armed conflict between El Salvador and Honduras that arose in 1969.
The conflict began on 14 July 1969 when the Salvadoran military launched an attack against Honduras.
Although the war only lasted four days, it had a devastating impact on both countries and left thousands of people dead.
The cause of the war was largely attributed to growing economic tensions between the two countries as well as rising resentment over immigration issues related to land reforms in El Salvador.
During this period, there was also increased tension between Honduras’ political party and El Salvador’s military government at the time.
While no official treaty ended the war, it did lead to a considerable cooling off of hostilities between the two countries.
As a result of this conflict, both countries established diplomatic relations with each other in 1980 which have remained intact ever since. Please share this article if you found it interesting, thank you.





One Comment
Pingback: